Sensitive electromagnetic field sensor
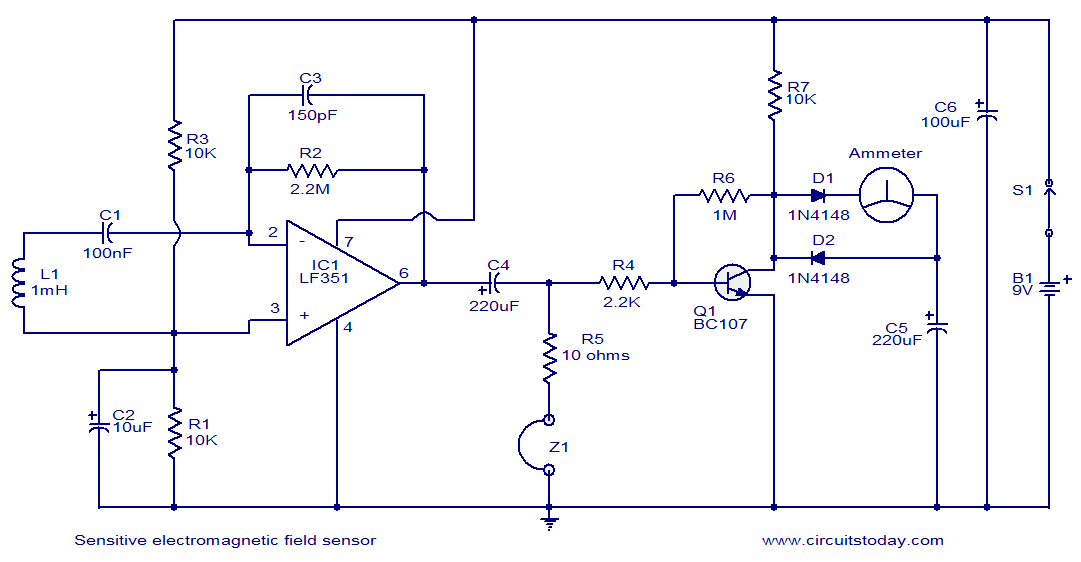
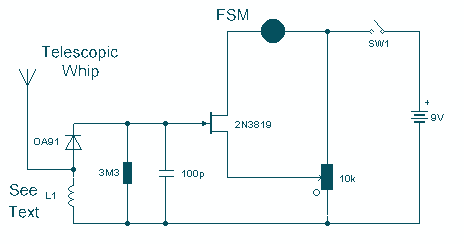
This circuit diagram represents a highly sensitive electromagnetic field sensor capable of detecting electromagnetic fields in the frequency range of 40Hz to 140Hz. The low-noise operational amplifier LF351, along with its associated components, comprises the pick-up section. A 1µH coil (L1) is utilized for sensing the electromagnetic field, while IC1 is responsible for the necessary amplification. If the detected electromagnetic field falls within the audio frequency range, it can be heard through headphone Z1. Additionally, there is a meter arrangement for accurate measurement of signal strength. Transistor Q1 provides further amplification of the detected signal to drive the meter.
The electromagnetic field sensor circuit is designed to operate effectively within the specified frequency range, making it suitable for various applications, including environmental monitoring and industrial safety. The LF351 operational amplifier is selected for its low noise characteristics, which enhances the sensor's sensitivity and accuracy. The pick-up section, consisting of the coil L1, captures the electromagnetic fields, converting them into a voltage signal that is subsequently amplified by IC1.
To ensure optimal performance, the circuit may include passive components such as resistors and capacitors, which help to filter out unwanted noise and stabilize the gain of the operational amplifier. The inclusion of the headphone Z1 allows for real-time audio feedback, enabling users to listen to the electromagnetic signals being detected. This feature is particularly useful in educational settings or for demonstrations.
The signal strength meter provides a visual representation of the detected electromagnetic field's intensity. Transistor Q1, functioning as a signal amplifier, boosts the output from IC1 sufficiently to drive the meter, ensuring that even weak signals can be accurately measured. The design may also incorporate calibration adjustments to allow for precise readings across different environmental conditions.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective tool for sensing and measuring electromagnetic fields, combining audio feedback and visual signal strength indicators to enhance user experience and application versatility.This is the circuit diagram of a very sensitive electromagnetic field sensor which can sense electromagnetic field from 40Hz to 140Hz. The low noise opamp LF351 and associated components forms the pick-up section. 1uH coil L1 is used for sensing the field and the IC1 performs the necessary amplification. If the picked electromagnetic field is in t he audio frequency range, it can be heard through the head phone Z1. There is also a meter arrangement for accurate measuring of the signal strength. Transistor Q1 performs additional amplification on the picked signal in order to drive the meter. 🔗 External reference
The electromagnetic field sensor circuit is designed to operate effectively within the specified frequency range, making it suitable for various applications, including environmental monitoring and industrial safety. The LF351 operational amplifier is selected for its low noise characteristics, which enhances the sensor's sensitivity and accuracy. The pick-up section, consisting of the coil L1, captures the electromagnetic fields, converting them into a voltage signal that is subsequently amplified by IC1.
To ensure optimal performance, the circuit may include passive components such as resistors and capacitors, which help to filter out unwanted noise and stabilize the gain of the operational amplifier. The inclusion of the headphone Z1 allows for real-time audio feedback, enabling users to listen to the electromagnetic signals being detected. This feature is particularly useful in educational settings or for demonstrations.
The signal strength meter provides a visual representation of the detected electromagnetic field's intensity. Transistor Q1, functioning as a signal amplifier, boosts the output from IC1 sufficiently to drive the meter, ensuring that even weak signals can be accurately measured. The design may also incorporate calibration adjustments to allow for precise readings across different environmental conditions.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective tool for sensing and measuring electromagnetic fields, combining audio feedback and visual signal strength indicators to enhance user experience and application versatility.This is the circuit diagram of a very sensitive electromagnetic field sensor which can sense electromagnetic field from 40Hz to 140Hz. The low noise opamp LF351 and associated components forms the pick-up section. 1uH coil L1 is used for sensing the field and the IC1 performs the necessary amplification. If the picked electromagnetic field is in t he audio frequency range, it can be heard through the head phone Z1. There is also a meter arrangement for accurate measuring of the signal strength. Transistor Q1 performs additional amplification on the picked signal in order to drive the meter. 🔗 External reference