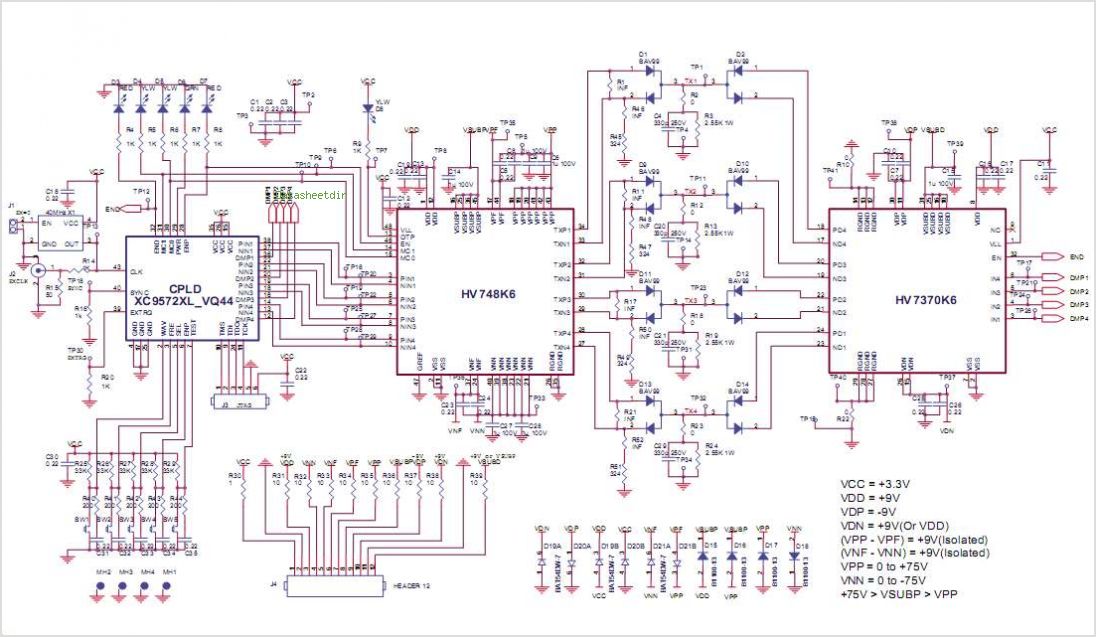
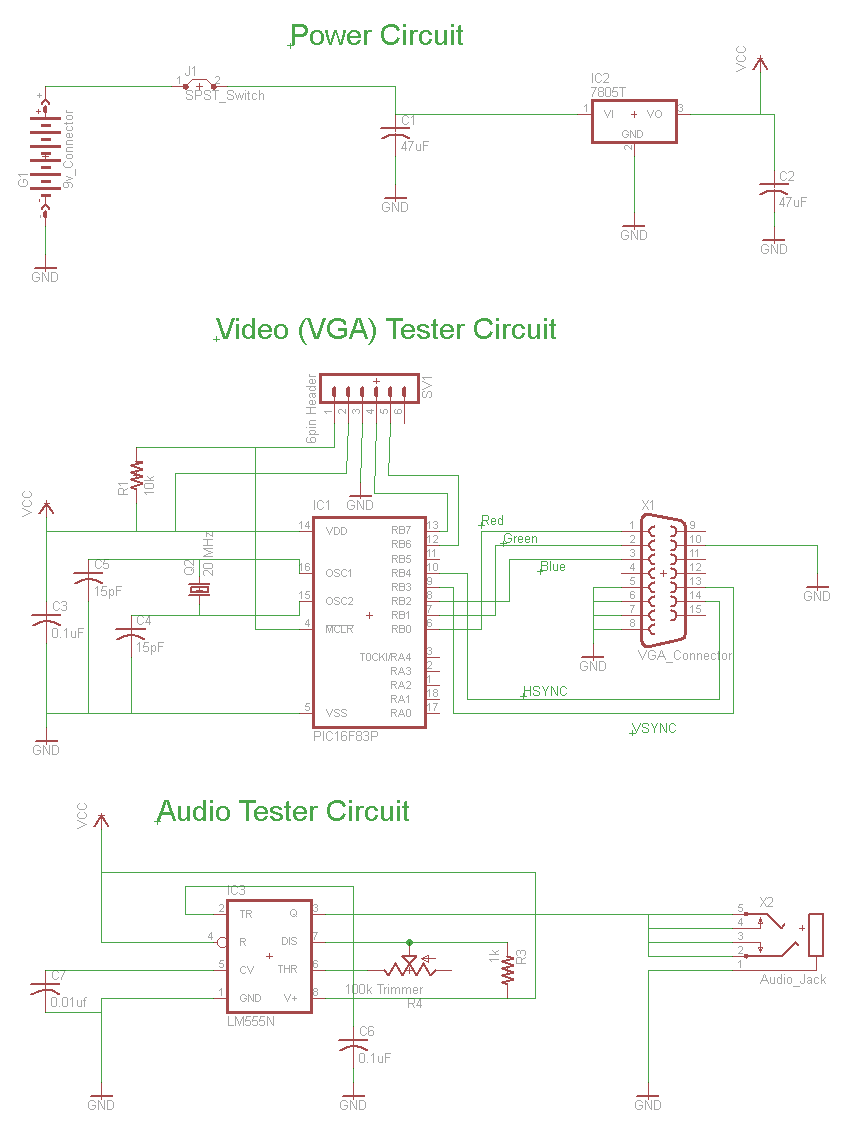
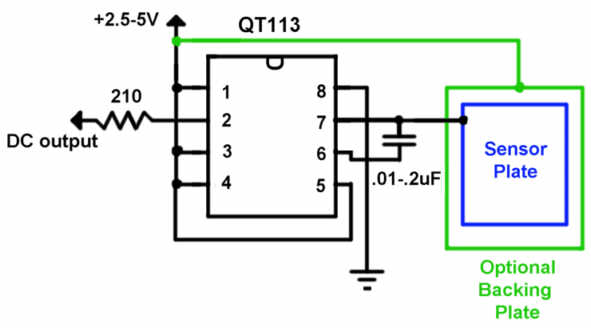
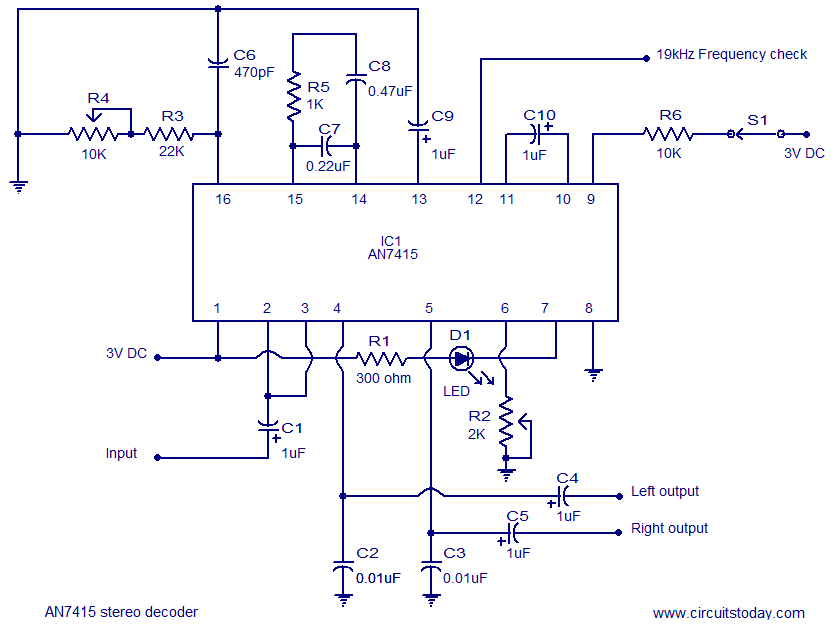
rfid How to design an Oscillator Circuit (500 MHz range) with no Op amps
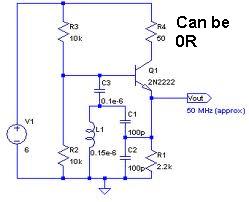
An oscillator circuit capable of generating a high-quality sine wave with a frequency of at least 500 MHz, intended for RFID applications. There have been attempts to utilize a class E oscillator, but the design has not yet been successfully achieved.
