Signals Logic Tester Circuit Using Display 7 Segment
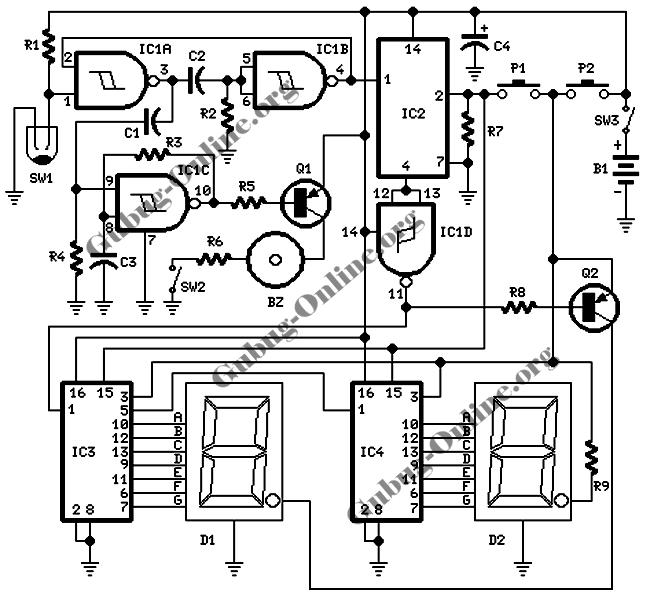
This design features a signal logic tester that utilizes a common cathode seven-segment display. The display indicates a logic level "1" (represented by an "H" on the display) or a logic level "0" (represented by an "L" on the display). If an undefined logic level is detected, the display will show an alternative indication.
The signal logic tester circuit operates by monitoring input signals and interpreting their logic levels. The common cathode seven-segment display is connected to a microcontroller or logic circuit that interprets the incoming signals. When the input signal is at a high logic level (logic "1"), the corresponding segment of the display illuminates to show an "H." Conversely, when the input signal is at a low logic level (logic "0"), the display shows an "L."
In the case of an undefined logic level, which may occur due to floating inputs or noise, the circuit is designed to provide a distinct visual cue. This could be achieved by illuminating a specific segment of the display or by activating an additional indicator, such as an LED, to alert the user that the signal is not within the expected range.
The circuit design typically includes a resistor network to limit current to the display segments and ensure proper operation. A microcontroller may be programmed to read the input levels and control the display outputs accordingly. The design may also incorporate debouncing techniques to filter out noise and provide stable readings.
Overall, this signal logic tester serves as a valuable tool for electronics engineers and technicians, allowing for quick and effective monitoring of digital signals in various applications.Here s a design of signals logic tester that is using indicate on a common cathode seven-segment display, if entry is at logic level ""1"" (one H on the display) or logic level (one L on the display). If an undefined level is detected will display .. 🔗 External reference
The signal logic tester circuit operates by monitoring input signals and interpreting their logic levels. The common cathode seven-segment display is connected to a microcontroller or logic circuit that interprets the incoming signals. When the input signal is at a high logic level (logic "1"), the corresponding segment of the display illuminates to show an "H." Conversely, when the input signal is at a low logic level (logic "0"), the display shows an "L."
In the case of an undefined logic level, which may occur due to floating inputs or noise, the circuit is designed to provide a distinct visual cue. This could be achieved by illuminating a specific segment of the display or by activating an additional indicator, such as an LED, to alert the user that the signal is not within the expected range.
The circuit design typically includes a resistor network to limit current to the display segments and ensure proper operation. A microcontroller may be programmed to read the input levels and control the display outputs accordingly. The design may also incorporate debouncing techniques to filter out noise and provide stable readings.
Overall, this signal logic tester serves as a valuable tool for electronics engineers and technicians, allowing for quick and effective monitoring of digital signals in various applications.Here s a design of signals logic tester that is using indicate on a common cathode seven-segment display, if entry is at logic level ""1"" (one H on the display) or logic level (one L on the display). If an undefined level is detected will display .. 🔗 External reference