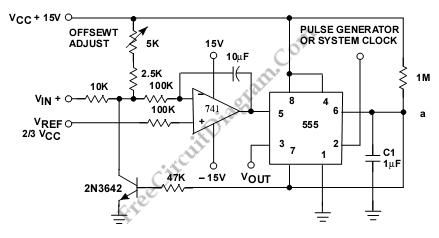
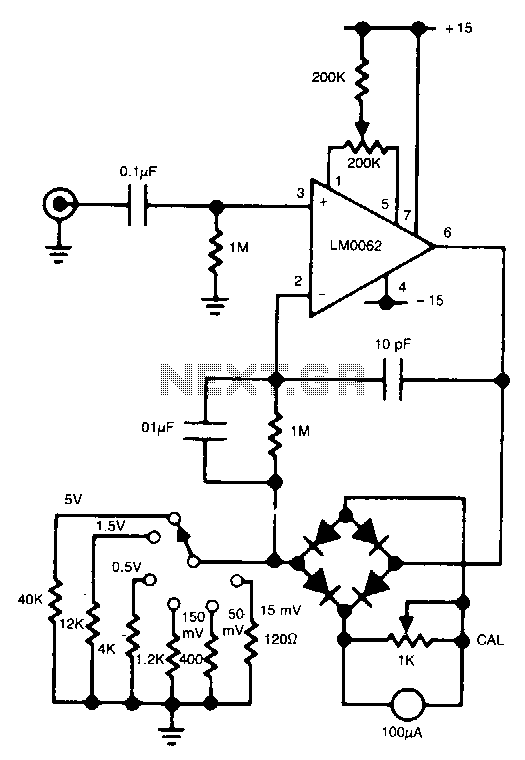
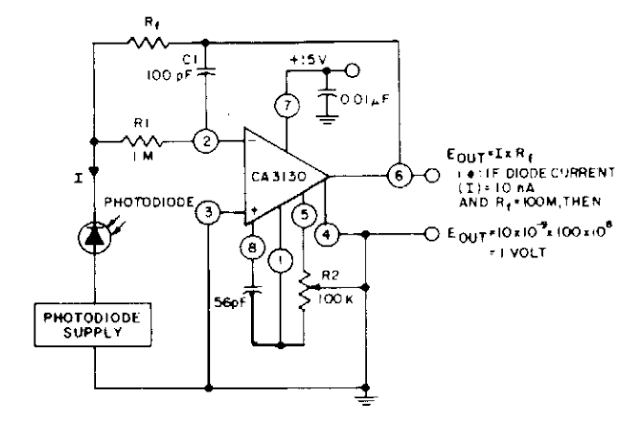
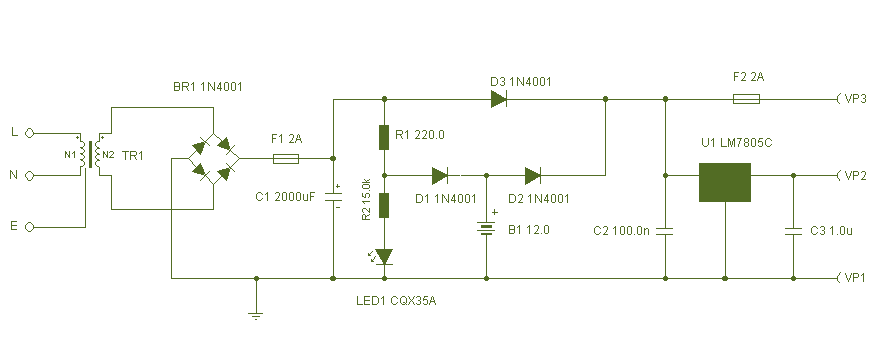
Regulated 12 Volt Supply
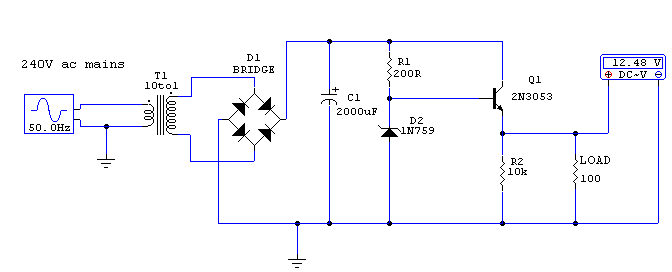
This circuit utilizes a 13-volt zener diode, D2, which is responsible for voltage regulation. Approximately 0.7 volts are dropped across the base-emitter junction of the transistors, resulting in a higher current output of 12.3 volts. The circuit is capable of supplying loads of up to 500 mA. This configuration is commonly referred to as an amplified zener circuit.
The circuit described operates on the principle of voltage regulation through the use of a zener diode in conjunction with a transistor amplifier. The 13-volt zener diode, D2, establishes a stable reference voltage. When the input voltage exceeds the zener breakdown voltage, the diode conducts and maintains the output voltage at approximately 12.3 volts after accounting for the voltage drop across the transistor's base-emitter junction.
The transistor serves to amplify the current capacity of the circuit, allowing it to deliver up to 500 mA to the load. This capability is essential for applications requiring a stable voltage supply for various electronic components. The configuration typically includes additional components such as resistors for biasing the transistor and capacitors for filtering to ensure stability and reduce noise in the output voltage.
In designing this circuit, careful consideration must be given to the selection of the zener diode and transistor to ensure they can handle the required voltage and current ratings. Additionally, heat dissipation mechanisms may be necessary, particularly if the circuit operates near its maximum load for extended periods, as both the zener diode and transistor can generate heat during operation. Proper thermal management will help maintain the reliability and longevity of the circuit.This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0. 7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12. 3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described operates on the principle of voltage regulation through the use of a zener diode in conjunction with a transistor amplifier. The 13-volt zener diode, D2, establishes a stable reference voltage. When the input voltage exceeds the zener breakdown voltage, the diode conducts and maintains the output voltage at approximately 12.3 volts after accounting for the voltage drop across the transistor's base-emitter junction.
The transistor serves to amplify the current capacity of the circuit, allowing it to deliver up to 500 mA to the load. This capability is essential for applications requiring a stable voltage supply for various electronic components. The configuration typically includes additional components such as resistors for biasing the transistor and capacitors for filtering to ensure stability and reduce noise in the output voltage.
In designing this circuit, careful consideration must be given to the selection of the zener diode and transistor to ensure they can handle the required voltage and current ratings. Additionally, heat dissipation mechanisms may be necessary, particularly if the circuit operates near its maximum load for extended periods, as both the zener diode and transistor can generate heat during operation. Proper thermal management will help maintain the reliability and longevity of the circuit.This circuit above uses a 13 volt zener diode, D2 which provides the voltage regulation. Aprroximately 0. 7 Volts are dropped across the transistors b-e junction, leaving a higher current 12. 3 Volt output supply. This circuit can supply loads of up to 500 mA. This circuit is also known as an amplified zener circuit. 🔗 External reference