The oscillator circuit for RFID applications requires careful consideration of various design parameters to ensure it functions effectively at high frequencies. A class E oscillator is a popular choice for generating high-frequency signals due to its efficiency and simplicity, but it necessitates precise component selection and configuration.
To create a reliable 500 MHz sine wave, the following components and considerations are essential:
1. **Transistor Selection**: A high-frequency transistor, such as a FET or a BJT rated for RF applications, should be chosen. The transistor must support the necessary frequency and provide sufficient gain.
2. **Resonant Tank Circuit**: The core of the oscillator is the resonant tank circuit, typically consisting of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C). The values of these components must be calculated to resonate at the desired frequency. The resonant frequency \( f \) can be calculated using the formula:
\[
f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}}
\]
Proper tuning of L and C is crucial to achieving the target frequency.
3. **Feedback Network**: A feedback network is required to sustain oscillation. This can be achieved through a combination of resistors and capacitors that ensure the correct phase shift and gain for oscillation.
4. **Power Supply**: The circuit must have a stable power supply to maintain consistent operation. Voltage regulation may be necessary to avoid fluctuations that could affect the output frequency.
5. **Output Filtering**: To obtain a clean sine wave, output filtering may be implemented. This can involve additional LC filters that remove harmonic content and ensure the output is suitable for RFID applications.
6. **PCB Design**: At high frequencies, the layout of the printed circuit board (PCB) becomes critical. Short traces, proper grounding, and minimized parasitic capacitance and inductance are essential to maintain signal integrity.
7. **Testing and Tuning**: After assembly, the circuit should be tested with an oscilloscope to verify the output waveform. Adjustments may be necessary to fine-tune the component values and ensure the oscillator operates at the desired frequency with minimal distortion.
By addressing these components and considerations, a functional class E oscillator capable of generating a 500 MHz sine wave for RFID applications can be successfully designed and implemented.An Oscillator circuit which can produce a good sine wave with a frequency of at least 500 Mhz. This is for RFID applications. I have tried to use an class E oscillator, but i cant seem to get the design right. Can anyone help me out 🔗 External reference
The oscillator circuit for RFID applications requires careful consideration of various design parameters to ensure it functions effectively at high frequencies. A class E oscillator is a popular choice for generating high-frequency signals due to its efficiency and simplicity, but it necessitates precise component selection and configuration.
To create a reliable 500 MHz sine wave, the following components and considerations are essential:
1. **Transistor Selection**: A high-frequency transistor, such as a FET or a BJT rated for RF applications, should be chosen. The transistor must support the necessary frequency and provide sufficient gain.
2. **Resonant Tank Circuit**: The core of the oscillator is the resonant tank circuit, typically consisting of an inductor (L) and a capacitor (C). The values of these components must be calculated to resonate at the desired frequency. The resonant frequency \( f \) can be calculated using the formula:
\[
f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{LC}}
\]
Proper tuning of L and C is crucial to achieving the target frequency.
3. **Feedback Network**: A feedback network is required to sustain oscillation. This can be achieved through a combination of resistors and capacitors that ensure the correct phase shift and gain for oscillation.
4. **Power Supply**: The circuit must have a stable power supply to maintain consistent operation. Voltage regulation may be necessary to avoid fluctuations that could affect the output frequency.
5. **Output Filtering**: To obtain a clean sine wave, output filtering may be implemented. This can involve additional LC filters that remove harmonic content and ensure the output is suitable for RFID applications.
6. **PCB Design**: At high frequencies, the layout of the printed circuit board (PCB) becomes critical. Short traces, proper grounding, and minimized parasitic capacitance and inductance are essential to maintain signal integrity.
7. **Testing and Tuning**: After assembly, the circuit should be tested with an oscilloscope to verify the output waveform. Adjustments may be necessary to fine-tune the component values and ensure the oscillator operates at the desired frequency with minimal distortion.
By addressing these components and considerations, a functional class E oscillator capable of generating a 500 MHz sine wave for RFID applications can be successfully designed and implemented.An Oscillator circuit which can produce a good sine wave with a frequency of at least 500 Mhz. This is for RFID applications. I have tried to use an class E oscillator, but i cant seem to get the design right. Can anyone help me out 🔗 External reference