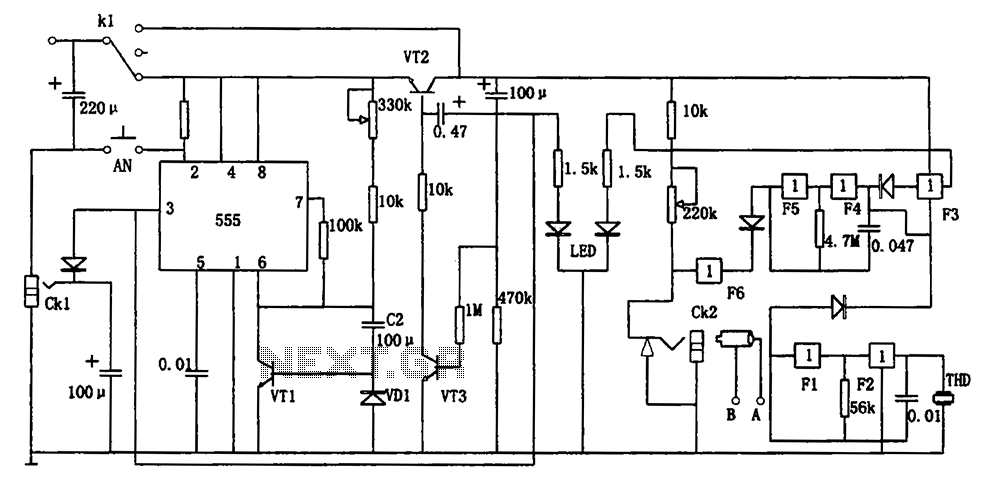
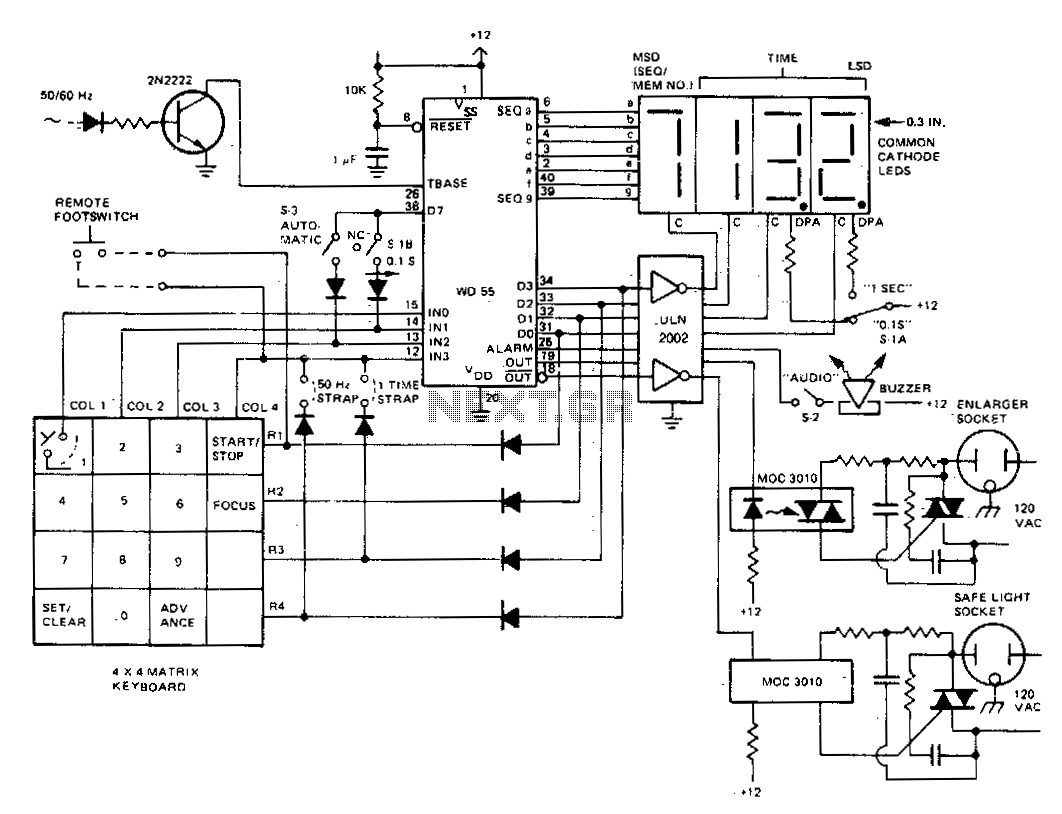
Repeating Timer No5
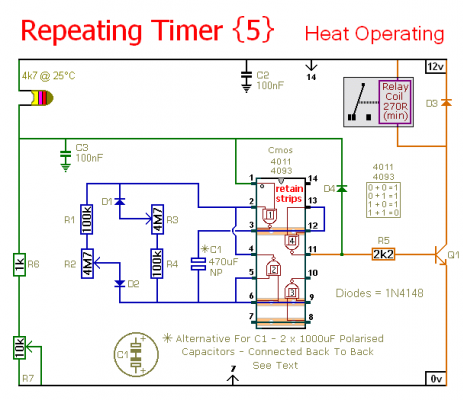
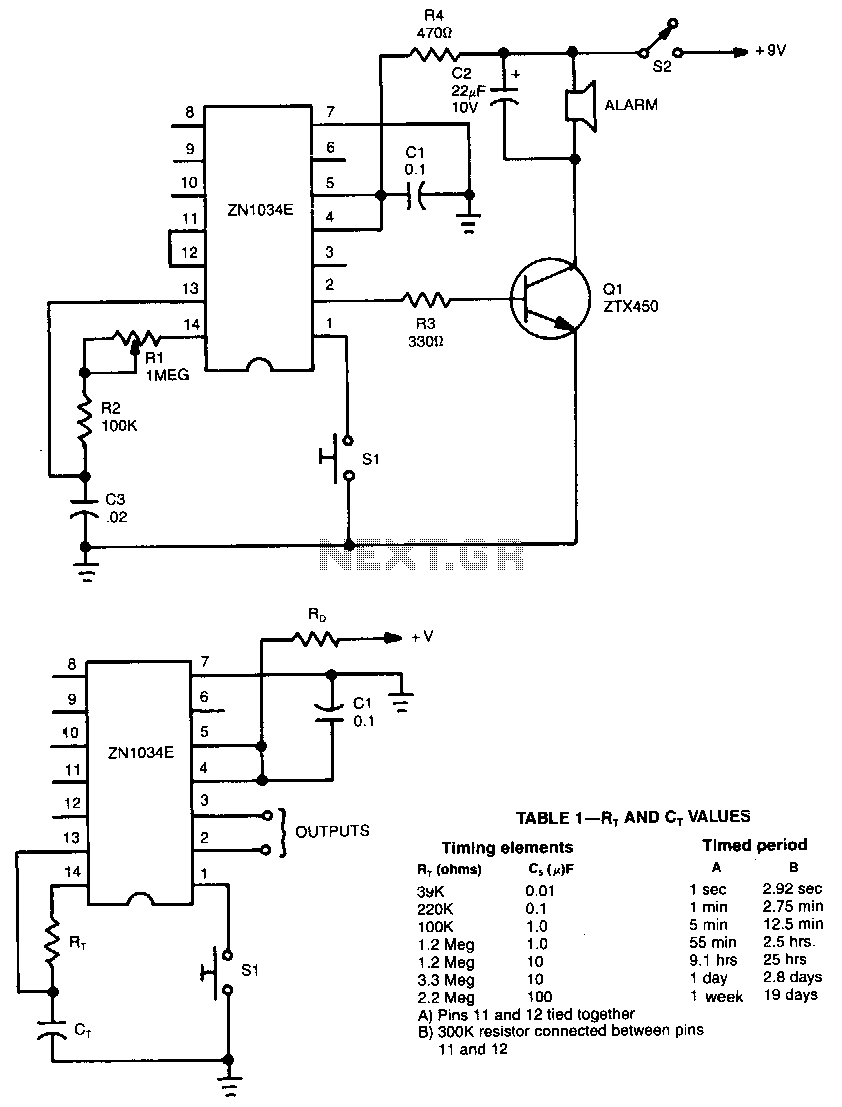
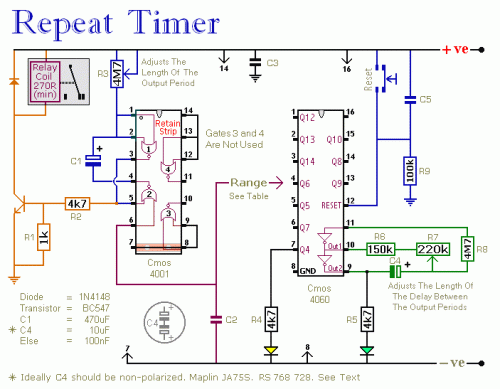
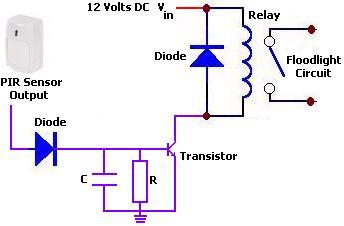
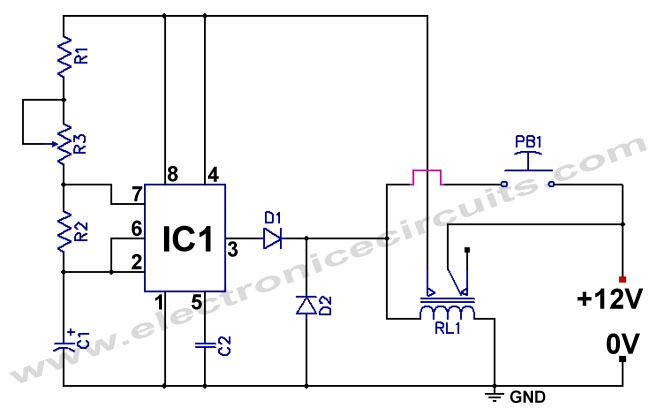
This circuit is a temperature-controlled version of Repeating Timer No. 3. The light-dependent resistor has been replaced by a temperature-dependent resistor, or thermistor. A small preset potentiometer allows the user to select the temperature threshold above which the timer will operate.
The temperature-controlled timer circuit employs a thermistor, which is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature changes. In this configuration, the thermistor is connected in a voltage divider arrangement with a fixed resistor, allowing the circuit to sense temperature variations effectively. The output from this arrangement is fed into a comparator or a microcontroller input, which determines if the thermistor's resistance has dropped below a predetermined level set by the preset potentiometer.
The preset potentiometer adjusts the reference voltage for the comparator, enabling customization of the temperature threshold. When the temperature exceeds the set point, the comparator triggers the timer circuit, activating the output device, which could be a relay or a transistor driving an external load.
