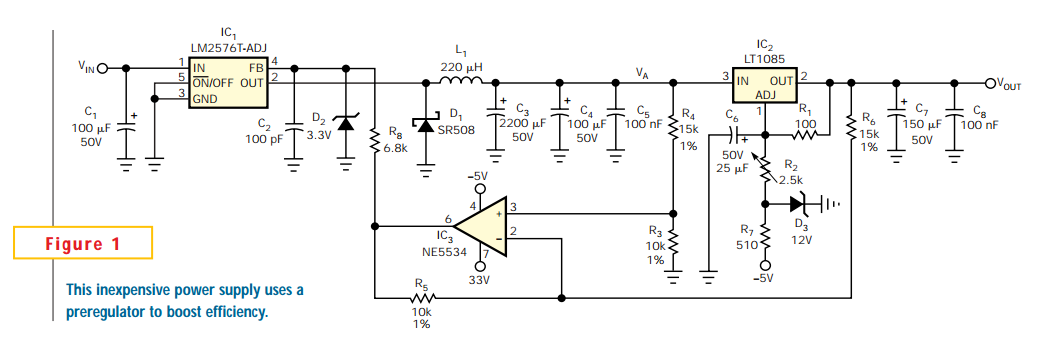
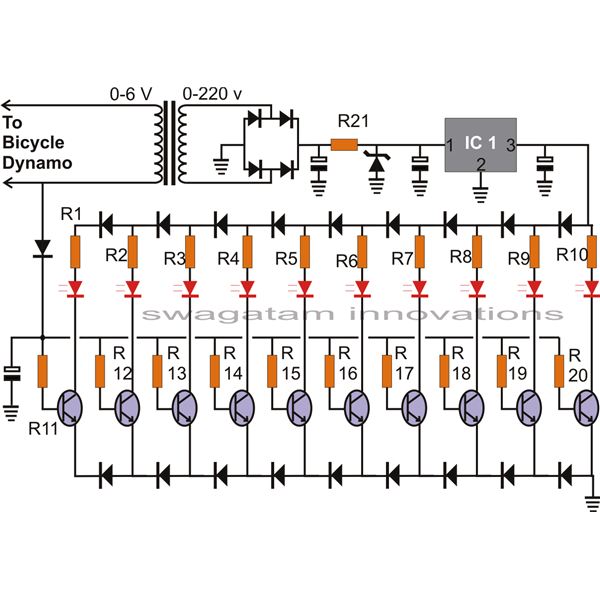
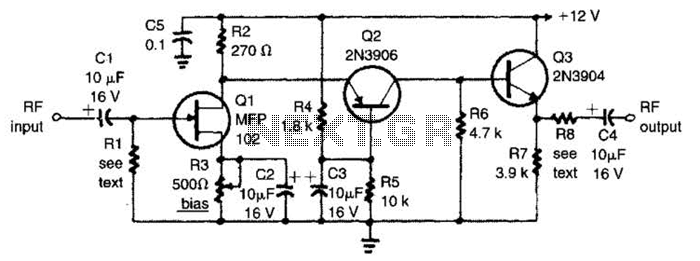
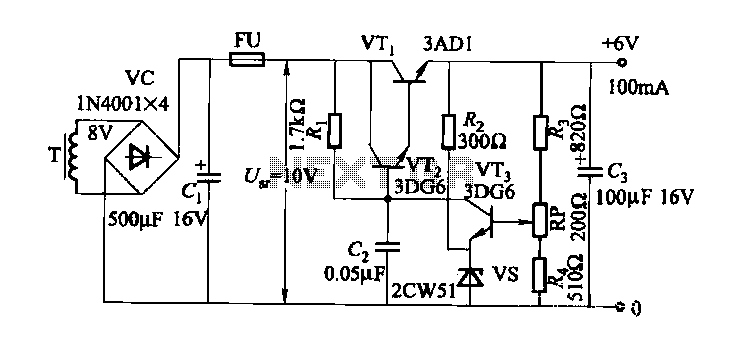
Full-band phase locked loop circuit diagram fast
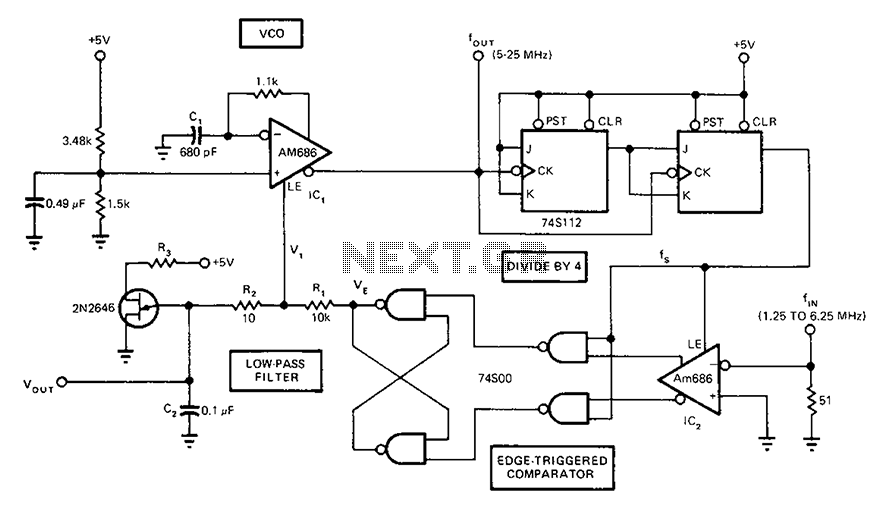
A circuit diagram of a phase-locked loop utilizes an AM686 latched comparator as a voltage-controlled oscillator, along with a TTL latch connected to generate edge-triggered comparators. The VCO and its comparison with the low-pass filter consisting of R1, R2, and C2 form the PLL.
The presented circuit diagram outlines a phase-locked loop (PLL) configuration that integrates an AM686 latched comparator functioning as the voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). This VCO is pivotal in generating a frequency output that is dependent on the input voltage. The circuit also incorporates a TTL latch, which is crucial for producing edge-triggered comparisons. This arrangement allows for precise synchronization of the output frequency with a reference frequency.
In this PLL design, the low-pass filter plays a significant role in smoothing the output signal from the VCO. The components R1, R2, and C2 are arranged to form a filter that effectively reduces high-frequency noise, ensuring that only the desired frequency components are passed through. The low-pass filter's cutoff frequency can be adjusted by selecting appropriate values for R1, R2, and C2, which directly influences the loop's stability and response time.
The operation of the PLL involves the VCO generating a signal that is compared to a reference signal. The edge-triggered comparators, enabled by the TTL latch, facilitate this comparison by detecting the phase difference between the two signals. The output of the comparator is then fed back to the VCO, adjusting its frequency to minimize the phase difference. This feedback mechanism is essential for maintaining lock and achieving stable frequency output.
