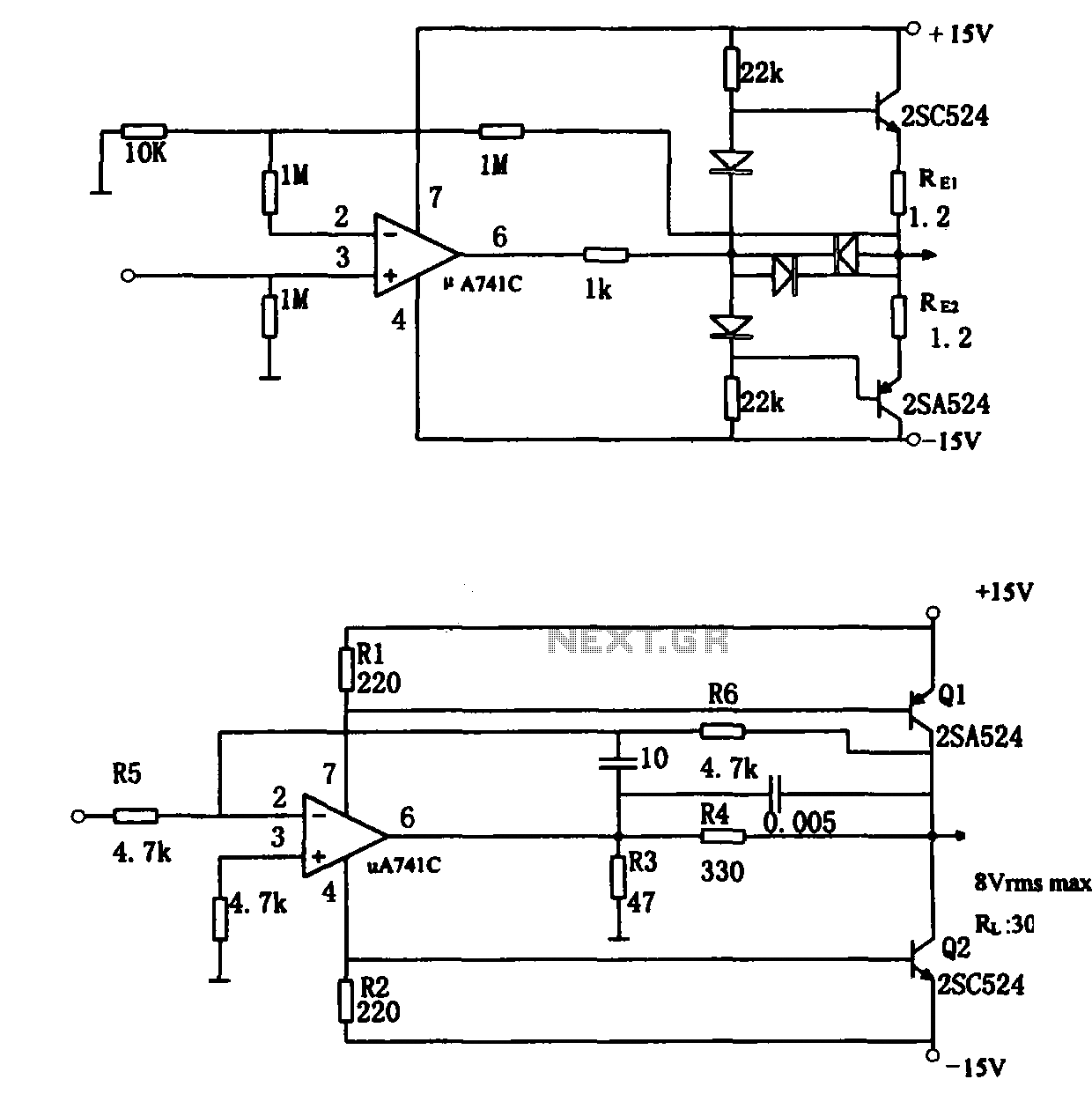
simple delay speaker circuit schematic
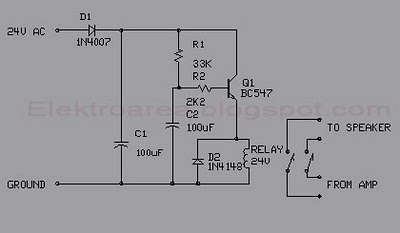
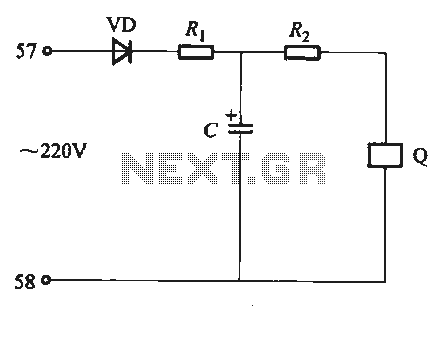
This circuit was designed for an audio amplifier project to control the speaker output relay. The primary function of this circuit is to manage the relay that activates the speaker output in the audio amplifier. The circuit introduces a delay of approximately five seconds after power-up before connecting the speakers to the amplifier output, thereby preventing the undesirable "thump" sound from the speakers. Additionally, this circuit immediately disconnects the speakers when the power to the amplifier is turned off, thus avoiding unpleasant noises during equipment shutdown. When power is applied to the circuit's input, the positive phase of the AC voltage charges capacitor C1. Subsequently, capacitor C2 begins to charge slowly through resistor R1. As the voltage across C2 increases, the emitter output voltage of transistor Q1 also rises in conjunction with the voltage on C2. Once the output voltage of transistor Q2 reaches a sufficient level (typically around 16 to 20V), the relay is activated, connecting the speakers to the amplifier output. The relay typically takes around five seconds to conduct after power-up, with the exact time depending on the capacitance of C2, the relay voltage, and the circuit input voltage.
