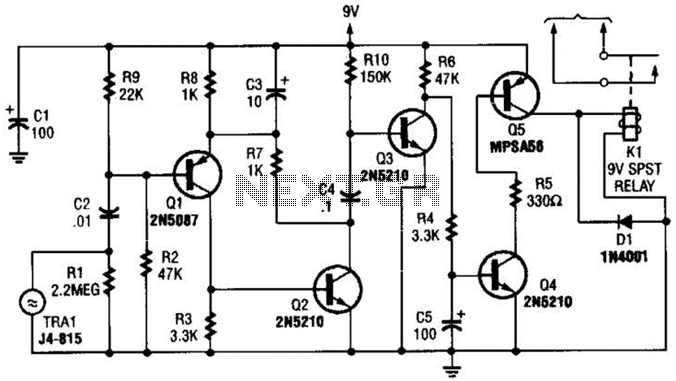
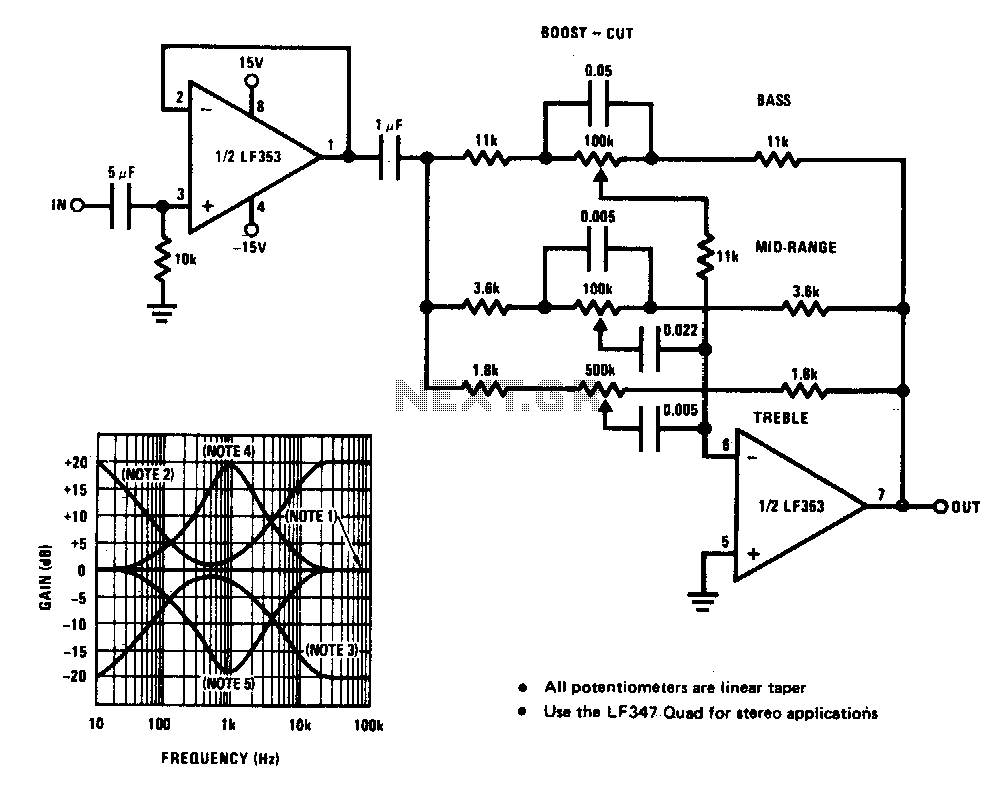
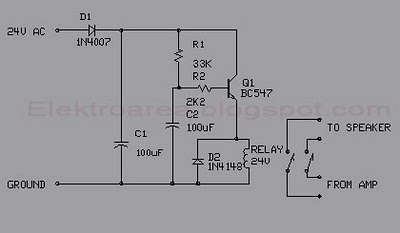
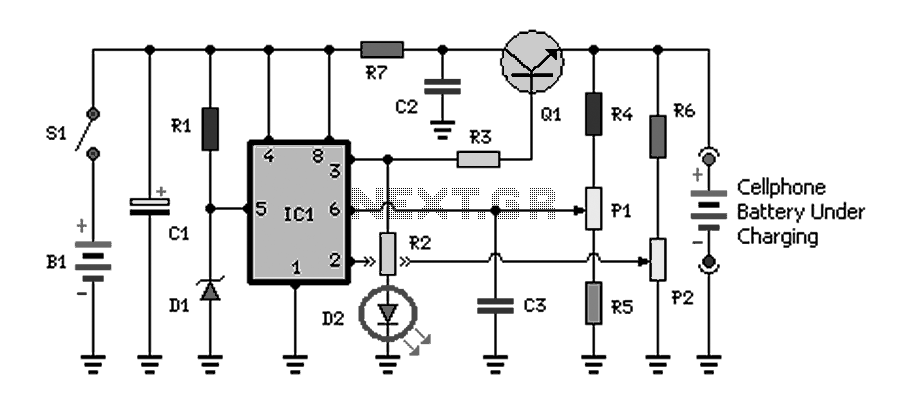
Simple Analog Multiplier Circuit Using LM107
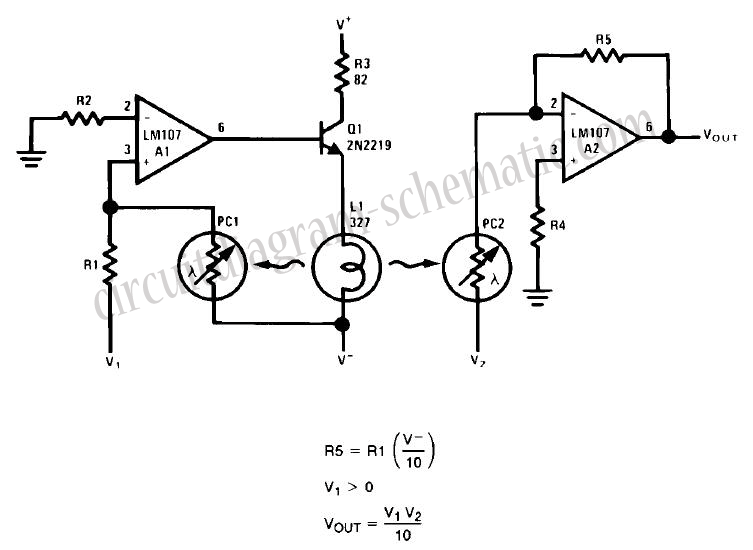
This circuit is a simple analog multiplier. The operation of the circuit can be understood by considering A2 as a controlled gain amplifier. It involves components such as an analog multiplier, a log-antilog circuit, and a summing junction, along with inverting amplifiers and photoconductors.
The described circuit functions as an analog multiplier, which is essential in various applications such as signal processing and control systems. The core of the circuit utilizes a controlled gain amplifier, designated as A2, which adjusts the gain based on the input signals. This enables the circuit to perform multiplication of two analog signals effectively.
In this configuration, the analog multiplier can be realized using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a specific arrangement. The log-antilog circuit is crucial for achieving the multiplication function, as it converts the input voltages into logarithmic values, allowing for the addition of these logarithmic signals. The summing junction, typically formed by an inverting amplifier, facilitates the addition of the logarithmic inputs.
Photoconductors may be integrated into the circuit to enable light-controlled operations, where the resistance of the photoconductor changes with light intensity, thereby affecting the gain of the amplifier. This feature allows for the modulation of the output based on ambient light conditions, making the circuit versatile for applications in light-sensitive environments.
Overall, the design and implementation of this analog multiplier circuit showcase the principles of analog signal processing, leveraging the characteristics of operational amplifiers and logarithmic functions to achieve accurate multiplication of input signals.This circuit a simple analog multiplier, the circuit operation may be understood by considering A2 as a controlled gain amplifier, Analog Multiplier, Multiplier Circuit, log-antilog circuit, analog multiplication, controlled gain amplifier, summing junction, photoconductors, inverting amplifier,. