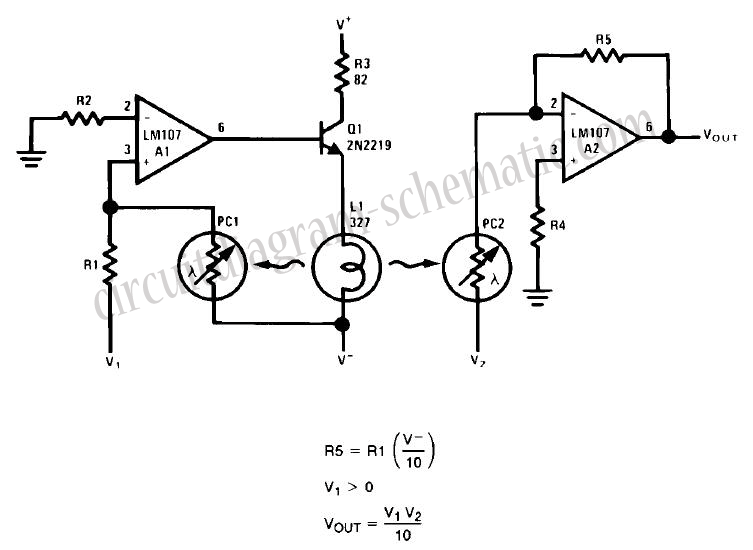
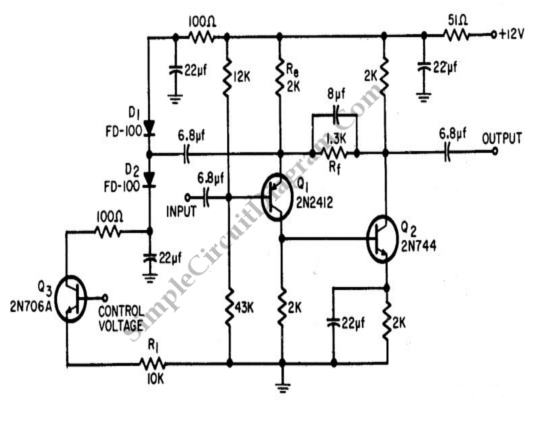
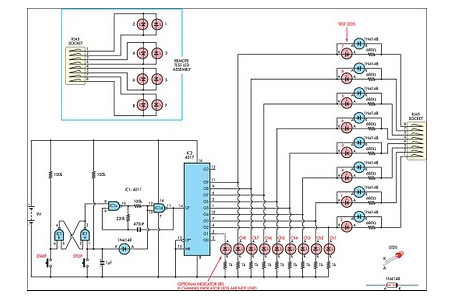
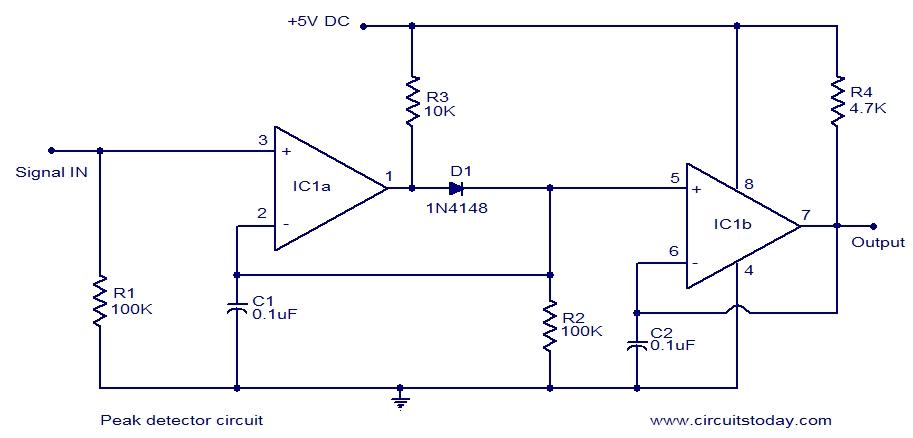
Simple FM Radio with improved audio gain
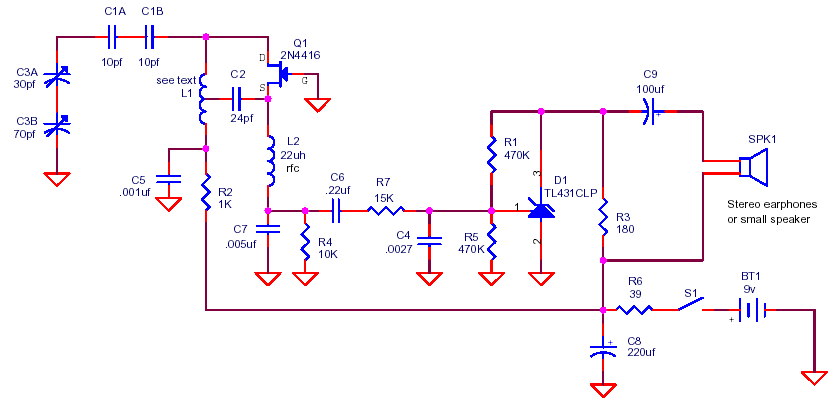
Wind 6 turns of solid wire on a pen or pencil that is just under 1/2 inch in diameter. Remove the wire from the pencil and spread the winding to make a length of 3/4 inch. Solder C2 somewhere near the middle of the coil.
To create an inductor using solid wire, begin by winding six turns of the wire around a cylindrical object, such as a pen or pencil, which should have a diameter of approximately 0.5 inches. After completing the winding process, carefully remove the coil from the cylindrical form. The next step involves gently spreading the coils apart to achieve a total length of approximately 0.75 inches.
Once the coil is properly shaped, the component labeled C2 should be soldered to the coil. The placement of C2 is critical; it should be positioned near the center of the coil to ensure optimal electrical performance. This configuration allows for effective inductance, which can be utilized in various electronic applications, such as filters, oscillators, or power supply circuits.
The solid wire used for winding should be of an appropriate gauge to handle the current requirements of the circuit while minimizing resistive losses. Additionally, the number of turns and the spacing between them can influence the inductance value, which can be calculated using the formula for inductance based on the coil's physical dimensions and the properties of the wire material. Proper insulation should be considered to prevent short circuits, especially if the coil is to be placed in a compact enclosure with other components.Wind 6 turns of solid wire on a pen or pencil that is just under 1/2 inch in diameter. Remove the wire from the pencil and spread the winding to make a length of 3/4 inch. Solder C2 somewhere near the middle of the coil. 🔗 External reference
To create an inductor using solid wire, begin by winding six turns of the wire around a cylindrical object, such as a pen or pencil, which should have a diameter of approximately 0.5 inches. After completing the winding process, carefully remove the coil from the cylindrical form. The next step involves gently spreading the coils apart to achieve a total length of approximately 0.75 inches.
Once the coil is properly shaped, the component labeled C2 should be soldered to the coil. The placement of C2 is critical; it should be positioned near the center of the coil to ensure optimal electrical performance. This configuration allows for effective inductance, which can be utilized in various electronic applications, such as filters, oscillators, or power supply circuits.
The solid wire used for winding should be of an appropriate gauge to handle the current requirements of the circuit while minimizing resistive losses. Additionally, the number of turns and the spacing between them can influence the inductance value, which can be calculated using the formula for inductance based on the coil's physical dimensions and the properties of the wire material. Proper insulation should be considered to prevent short circuits, especially if the coil is to be placed in a compact enclosure with other components.Wind 6 turns of solid wire on a pen or pencil that is just under 1/2 inch in diameter. Remove the wire from the pencil and spread the winding to make a length of 3/4 inch. Solder C2 somewhere near the middle of the coil. 🔗 External reference