Simple Pyro RF Transmitter (27 MHz) Circuit
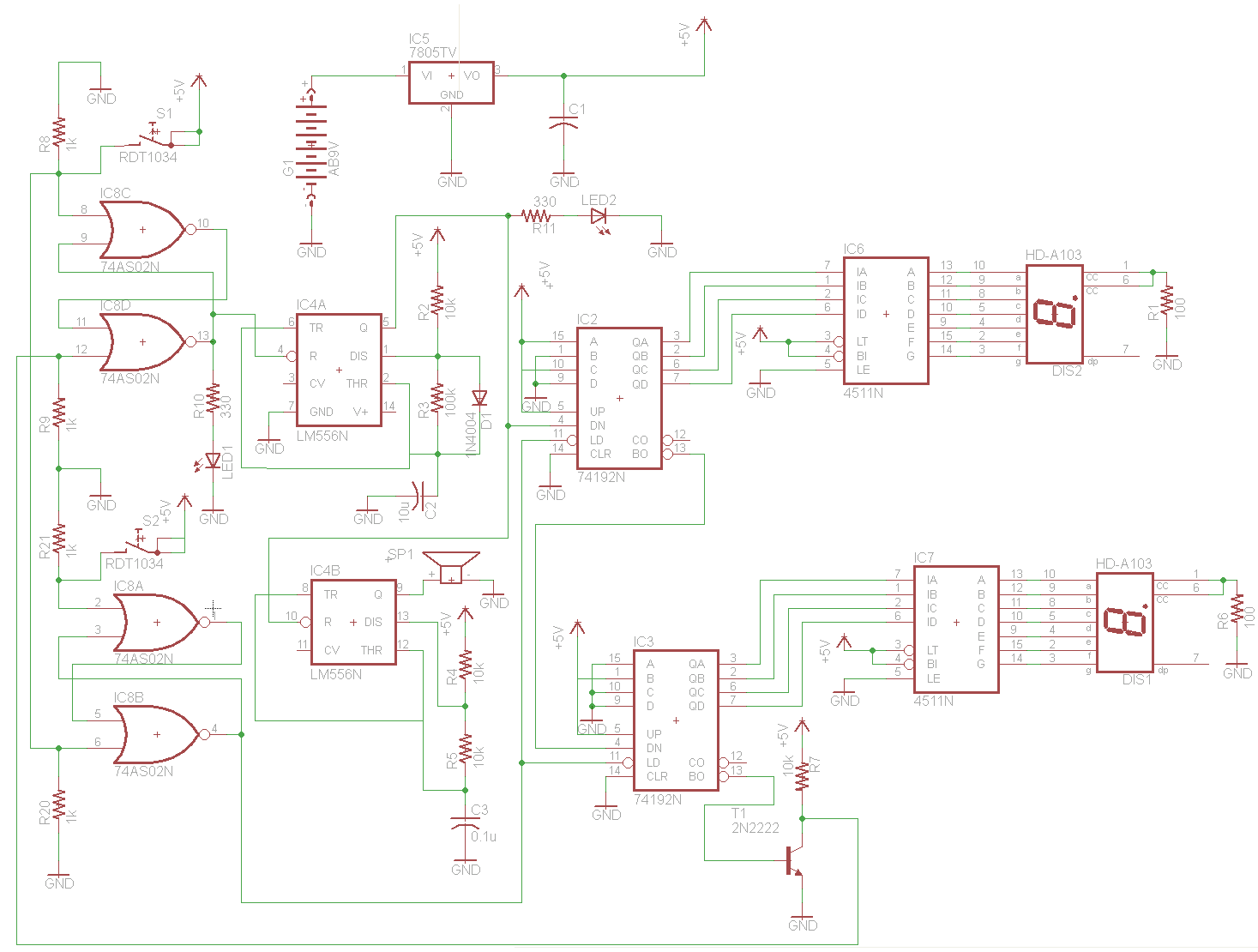
The schematic for this project is deceptively simple compared to the complexity of the circuit's operation. The two signals generated are mixed together at the base of transistor T2, and once it exits the collector of the transistor, the continuous wave RF transmission signal is prepared. The board layout is designed to tightly compact all components. Achieving this with through-hole parts is challenging but feasible. A ground plane covers the entire board, although it is interrupted by traces, ensuring that all components requiring ground access can connect easily. The ground plane also serves as part of the antenna. A thicker trace width was selected for effective PCB construction; however, smaller trace widths are generally preferred in RF circuit design. At these low frequencies, the difference in performance is not significant. The PCB design included extra space, which was utilized for additional text from PyroElectro.com. The text appears reversed due to the toner transfer process, where the bottom layer is printed backward, but it reads correctly once transferred to the PCB.
