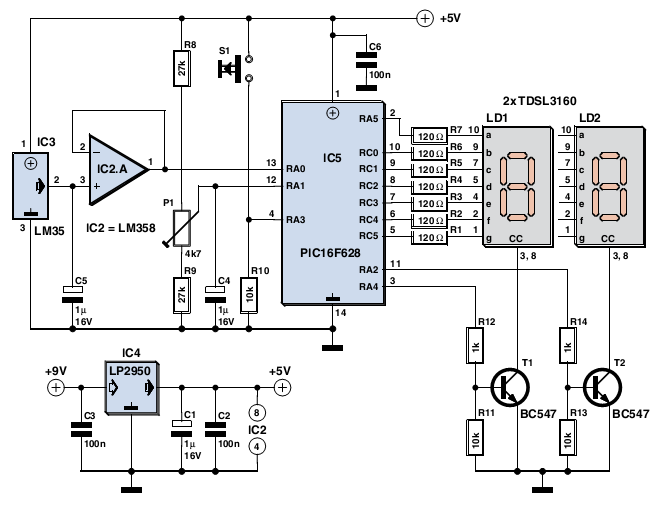
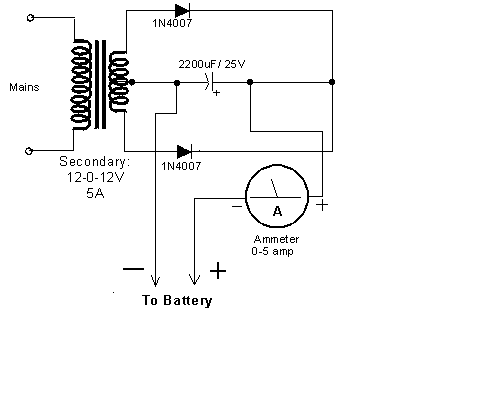
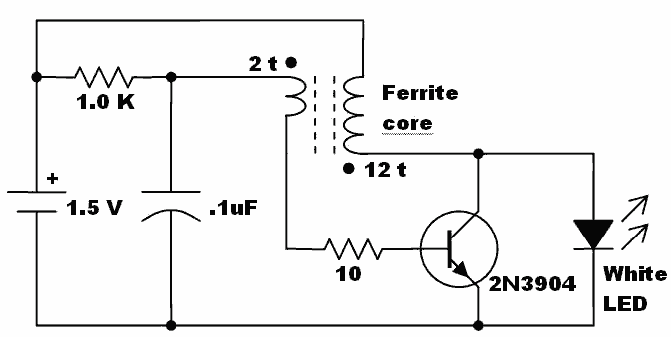
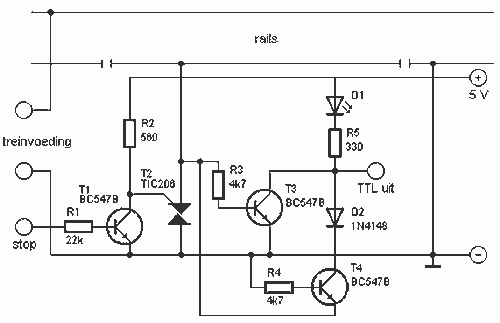
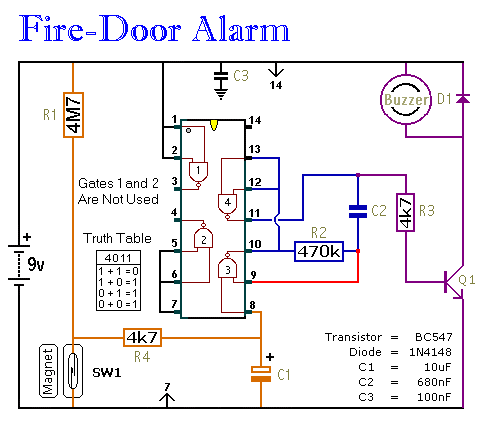
Simple Multi-Tone Alarm Circuit

The figure illustrates the circuit diagram of a multi-tone alarm, which fundamentally operates as an amplifier circuit. The core component of this circuit is the dual.
The multi-tone alarm circuit is designed to produce various sound tones, enhancing its alerting capabilities. The primary function of the amplifier within the circuit is to increase the audio signal generated by a sound source, enabling it to drive a speaker or buzzer effectively.
At the heart of this circuit is a dual operational amplifier (op-amp), which can be configured to generate different frequencies. The circuit typically includes resistors and capacitors that determine the output tone's frequency and duration. By adjusting the values of these passive components, the user can fine-tune the sound output to meet specific requirements.
The circuit may also incorporate a microcontroller or timer IC to automate the tone generation process. This addition allows for programmable sequences of tones, further enhancing the alarm's functionality. The output stage usually consists of a transistor amplifier that provides sufficient power to drive a larger speaker, ensuring that the alarm can be heard over considerable distances.
Power supply considerations are crucial for this type of circuit. It is typically powered by a DC source, such as batteries or a regulated power supply, which ensures stable operation. Protection components, such as diodes, may be included to safeguard the circuit from voltage spikes.
Overall, the multi-tone alarm circuit is a versatile design that can be adapted for various applications, including security systems, alert systems in industrial settings, and personal safety devices. Its ability to produce multiple tones makes it an effective tool for drawing attention in emergency situations.Figure shows the circuit diagram of multi tone alarm. This is basically an amplifier circuit. The central part of this circuit is the dual. 🔗 External reference
The multi-tone alarm circuit is designed to produce various sound tones, enhancing its alerting capabilities. The primary function of the amplifier within the circuit is to increase the audio signal generated by a sound source, enabling it to drive a speaker or buzzer effectively.
At the heart of this circuit is a dual operational amplifier (op-amp), which can be configured to generate different frequencies. The circuit typically includes resistors and capacitors that determine the output tone's frequency and duration. By adjusting the values of these passive components, the user can fine-tune the sound output to meet specific requirements.
The circuit may also incorporate a microcontroller or timer IC to automate the tone generation process. This addition allows for programmable sequences of tones, further enhancing the alarm's functionality. The output stage usually consists of a transistor amplifier that provides sufficient power to drive a larger speaker, ensuring that the alarm can be heard over considerable distances.
Power supply considerations are crucial for this type of circuit. It is typically powered by a DC source, such as batteries or a regulated power supply, which ensures stable operation. Protection components, such as diodes, may be included to safeguard the circuit from voltage spikes.
Overall, the multi-tone alarm circuit is a versatile design that can be adapted for various applications, including security systems, alert systems in industrial settings, and personal safety devices. Its ability to produce multiple tones makes it an effective tool for drawing attention in emergency situations.Figure shows the circuit diagram of multi tone alarm. This is basically an amplifier circuit. The central part of this circuit is the dual. 🔗 External reference