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as an analog multiplier, which is essential in various applications such as signal processing and control systems. The core of the circuit utilizes a controlled gain amplifier, designated as A2, which adjusts the gain based on the input signals. This enables the circuit to perform multiplication of two analog signals effectively.
In this configuration, the analog multiplier can be realized using operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a specific arrangement. The log-antilog circuit is crucial for achieving the multiplication function, as it converts the input voltages into logarithmic values, allowing for the addition of these logarithmic signals. The summing junction, typically formed by an inverting amplifier, facilitates the addition of the logarithmic inputs.
Photoconductors may be integrated into the circuit to enable light-controlled operations, where the resistance of the photoconductor changes with light intensity, thereby affecting the gain of the amplifier. This feature allows for the modulation of the output based on ambient light conditions, making the circuit versatile for applications in light-sensitive environments.
Overall, the design and implementation of this analog multiplier circuit showcase the principles of analog signal processing, leveraging the characteristics of operational amplifiers and logarithmic functions to achieve accurate multiplication of input signals.This circuit a simple analog multiplier, the circuit operation may be understood by considering A2 as a controlled gain amplifier, Analog Multiplier, Multiplier Circuit, log-antilog circuit, analog multiplication, controlled gain amplifier, summing junction, photoconductors, inverting amplifier,. 🔗 External reference