The circuit schematic represents a compact design that efficiently integrates multiple functionalities within a limited space. The mixing of signals at the base of transistor T2 is a critical operation, as it allows for the modulation of the RF transmission signal. The careful selection of through-hole components is essential to maintain the integrity of the circuit while maximizing space utilization.
The ground plane is a vital component of the design, as it not only provides a common reference point for all components but also enhances the performance of the antenna. The thickness of the traces is a consideration in the design process, as it can influence the overall performance of the circuit, especially in RF applications. While smaller traces are typically recommended for higher frequency applications to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance, the chosen width is adequate for the low-frequency operation of this circuit.
The layout also emphasizes the importance of the toner transfer method in PCB fabrication, where the reversed text is a common occurrence. This method requires careful attention to detail to ensure that the final product meets design specifications. The integration of additional features, such as the PyroElectro.com text, demonstrates the flexibility of the PCB design process and the ability to incorporate branding or identification into the layout without compromising functionality. Overall, the schematic effectively illustrates a well-thought-out design that balances complexity and simplicity in its execution.The schematic for this project is actually deceivingly simple compared to the complexity of what is happening in the circuit. So take a look below or click to view the full sized schematic. The two signals we`ve just generated are mixed together at the base of T2 and once it goes out of the collector of the transistor our continuous wave RF trans
mission signal is ready. The board layout was done in a way so that everything was crammed together very tight. This is a difficult thing to do with through-hole parts, but not impossible. A ground plan covers the entire board (but is chopped up by the traces) so that all parts that need access to ground can have it easily. The ground plan is also very important as its acts as part of our antenna. I just chose a nice thick width that would transfer over nicely when building the PCB, however smaller trace widths seem to be a better choice when designing RF circuits.
but at these low frequencies I don`t believe there will be any performance benefit. My PC board had extra space so I plugged in PyroElectro. com. You`ll notice the text is backwards, this is because during the toner transfer process, a bottom layer is technically printed out backwards, but once on the PCB it reads correctly. 🔗 External reference
The circuit schematic represents a compact design that efficiently integrates multiple functionalities within a limited space. The mixing of signals at the base of transistor T2 is a critical operation, as it allows for the modulation of the RF transmission signal. The careful selection of through-hole components is essential to maintain the integrity of the circuit while maximizing space utilization.
The ground plane is a vital component of the design, as it not only provides a common reference point for all components but also enhances the performance of the antenna. The thickness of the traces is a consideration in the design process, as it can influence the overall performance of the circuit, especially in RF applications. While smaller traces are typically recommended for higher frequency applications to reduce parasitic capacitance and inductance, the chosen width is adequate for the low-frequency operation of this circuit.
The layout also emphasizes the importance of the toner transfer method in PCB fabrication, where the reversed text is a common occurrence. This method requires careful attention to detail to ensure that the final product meets design specifications. The integration of additional features, such as the PyroElectro.com text, demonstrates the flexibility of the PCB design process and the ability to incorporate branding or identification into the layout without compromising functionality. Overall, the schematic effectively illustrates a well-thought-out design that balances complexity and simplicity in its execution.The schematic for this project is actually deceivingly simple compared to the complexity of what is happening in the circuit. So take a look below or click to view the full sized schematic. The two signals we`ve just generated are mixed together at the base of T2 and once it goes out of the collector of the transistor our continuous wave RF trans
mission signal is ready. The board layout was done in a way so that everything was crammed together very tight. This is a difficult thing to do with through-hole parts, but not impossible. A ground plan covers the entire board (but is chopped up by the traces) so that all parts that need access to ground can have it easily. The ground plan is also very important as its acts as part of our antenna. I just chose a nice thick width that would transfer over nicely when building the PCB, however smaller trace widths seem to be a better choice when designing RF circuits.
but at these low frequencies I don`t believe there will be any performance benefit. My PC board had extra space so I plugged in PyroElectro. com. You`ll notice the text is backwards, this is because during the toner transfer process, a bottom layer is technically printed out backwards, but once on the PCB it reads correctly. 🔗 External reference