The circuit employs a relay to manage speaker connection and disconnection based on the amplifier's power state. The delay mechanism is crucial for preventing speaker damage and undesirable audio artifacts during power transitions. The charging of C1 and C2 is integral to the timing aspect; C1 provides initial power stabilization while C2's charging rate, governed by R1, dictates the delay duration. The choice of components, particularly the values of C2 and R1, allows for customization of the delay period to suit specific application needs.
Transistors Q1 and Q2 serve as the control elements within the circuit. Q1 operates as a switch that is turned on when the voltage across C2 reaches a certain threshold, allowing current to flow and energizing the relay. Q2 amplifies the control signal from Q1, ensuring that the relay is adequately driven to its on state, which is essential for reliable operation. The relay itself must be rated appropriately for the speaker load and the amplifier's output characteristics to ensure safe and effective operation.
In summary, this circuit effectively integrates timing and control elements to enhance the performance of audio amplifiers, providing a practical solution to common issues associated with speaker connection and disconnection during power transitions.This is scircuit which I built to one of audio amplifier projects to control the speaker output relay. The purpose of this circuit is to control the relay which turns on the speaker output relay in the audio amplifier.
The idea of the circuit is wait around 5 seconds ofter the power up until the spakers are switched to the amplfier output to avoid annoying "thump" sound from the speakers. Another feeature of this circuit is that is disconnects the speaker immdiatly when the power in the amplifier is cut off, so avoinding sometimes nasty sounds when you turn the equipments off. Then power is applied to the power input of the circuit, the positive phase of AC voltage charges C1.
Then C2 starts to charge slowly through R1. When the voltage in C2 rises, the emitter output voltage of Q1 rises tigether with voltage on C2. When the output voltage of Q2 is high enough (typically around 16. 20V) the relay goes to on state and the relay witches connect the speakers to the amplifier output. It takes typically around 5 seconds after power up until the relay starts to condict (at absolute time depends on the size of C2, relay voltage and circuit input voltage). 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a relay to manage speaker connection and disconnection based on the amplifier's power state. The delay mechanism is crucial for preventing speaker damage and undesirable audio artifacts during power transitions. The charging of C1 and C2 is integral to the timing aspect; C1 provides initial power stabilization while C2's charging rate, governed by R1, dictates the delay duration. The choice of components, particularly the values of C2 and R1, allows for customization of the delay period to suit specific application needs.
Transistors Q1 and Q2 serve as the control elements within the circuit. Q1 operates as a switch that is turned on when the voltage across C2 reaches a certain threshold, allowing current to flow and energizing the relay. Q2 amplifies the control signal from Q1, ensuring that the relay is adequately driven to its on state, which is essential for reliable operation. The relay itself must be rated appropriately for the speaker load and the amplifier's output characteristics to ensure safe and effective operation.
In summary, this circuit effectively integrates timing and control elements to enhance the performance of audio amplifiers, providing a practical solution to common issues associated with speaker connection and disconnection during power transitions.This is scircuit which I built to one of audio amplifier projects to control the speaker output relay. The purpose of this circuit is to control the relay which turns on the speaker output relay in the audio amplifier.
The idea of the circuit is wait around 5 seconds ofter the power up until the spakers are switched to the amplfier output to avoid annoying "thump" sound from the speakers. Another feeature of this circuit is that is disconnects the speaker immdiatly when the power in the amplifier is cut off, so avoinding sometimes nasty sounds when you turn the equipments off. Then power is applied to the power input of the circuit, the positive phase of AC voltage charges C1.
Then C2 starts to charge slowly through R1. When the voltage in C2 rises, the emitter output voltage of Q1 rises tigether with voltage on C2. When the output voltage of Q2 is high enough (typically around 16. 20V) the relay goes to on state and the relay witches connect the speakers to the amplifier output. It takes typically around 5 seconds after power up until the relay starts to condict (at absolute time depends on the size of C2, relay voltage and circuit input voltage). 🔗 External reference