Simple circuit diagram repellent

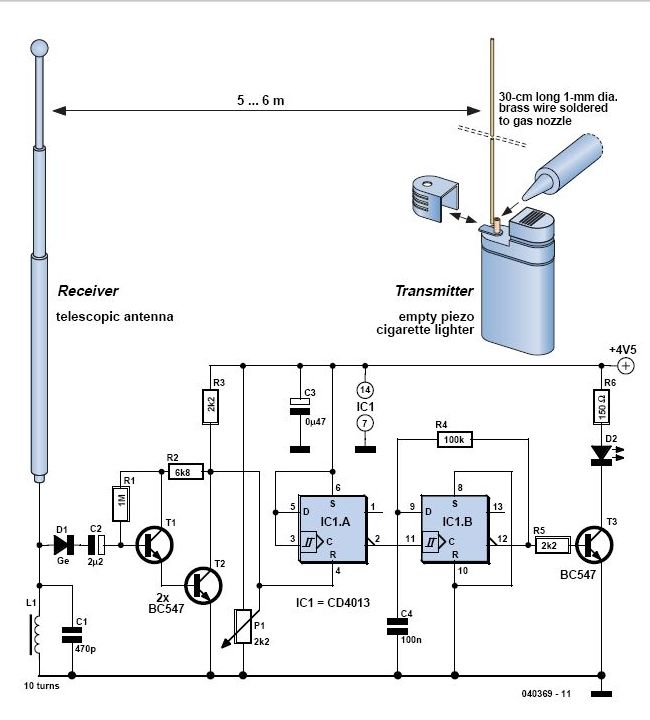
A low-cost and straightforward repellent circuit can be utilized for deterring rats, mice, and other animals, as illustrated in the electronic figure below. The circuit employs a CMOS integrated circuit of type 4047, which functions as a relaxation oscillator. Its frequency can be adjusted between 5 kHz to 30 kHz using potentiometer P1. The Q and Q outputs from each section are connected to non-inverting amplifiers of type 4050, designated as IC2 and IC3. The six stages of the integrated circuit are connected in parallel, allowing simultaneous activation of transistors T1/T2 and T3/T4. These transistor pairs can drive a piezoelectric speaker, with the circuit providing an output of 15-18 VDC.
The described circuit operates by generating high-frequency sound waves that are unpleasant to rodents and other small animals, effectively acting as a deterrent. The core component, the CMOS 4047 integrated circuit, is configured as a relaxation oscillator. This configuration enables the circuit to produce a square wave output, the frequency of which can be fine-tuned using the adjustable potentiometer P1. The output frequency range of 5 kHz to 30 kHz is particularly effective, as many pests are sensitive to ultrasonic frequencies.
The non-inverting amplifiers (IC2 and IC3) serve to boost the output signal from the 4047 circuit, ensuring that sufficient power is delivered to the subsequent transistor stages. The parallel connection of the six stages enhances the overall output power, allowing for more robust operation of the connected transistors. Transistors T1 and T2, as well as T3 and T4, work in pairs to drive the piezoelectric speaker, which converts the electrical signals into sound waves.
The circuit operates with a power supply providing 15-18 VDC, which is adequate for the functioning of the amplifiers and transistors. The piezoelectric speaker is chosen for its ability to produce high-frequency sounds efficiently, contributing to the effectiveness of the repellent circuit. This design is particularly advantageous for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it accessible for widespread use in pest control applications.A very cheap and simple repellents can be used for rats, mice and other animals may use electronic figure below. Circuit using CMOS integrated circuit type 4047 is connected to function as a relaxation oscillator whose frequency can be adjusted between 5 kHz to 30 kHz, the potentiometer P1. Q and Q outputs of each section are applicable to each of the non-inverting amplifier 4050 type, IC2 and IC3.
Each of the six stages of the integrated circuit, connected in parallel, allowing direct attack transistors T1/T2, respectively T3/T4 T1 or T2 and T4 and T3 simultaneously. These pairs of transistors can attack the piezoelectric speaker. Circuit provides a 15-18 Vdc
The described circuit operates by generating high-frequency sound waves that are unpleasant to rodents and other small animals, effectively acting as a deterrent. The core component, the CMOS 4047 integrated circuit, is configured as a relaxation oscillator. This configuration enables the circuit to produce a square wave output, the frequency of which can be fine-tuned using the adjustable potentiometer P1. The output frequency range of 5 kHz to 30 kHz is particularly effective, as many pests are sensitive to ultrasonic frequencies.
The non-inverting amplifiers (IC2 and IC3) serve to boost the output signal from the 4047 circuit, ensuring that sufficient power is delivered to the subsequent transistor stages. The parallel connection of the six stages enhances the overall output power, allowing for more robust operation of the connected transistors. Transistors T1 and T2, as well as T3 and T4, work in pairs to drive the piezoelectric speaker, which converts the electrical signals into sound waves.
The circuit operates with a power supply providing 15-18 VDC, which is adequate for the functioning of the amplifiers and transistors. The piezoelectric speaker is chosen for its ability to produce high-frequency sounds efficiently, contributing to the effectiveness of the repellent circuit. This design is particularly advantageous for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it accessible for widespread use in pest control applications.A very cheap and simple repellents can be used for rats, mice and other animals may use electronic figure below. Circuit using CMOS integrated circuit type 4047 is connected to function as a relaxation oscillator whose frequency can be adjusted between 5 kHz to 30 kHz, the potentiometer P1. Q and Q outputs of each section are applicable to each of the non-inverting amplifier 4050 type, IC2 and IC3.
Each of the six stages of the integrated circuit, connected in parallel, allowing direct attack transistors T1/T2, respectively T3/T4 T1 or T2 and T4 and T3 simultaneously. These pairs of transistors can attack the piezoelectric speaker. Circuit provides a 15-18 Vdc