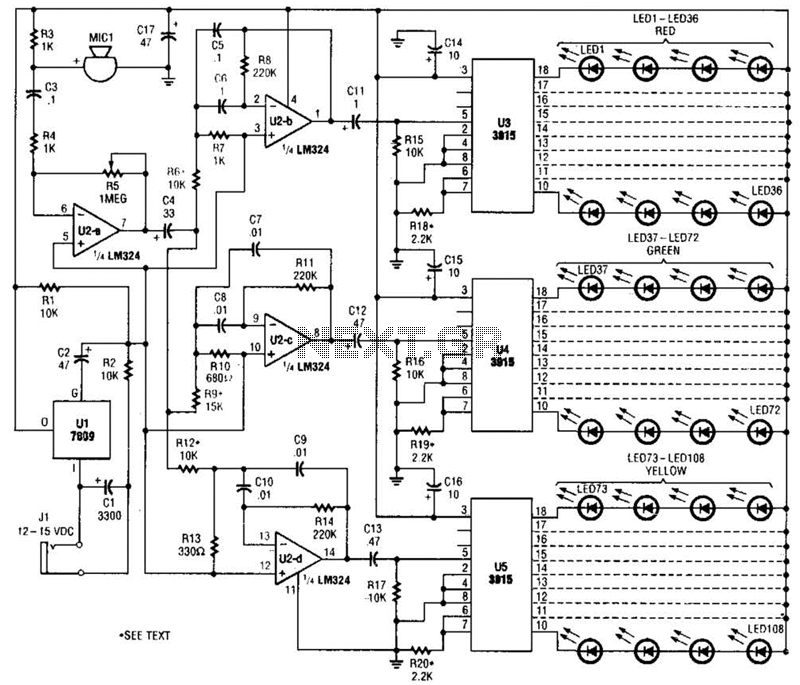
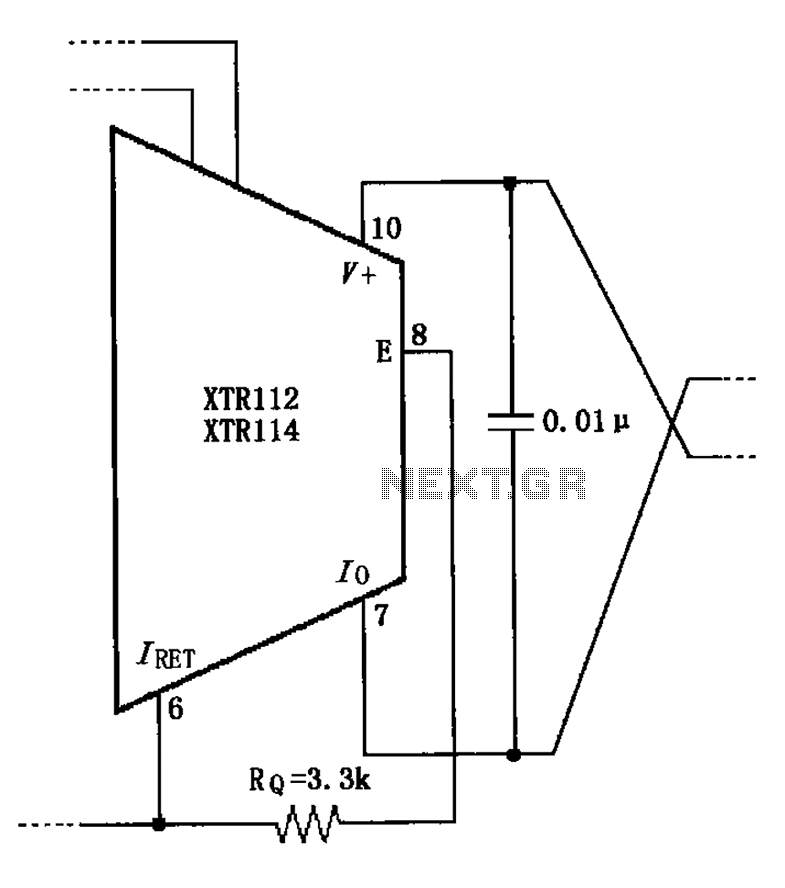
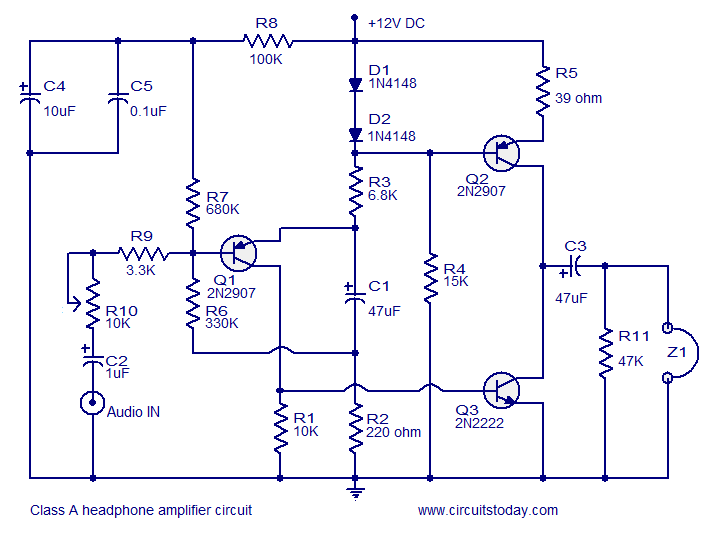
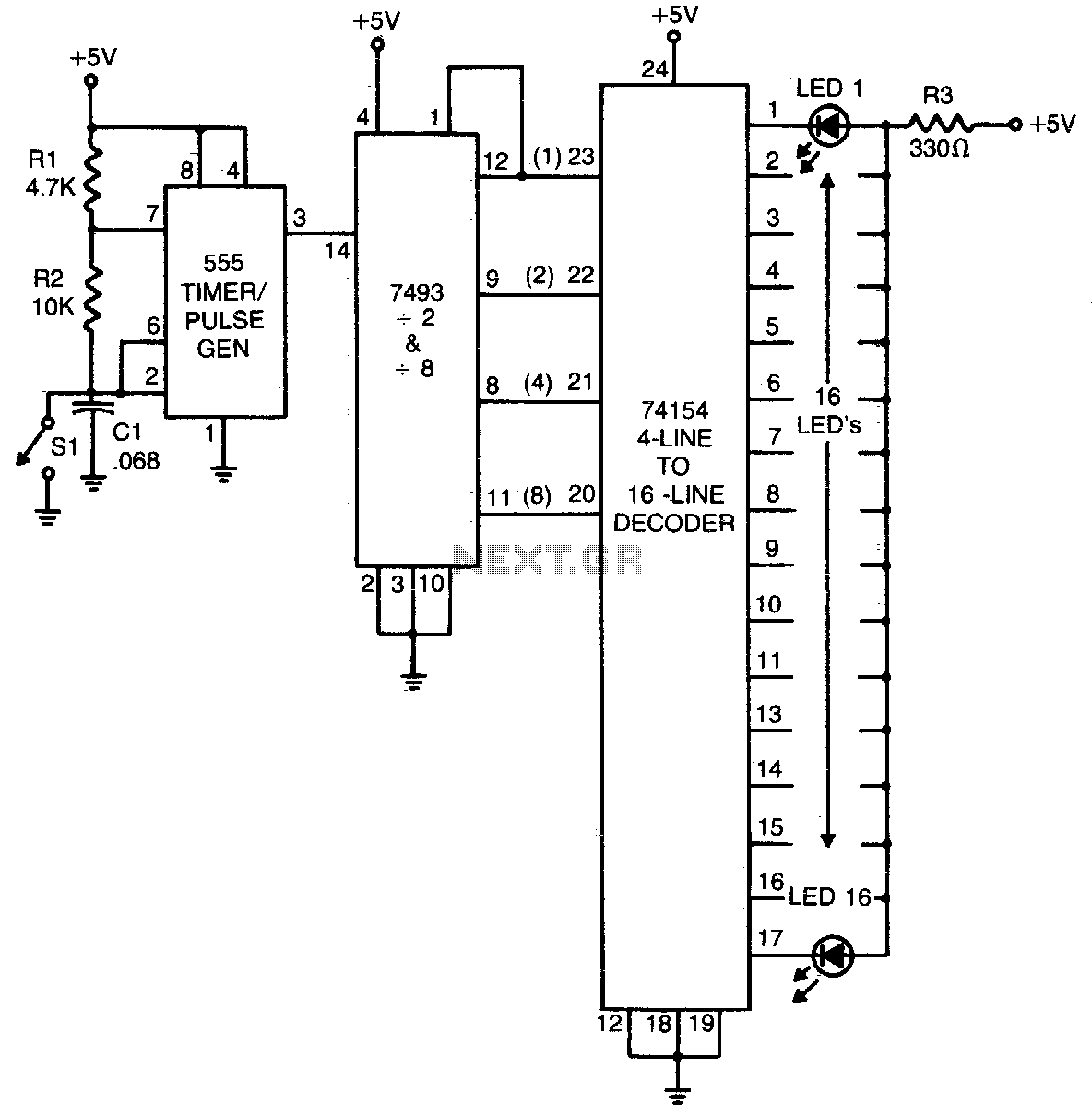
usb cellphone charger circuit
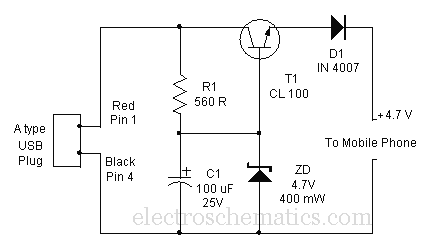
Comprehensive information about a USB cellphone charger circuit is available for learning and downloading online.
The USB cellphone charger circuit is designed to convert AC mains voltage into a stable DC voltage suitable for charging mobile devices. This circuit typically utilizes a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and various passive components to ensure efficient operation and safety.
The primary component, the transformer, steps down the high AC voltage from the mains to a lower AC voltage, which is then fed into a rectifier circuit. The rectifier, usually composed of diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC. Following the rectification process, a filter capacitor is employed to smooth the pulsating DC output, reducing voltage ripple and providing a more stable voltage.
To regulate the output voltage to the desired level (commonly 5V for USB charging), a voltage regulator is integrated into the circuit. This component ensures that the output voltage remains constant despite variations in load or input voltage. Commonly used voltage regulators for USB applications include the LM7805 for linear regulation or switching regulators for improved efficiency.
Additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly a fuse are included to enhance circuit performance, provide noise filtering, and protect against overcurrent conditions. The circuit design may also incorporate protection features such as a diode to prevent reverse polarity and a surge protector to safeguard against voltage spikes.
The final output is typically connected to a USB port, allowing for compatibility with various mobile devices. The design may vary depending on specific requirements, such as output current capacity and efficiency considerations. Overall, the USB cellphone charger circuit is a practical and essential design in modern electronics, providing a reliable means to charge portable devices.Good information about USB Cellphone Charger Circuit You can learn and download USB Cellphone Charger Circuit online here.. 🔗 External reference
The USB cellphone charger circuit is designed to convert AC mains voltage into a stable DC voltage suitable for charging mobile devices. This circuit typically utilizes a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and various passive components to ensure efficient operation and safety.
The primary component, the transformer, steps down the high AC voltage from the mains to a lower AC voltage, which is then fed into a rectifier circuit. The rectifier, usually composed of diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC. Following the rectification process, a filter capacitor is employed to smooth the pulsating DC output, reducing voltage ripple and providing a more stable voltage.
To regulate the output voltage to the desired level (commonly 5V for USB charging), a voltage regulator is integrated into the circuit. This component ensures that the output voltage remains constant despite variations in load or input voltage. Commonly used voltage regulators for USB applications include the LM7805 for linear regulation or switching regulators for improved efficiency.
Additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly a fuse are included to enhance circuit performance, provide noise filtering, and protect against overcurrent conditions. The circuit design may also incorporate protection features such as a diode to prevent reverse polarity and a surge protector to safeguard against voltage spikes.
The final output is typically connected to a USB port, allowing for compatibility with various mobile devices. The design may vary depending on specific requirements, such as output current capacity and efficiency considerations. Overall, the USB cellphone charger circuit is a practical and essential design in modern electronics, providing a reliable means to charge portable devices.Good information about USB Cellphone Charger Circuit You can learn and download USB Cellphone Charger Circuit online here.. 🔗 External reference