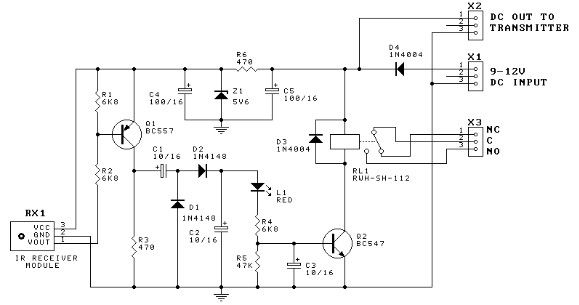
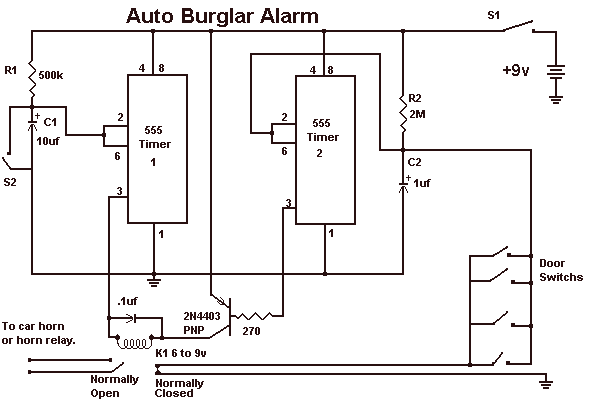
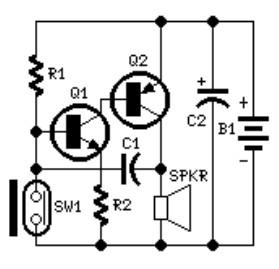
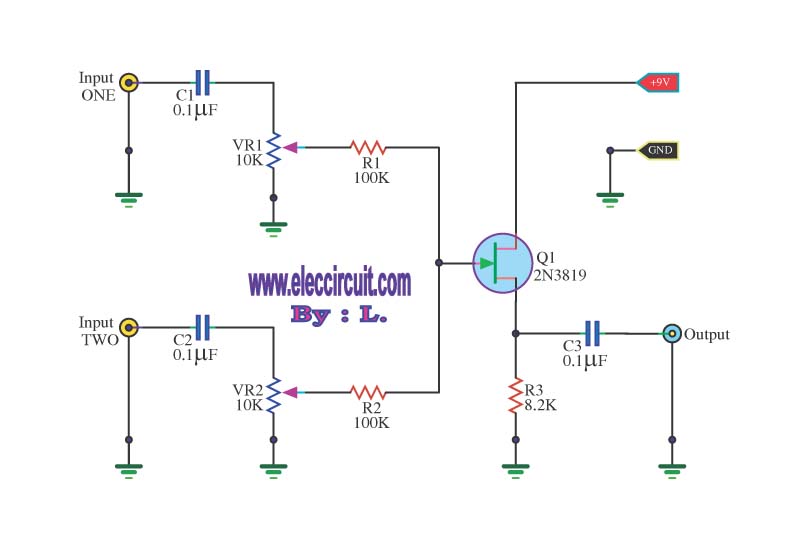
Simple 555 Vco
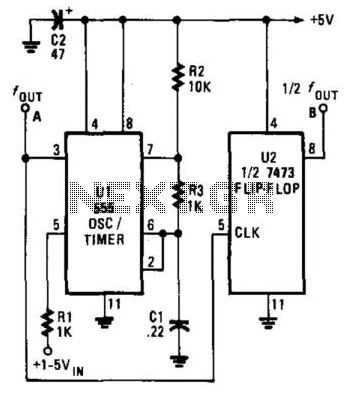
The Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) has an output frequency that ranges from 1500 Hz at Vcontrol = 1 V to 300 Hz at Vcontrol = 5 V. The resistive component R1 or the capacitive component C1 can be adjusted to modify this frequency range. U2 generates a symmetrical square-wave output at half the timer frequency.
The described Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) operates by varying its output frequency based on the control voltage applied. The specified frequency range indicates that at a lower control voltage of 1 V, the output frequency peaks at 1500 Hz, while at a higher control voltage of 5 V, the frequency decreases to 300 Hz. This characteristic allows for fine-tuning of the oscillator's frequency by adjusting either the resistor R1 or the capacitor C1, which are integral components in determining the time constant of the oscillator circuit.
The component U2 plays a crucial role in this configuration by providing a symmetrical square-wave output. This output is significant as it is generated at half the frequency of the main timer frequency, effectively allowing for dual frequency operation from a single circuit configuration. The symmetrical nature of the square wave ensures that the output has equal high and low durations, which is essential for many digital applications where timing and signal integrity are critical.
In designing the VCO circuit, careful selection of R1 and C1 is necessary to achieve the desired frequency range and stability. The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against voltage spikes, or op-amps for signal conditioning, depending on the intended application. The overall layout should ensure minimal interference and optimal performance, with considerations for power supply decoupling to maintain signal integrity.
This VCO configuration is useful in various applications, including modulation schemes in communication systems, signal generation for testing and measurement equipment, and as a timing source in digital circuits. The VCO has an output frequency that ranges from 1500Hz at V;,= 1 V to 300Hz at V;,=5 V. R1 or C1 can be varied to change th is range. U2 provides a symmetrical square-wave output of half the timer frequency.
The described Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) operates by varying its output frequency based on the control voltage applied. The specified frequency range indicates that at a lower control voltage of 1 V, the output frequency peaks at 1500 Hz, while at a higher control voltage of 5 V, the frequency decreases to 300 Hz. This characteristic allows for fine-tuning of the oscillator's frequency by adjusting either the resistor R1 or the capacitor C1, which are integral components in determining the time constant of the oscillator circuit.
The component U2 plays a crucial role in this configuration by providing a symmetrical square-wave output. This output is significant as it is generated at half the frequency of the main timer frequency, effectively allowing for dual frequency operation from a single circuit configuration. The symmetrical nature of the square wave ensures that the output has equal high and low durations, which is essential for many digital applications where timing and signal integrity are critical.
In designing the VCO circuit, careful selection of R1 and C1 is necessary to achieve the desired frequency range and stability. The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for protection against voltage spikes, or op-amps for signal conditioning, depending on the intended application. The overall layout should ensure minimal interference and optimal performance, with considerations for power supply decoupling to maintain signal integrity.
This VCO configuration is useful in various applications, including modulation schemes in communication systems, signal generation for testing and measurement equipment, and as a timing source in digital circuits. The VCO has an output frequency that ranges from 1500Hz at V;,= 1 V to 300Hz at V;,=5 V. R1 or C1 can be varied to change th is range. U2 provides a symmetrical square-wave output of half the timer frequency.