The timer function can be realized using various components, such as a 555 timer IC configured in monostable mode, where the output remains high for a duration set by external resistors and capacitors. Alternatively, a microcontroller can be programmed to manage timing and control outputs based on temperature readings.
This circuit finds applications in temperature-sensitive environments, such as heating systems, temperature alarms, or automatic fan controls, where maintaining a specific temperature range is crucial. Proper layout and component selection are essential to ensure reliability and accuracy of the temperature sensing and timing functions.This circuit is a temperature controlled version of Repeating Timer No.3 . The light dependent resistor has been replaced by a temperature dependent resistor or thermistor. And a small preset potentiometer lets you choose the temperature above which the timer will operate 🔗 External reference
The temperature-controlled timer circuit employs a thermistor, which is a type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature changes. In this configuration, the thermistor is connected in a voltage divider arrangement with a fixed resistor, allowing the circuit to sense temperature variations effectively. The output from this arrangement is fed into a comparator or a microcontroller input, which determines if the thermistor's resistance has dropped below a predetermined level set by the preset potentiometer.
The preset potentiometer adjusts the reference voltage for the comparator, enabling customization of the temperature threshold. When the temperature exceeds the set point, the comparator triggers the timer circuit, activating the output device, which could be a relay or a transistor driving an external load.
The timer function can be realized using various components, such as a 555 timer IC configured in monostable mode, where the output remains high for a duration set by external resistors and capacitors. Alternatively, a microcontroller can be programmed to manage timing and control outputs based on temperature readings.
This circuit finds applications in temperature-sensitive environments, such as heating systems, temperature alarms, or automatic fan controls, where maintaining a specific temperature range is crucial. Proper layout and component selection are essential to ensure reliability and accuracy of the temperature sensing and timing functions.This circuit is a temperature controlled version of Repeating Timer No.3 . The light dependent resistor has been replaced by a temperature dependent resistor or thermistor. And a small preset potentiometer lets you choose the temperature above which the timer will operate 🔗 External reference