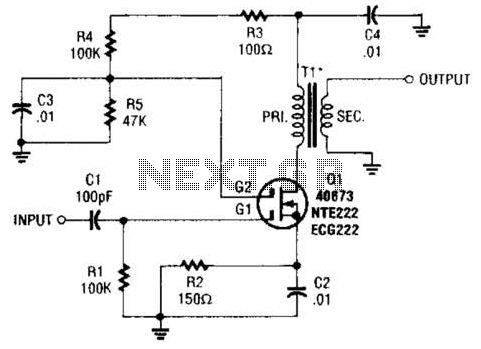
Simple light-operated street lamp circuit diagram(3)
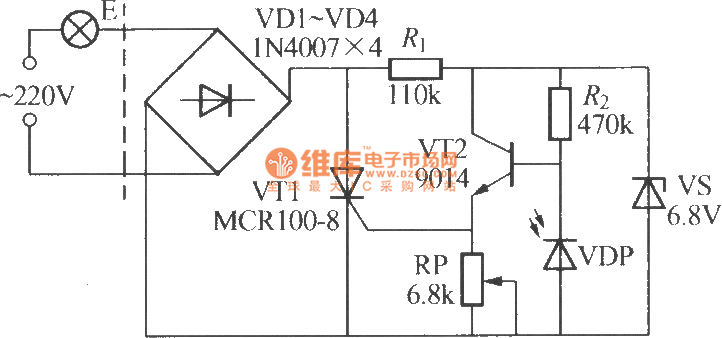
The VDP is a photodiode that exhibits low resistance during the day, approximately 1 kΩ. As a result, transistor VT2 remains off, which keeps thyristor VT1 in the off-state due to the absence of trigger current at the gate, preventing the emitter (E) from being activated. At night, the photodiode shows high resistance due to the lack of light exposure, around 100 kΩ, causing VT2 to turn on and allowing the emitter to output a positive signal.
The circuit involves a photodiode (VDP) functioning as a light sensor, controlling the state of a transistor (VT2) and a thyristor (VT1). During daylight, the low resistance of the photodiode results in VT2 being non-conductive, which in turn ensures that VT1 remains off since there is no gate current to trigger it. Consequently, the emitter (E) does not receive power, thus remaining inactive.
In contrast, during nighttime, the photodiode's resistance increases significantly due to the absence of light, reaching approximately 100 kΩ. This high resistance activates VT2, allowing it to conduct. The activation of VT2 subsequently provides the necessary trigger current to the gate of thyristor VT1, turning it on. When VT1 is triggered, it allows current to flow to the emitter (E), resulting in its activation.
This configuration can be utilized in various applications, such as automatic lighting systems, where the circuit responds to ambient light levels. The transition between day and night conditions is critical for the operation of this circuit, ensuring that the emitter is only powered in low-light conditions. Proper selection of components, such as the photodiode, transistors, and thyristor, is essential to achieve the desired response times and sensitivity to light changes. The circuit may also include additional elements such as resistors for biasing and capacitors for filtering, which can enhance performance and stability.VDP is the photodiode and it has low resistance in the day, and resistance ? 1k?, then transistor VT2 is turned off, then thyristor VT1 is in the off-state as the gate has no trigger current, and E can not be lit. In the night, VL shows a high resistance as no light exposure, and the resistance ? 100k?, then VT2 is turned on, and the emitter can output pos.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit involves a photodiode (VDP) functioning as a light sensor, controlling the state of a transistor (VT2) and a thyristor (VT1). During daylight, the low resistance of the photodiode results in VT2 being non-conductive, which in turn ensures that VT1 remains off since there is no gate current to trigger it. Consequently, the emitter (E) does not receive power, thus remaining inactive.
In contrast, during nighttime, the photodiode's resistance increases significantly due to the absence of light, reaching approximately 100 kΩ. This high resistance activates VT2, allowing it to conduct. The activation of VT2 subsequently provides the necessary trigger current to the gate of thyristor VT1, turning it on. When VT1 is triggered, it allows current to flow to the emitter (E), resulting in its activation.
This configuration can be utilized in various applications, such as automatic lighting systems, where the circuit responds to ambient light levels. The transition between day and night conditions is critical for the operation of this circuit, ensuring that the emitter is only powered in low-light conditions. Proper selection of components, such as the photodiode, transistors, and thyristor, is essential to achieve the desired response times and sensitivity to light changes. The circuit may also include additional elements such as resistors for biasing and capacitors for filtering, which can enhance performance and stability.VDP is the photodiode and it has low resistance in the day, and resistance ? 1k?, then transistor VT2 is turned off, then thyristor VT1 is in the off-state as the gate has no trigger current, and E can not be lit. In the night, VL shows a high resistance as no light exposure, and the resistance ? 100k?, then VT2 is turned on, and the emitter can output pos.. 🔗 External reference