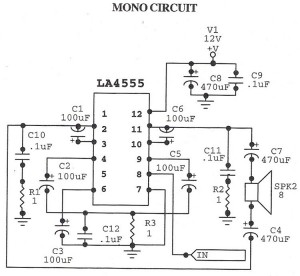
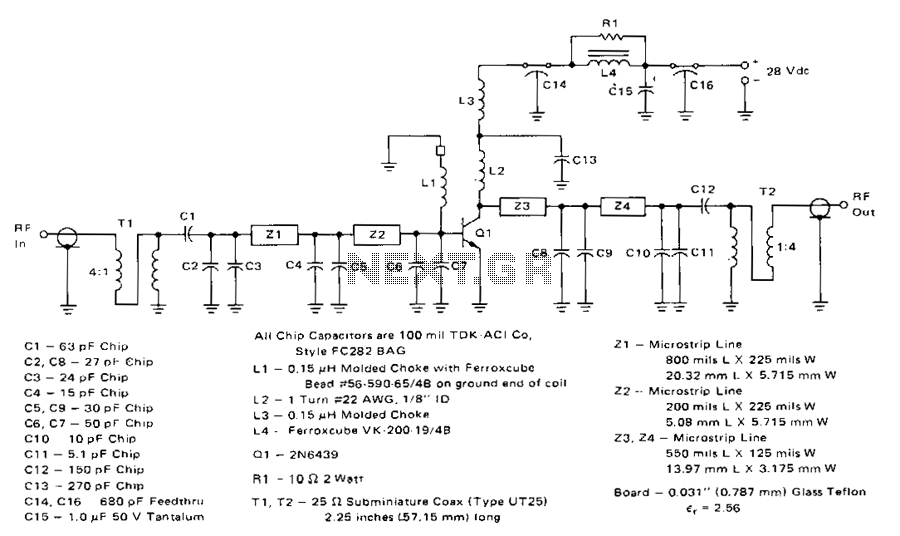
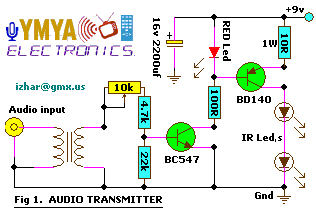
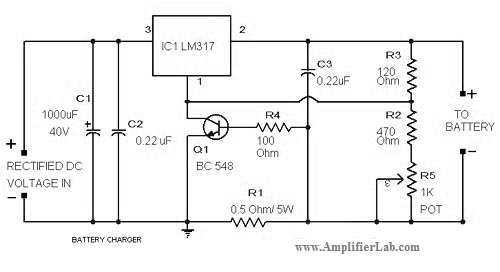
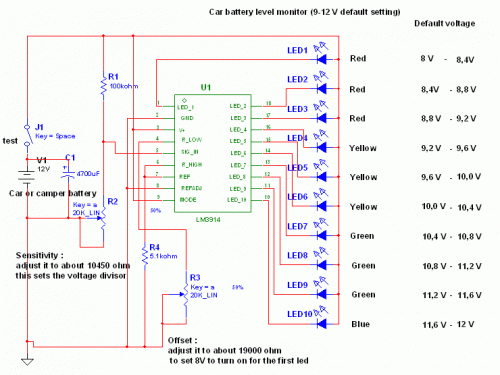
Simple 2 Transistor Headphone Amplifier
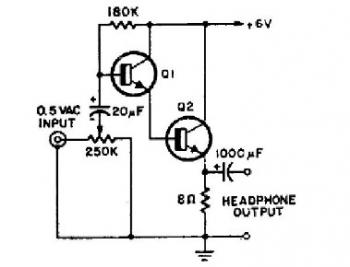
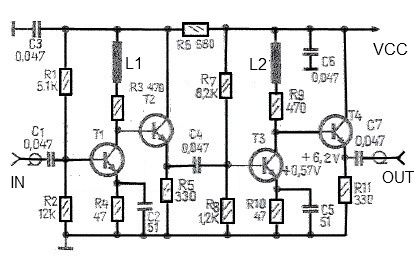
This schematic diagram illustrates a simple headphone amplifier circuit constructed using two NPN transistors. Suitable transistor options include the BC549C, as well as other NPN transistors such as the European equivalents BC548C, BC547C, BC239, 2N5818, or 2N2222. An audio amplifier is an electronic device designed to amplify low-power audio signals, which primarily consist of frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the range of human hearing. The amplifier raises these signals to a level appropriate for driving loudspeakers and serves as the final stage in a standard audio playback chain. Prior stages in this chain include low-power audio amplifiers that handle tasks such as pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, and mixing effects, as well as audio sources like record players, CD players, and cassette players. Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to meet line level standards. While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output can reach tens, hundreds, or even thousands of watts. Further information about power audio amplifiers can be found on Wikipedia. Additionally, a video tutorial is available for constructing a very simple audio amplifier based on the LM386 amplifier chip, which can be built for less than $20, or potentially under $8 in some regions, and can amplify any low-level audio signal, including those from guitars, bass instruments, or MP3 players.
