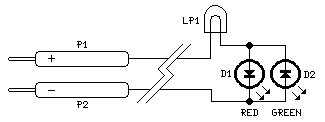
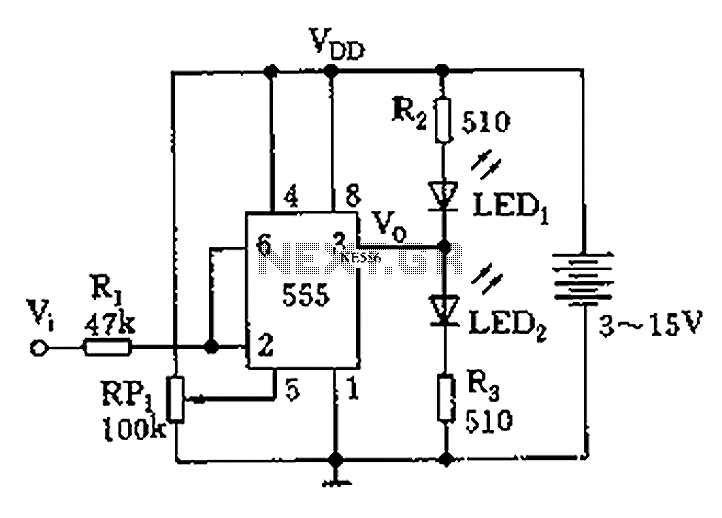
Simple Discrete Logic Probe

This is a simple logic probe circuit. A logic probe is used to determine if a point in a circuit has a high or low state when the circuit is in operation.
The logic probe circuit is a fundamental tool in electronics, serving to indicate the logical state of a digital signal at various points within a circuit. The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a power supply, a resistor, a diode, and an LED (Light Emitting Diode).
When the probe tip is connected to a point in the circuit, the circuit must be powered. If the point is at a high state (usually representing a logical '1'), the voltage at that point will exceed a certain threshold, allowing current to flow through the circuit. This current passes through the resistor and the LED, causing the LED to illuminate, indicating a high state.
Conversely, if the point is at a low state (representing a logical '0'), the voltage will be insufficient to forward bias the diode, and the LED will remain off, indicating a low state.
To enhance the functionality of the logic probe, additional features can be integrated. These may include a built-in buzzer that sounds when a high state is detected or a switch that allows the user to select between different voltage thresholds for testing. The design may also incorporate a multi-colored LED to provide more intuitive feedback, such as green for high and red for low.
The logic probe circuit is essential for troubleshooting and verifying the operation of digital circuits, making it an invaluable tool for engineers and hobbyists alike. Proper understanding and implementation of this circuit can aid in the efficient diagnosis of circuit issues, ensuring reliable performance in electronic systems.This is simple logic probe circuit. Logic probe is used to determine if a point in a circuit has high or low state when the circuit is in operation.? Here is. 🔗 External reference
The logic probe circuit is a fundamental tool in electronics, serving to indicate the logical state of a digital signal at various points within a circuit. The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a power supply, a resistor, a diode, and an LED (Light Emitting Diode).
When the probe tip is connected to a point in the circuit, the circuit must be powered. If the point is at a high state (usually representing a logical '1'), the voltage at that point will exceed a certain threshold, allowing current to flow through the circuit. This current passes through the resistor and the LED, causing the LED to illuminate, indicating a high state.
Conversely, if the point is at a low state (representing a logical '0'), the voltage will be insufficient to forward bias the diode, and the LED will remain off, indicating a low state.
To enhance the functionality of the logic probe, additional features can be integrated. These may include a built-in buzzer that sounds when a high state is detected or a switch that allows the user to select between different voltage thresholds for testing. The design may also incorporate a multi-colored LED to provide more intuitive feedback, such as green for high and red for low.
The logic probe circuit is essential for troubleshooting and verifying the operation of digital circuits, making it an invaluable tool for engineers and hobbyists alike. Proper understanding and implementation of this circuit can aid in the efficient diagnosis of circuit issues, ensuring reliable performance in electronic systems.This is simple logic probe circuit. Logic probe is used to determine if a point in a circuit has high or low state when the circuit is in operation.? Here is. 🔗 External reference