Simple Photoelectric Light Controller
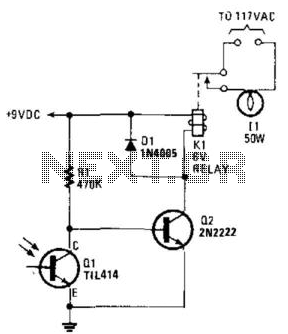
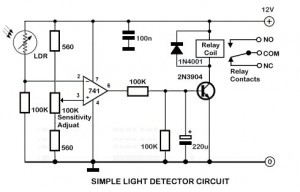
A phototransistor detects daylight. At dusk, it stops conducting, and Rl biases Q2, activating Kl, which turns on the light. At dawn, Ql begins to conduct, cutting off Q2. Kl deactivates, and the light turns off.
The circuit utilizes a phototransistor to monitor ambient light levels. During daylight, the phototransistor remains in a conductive state, allowing current to flow through it. As the sun sets and the light diminishes, the phototransistor transitions to a non-conductive state. This change in state is critical as it allows resistor Rl to provide biasing to transistor Q2. When Q2 is activated, it triggers relay Kl, which in turn powers the connected light source, illuminating the area.
As dawn approaches and light levels increase, phototransistor Ql begins to conduct again. This conduction effectively cuts off the biasing current to Q2, leading to its deactivation. Consequently, relay Kl is also deactivated, which turns off the light. The interplay between the phototransistor and the transistors provides an automatic lighting solution that responds to environmental changes, ensuring that lights are only on when needed.
In summary, this circuit design exemplifies efficient light control through the use of a phototransistor and associated components, creating an automated system that enhances convenience and energy efficiency. A phototransistor senses daylight. At dusk, it ceases to conduct and Rl biases Q2, activates Kl, and switches on the light. At dawn, Ql starts to conduct, and Q2 is cut off. Kl drops out and the light goes out.
The circuit utilizes a phototransistor to monitor ambient light levels. During daylight, the phototransistor remains in a conductive state, allowing current to flow through it. As the sun sets and the light diminishes, the phototransistor transitions to a non-conductive state. This change in state is critical as it allows resistor Rl to provide biasing to transistor Q2. When Q2 is activated, it triggers relay Kl, which in turn powers the connected light source, illuminating the area.
As dawn approaches and light levels increase, phototransistor Ql begins to conduct again. This conduction effectively cuts off the biasing current to Q2, leading to its deactivation. Consequently, relay Kl is also deactivated, which turns off the light. The interplay between the phototransistor and the transistors provides an automatic lighting solution that responds to environmental changes, ensuring that lights are only on when needed.
In summary, this circuit design exemplifies efficient light control through the use of a phototransistor and associated components, creating an automated system that enhances convenience and energy efficiency. A phototransistor senses daylight. At dusk, it ceases to conduct and Rl biases Q2, activates Kl, and switches on the light. At dawn, Ql starts to conduct, and Q2 is cut off. Kl drops out and the light goes out.