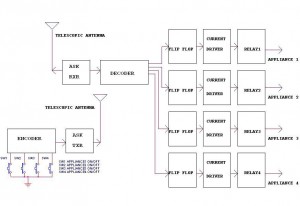
Remote control Encoder M145026B-1
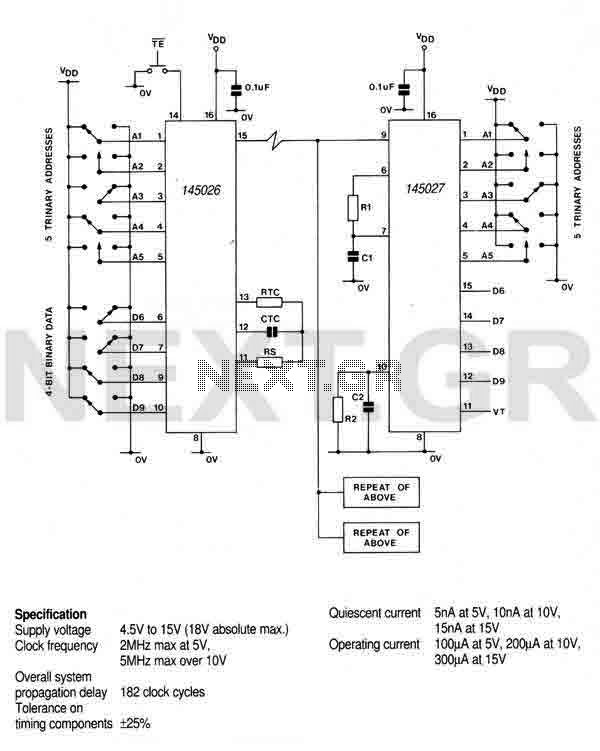
This encoder can generate up to 19,683 codes from 9 address lines by detecting 1, 0, or an open circuit. To initiate the transmit sequence, pin 14 should be pulsed low. The encoder will output a data stream on pin 15 that represents the condition on each of the address/data pins in turn, repeating the operation to transmit two complete identical words. If pin 14 is held low, the output will be continuous; otherwise, two identical words are output for each pulse on pin 14. A '1' is transmitted as two long pulses, a '0' as two short pulses, and an open circuit as a long pulse followed by a short pulse. The device is constructed in CMOS technology and adheres to the characteristics of standard 4000B devices. If an external oscillator is used, it should be connected to pin 11, while pins 12 and 13 should be left open. The output can drive RF, ultrasonic, or infrared transmitters.
The encoder is a versatile device designed to convert binary inputs from its address lines into a coded output suitable for various communication applications. With the capability of generating 19,683 distinct codes, it operates through a simple yet effective mechanism of pulse modulation. The nine address lines allow for a wide range of input combinations, making it suitable for applications requiring multiple signal states.
To begin the transmission process, a low pulse on pin 14 serves as the trigger. This initiates the encoder's sequence, where it sequentially evaluates the states of the address/data pins and generates a corresponding output on pin 15. The dual transmission of identical words ensures reliability in data communication, as it minimizes the chances of errors during data reception.
The encoding scheme utilizes distinct pulse patterns for different states: a binary '1' is represented by two long pulses, a binary '0' by two short pulses, and an open circuit state is indicated by a long pulse followed by a short pulse. This pulse-width modulation technique allows for clear differentiation between the transmitted states, facilitating accurate decoding at the receiving end.
Constructed using CMOS technology, the encoder benefits from low power consumption and high noise immunity, characteristic of the 4000B series devices. For applications requiring precise timing, an external oscillator can be integrated by connecting it to pin 11, while ensuring that pins 12 and 13 remain unconnected. This flexibility allows the encoder to adapt to various operational requirements.
The output of the encoder is capable of driving various types of transmitters, including RF, ultrasonic, and infrared, making it suitable for a wide array of wireless communication systems. This adaptability enhances its utility in remote control applications, data transmission, and other electronic communication systems where reliable and efficient signal encoding is paramount.This encoder can generate up to 19,683 codes from 9 address lines by detecting 1,0, or open circuit. To initiate the transmit sequence, pin 14 should be pulsed low. The encoder will now output on pin 15 a data stream representing the condition on each of the address/data pins in turn and then repeat the operation, so that two complete identical words are transmitted. If pin 14 is held low, the output will be continuous, otherwise two identical words are output for each pulse on pin 14.
A 1 is transmitted as two long pulses, a 0 as two short pulses, and an open circuit as a long pulse followed by a short pulse. The device is constructed in CMOS and all characteristics are as the standard 4000B devices. If an external oscillator is used, it should be connected to pin 11 and pins 12 and 13 left open. The output can drive rf, ultrasonic or infrared transmitters.
The encoder is a versatile device designed to convert binary inputs from its address lines into a coded output suitable for various communication applications. With the capability of generating 19,683 distinct codes, it operates through a simple yet effective mechanism of pulse modulation. The nine address lines allow for a wide range of input combinations, making it suitable for applications requiring multiple signal states.
To begin the transmission process, a low pulse on pin 14 serves as the trigger. This initiates the encoder's sequence, where it sequentially evaluates the states of the address/data pins and generates a corresponding output on pin 15. The dual transmission of identical words ensures reliability in data communication, as it minimizes the chances of errors during data reception.
The encoding scheme utilizes distinct pulse patterns for different states: a binary '1' is represented by two long pulses, a binary '0' by two short pulses, and an open circuit state is indicated by a long pulse followed by a short pulse. This pulse-width modulation technique allows for clear differentiation between the transmitted states, facilitating accurate decoding at the receiving end.
Constructed using CMOS technology, the encoder benefits from low power consumption and high noise immunity, characteristic of the 4000B series devices. For applications requiring precise timing, an external oscillator can be integrated by connecting it to pin 11, while ensuring that pins 12 and 13 remain unconnected. This flexibility allows the encoder to adapt to various operational requirements.
The output of the encoder is capable of driving various types of transmitters, including RF, ultrasonic, and infrared, making it suitable for a wide array of wireless communication systems. This adaptability enhances its utility in remote control applications, data transmission, and other electronic communication systems where reliable and efficient signal encoding is paramount.This encoder can generate up to 19,683 codes from 9 address lines by detecting 1,0, or open circuit. To initiate the transmit sequence, pin 14 should be pulsed low. The encoder will now output on pin 15 a data stream representing the condition on each of the address/data pins in turn and then repeat the operation, so that two complete identical words are transmitted. If pin 14 is held low, the output will be continuous, otherwise two identical words are output for each pulse on pin 14.
A 1 is transmitted as two long pulses, a 0 as two short pulses, and an open circuit as a long pulse followed by a short pulse. The device is constructed in CMOS and all characteristics are as the standard 4000B devices. If an external oscillator is used, it should be connected to pin 11 and pins 12 and 13 left open. The output can drive rf, ultrasonic or infrared transmitters.