Overall, this PLL circuit is designed for applications requiring precise frequency control and stability, making it suitable for various electronic systems where synchronization of signals is critical.A circuit diagram of a phase locked loop fast the whole band takes a Am686 latched comparator as voltage controlled oscillator, and the other with a TTL latch coupled to genera te edge-triggered comparators. VCO and comparison with the low-pass filter R1, R2, C2 link, constitute PLL.
The presented circuit diagram outlines a phase-locked loop (PLL) configuration that integrates an AM686 latched comparator functioning as the voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO). This VCO is pivotal in generating a frequency output that is dependent on the input voltage. The circuit also incorporates a TTL latch, which is crucial for producing edge-triggered comparisons. This arrangement allows for precise synchronization of the output frequency with a reference frequency.
In this PLL design, the low-pass filter plays a significant role in smoothing the output signal from the VCO. The components R1, R2, and C2 are arranged to form a filter that effectively reduces high-frequency noise, ensuring that only the desired frequency components are passed through. The low-pass filter's cutoff frequency can be adjusted by selecting appropriate values for R1, R2, and C2, which directly influences the loop's stability and response time.
The operation of the PLL involves the VCO generating a signal that is compared to a reference signal. The edge-triggered comparators, enabled by the TTL latch, facilitate this comparison by detecting the phase difference between the two signals. The output of the comparator is then fed back to the VCO, adjusting its frequency to minimize the phase difference. This feedback mechanism is essential for maintaining lock and achieving stable frequency output.
Overall, this PLL circuit is designed for applications requiring precise frequency control and stability, making it suitable for various electronic systems where synchronization of signals is critical.A circuit diagram of a phase locked loop fast the whole band takes a Am686 latched comparator as voltage controlled oscillator, and the other with a TTL latch coupled to genera te edge-triggered comparators. VCO and comparison with the low-pass filter R1, R2, C2 link, constitute PLL.