The headphone amplifier circuit described utilizes two NPN transistors to achieve amplification of audio signals. The choice of transistors, such as the BC549C or its equivalents, ensures compatibility and reliability in performance. The circuit is designed to operate within the audio frequency range of 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which is essential for clear sound reproduction in audio applications.
In this configuration, the first transistor acts as a common-emitter amplifier, where the input audio signal is applied to the base terminal. This configuration provides voltage gain and inverts the signal. The output from the collector of the first transistor is then fed into the base of the second transistor, which serves to further amplify the signal. The overall gain of the circuit can be adjusted by varying the resistor values in the feedback loop and the biasing network.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the operation of the amplifier. It is recommended to use a regulated power supply to ensure stable operation and minimize noise. Capacitors may be included at the input and output stages to block any DC offset and to couple the audio signal, ensuring that only the AC component is amplified.
The headphone amplifier circuit can be used in various applications, including personal audio devices, DIY projects, or as part of a larger audio system. It is particularly beneficial for enhancing the audio output from low-level sources, providing a more robust audio experience for the user. The simplicity of the design allows for easy construction and troubleshooting, making it an excellent choice for both novice and experienced electronics enthusiasts.This is the schematic diagram of very simple headphone amplifier circuit. The circuit built using two NPN transistors. You can use transistor BC549C or other NPN transistors such as European equivalent: BC548C, BC547C, BC239, 2N5818 or 2N2222 An audio amplifier is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power audio signals (signals composed pri marily of frequencies between 20 - 20 000 Hz, the human range of hearing) to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers and is the final stage in a typical audio playback chain. The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, mixing/effects, or audio sources like record players, CD players, and cassette players.
Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to adhere to line levels. While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output may be tens, hundreds, or thousands of watts. More explanation about power audio amplifier can be found at wikipedia. org This is a video tutorial about how to a very simple audio amplifier based on the LM386 amplifier chip.
It can be built for less than $20 (or might be less than $8 in some countries) and used to amplify any low level audio signal including a guitar, bass or mp3 player. 🔗 External reference
The headphone amplifier circuit described utilizes two NPN transistors to achieve amplification of audio signals. The choice of transistors, such as the BC549C or its equivalents, ensures compatibility and reliability in performance. The circuit is designed to operate within the audio frequency range of 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which is essential for clear sound reproduction in audio applications.
In this configuration, the first transistor acts as a common-emitter amplifier, where the input audio signal is applied to the base terminal. This configuration provides voltage gain and inverts the signal. The output from the collector of the first transistor is then fed into the base of the second transistor, which serves to further amplify the signal. The overall gain of the circuit can be adjusted by varying the resistor values in the feedback loop and the biasing network.
Power supply considerations are crucial for the operation of the amplifier. It is recommended to use a regulated power supply to ensure stable operation and minimize noise. Capacitors may be included at the input and output stages to block any DC offset and to couple the audio signal, ensuring that only the AC component is amplified.
The headphone amplifier circuit can be used in various applications, including personal audio devices, DIY projects, or as part of a larger audio system. It is particularly beneficial for enhancing the audio output from low-level sources, providing a more robust audio experience for the user. The simplicity of the design allows for easy construction and troubleshooting, making it an excellent choice for both novice and experienced electronics enthusiasts.This is the schematic diagram of very simple headphone amplifier circuit. The circuit built using two NPN transistors. You can use transistor BC549C or other NPN transistors such as European equivalent: BC548C, BC547C, BC239, 2N5818 or 2N2222 An audio amplifier is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power audio signals (signals composed pri marily of frequencies between 20 - 20 000 Hz, the human range of hearing) to a level suitable for driving loudspeakers and is the final stage in a typical audio playback chain. The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification, equalization, tone control, mixing/effects, or audio sources like record players, CD players, and cassette players.
Most audio amplifiers require these low-level inputs to adhere to line levels. While the input signal to an audio amplifier may measure only a few hundred microwatts, its output may be tens, hundreds, or thousands of watts. More explanation about power audio amplifier can be found at wikipedia. org This is a video tutorial about how to a very simple audio amplifier based on the LM386 amplifier chip.
It can be built for less than $20 (or might be less than $8 in some countries) and used to amplify any low level audio signal including a guitar, bass or mp3 player. 🔗 External reference