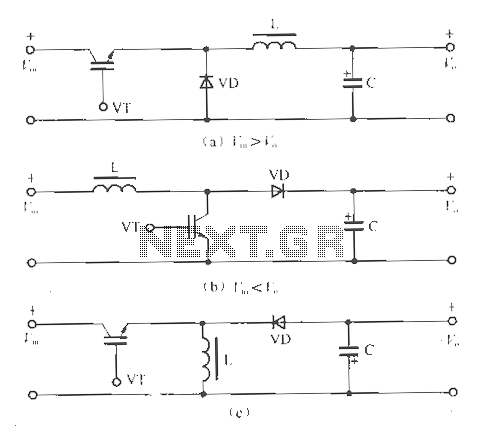
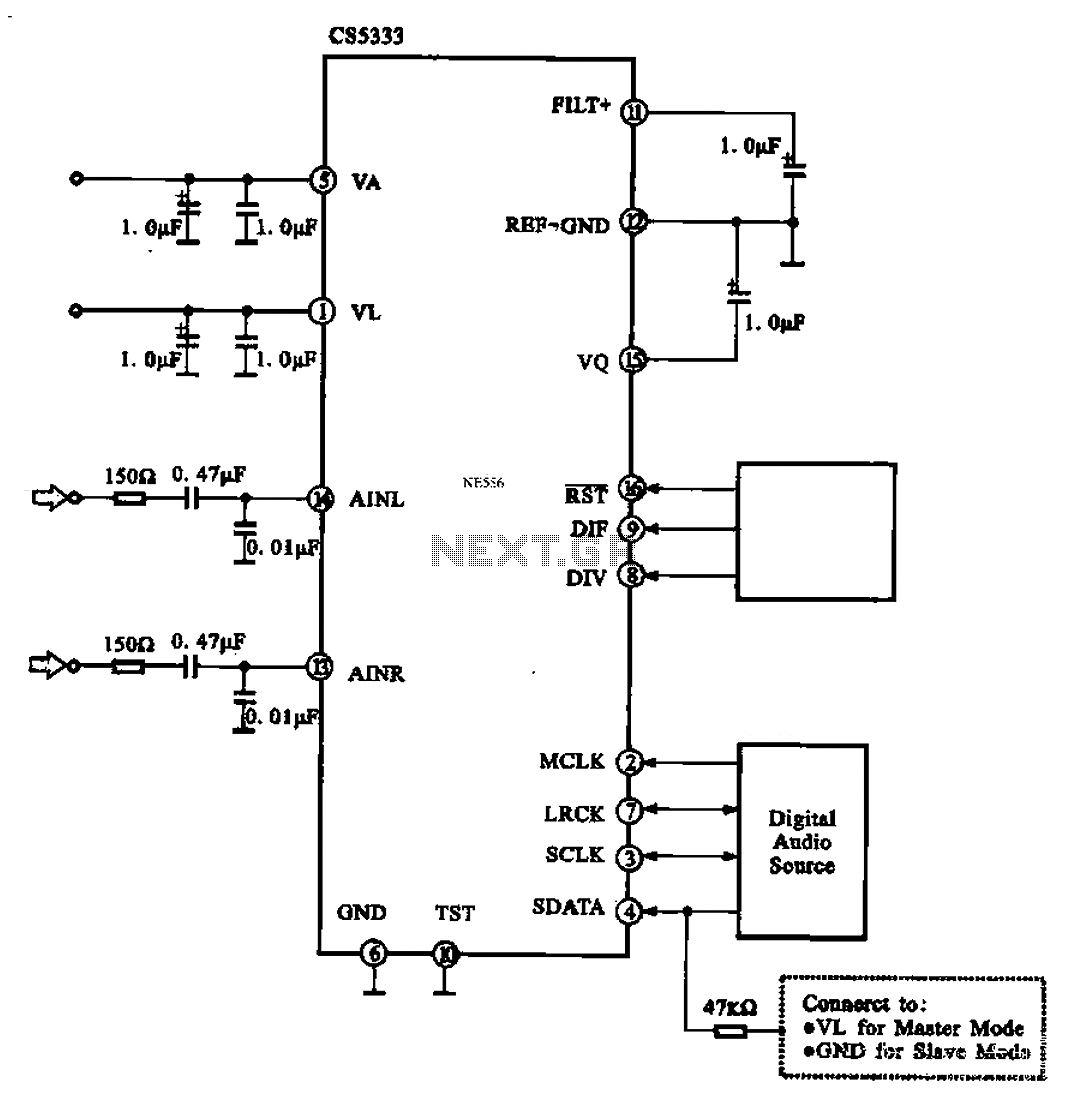
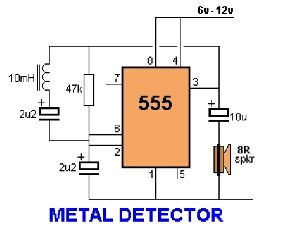
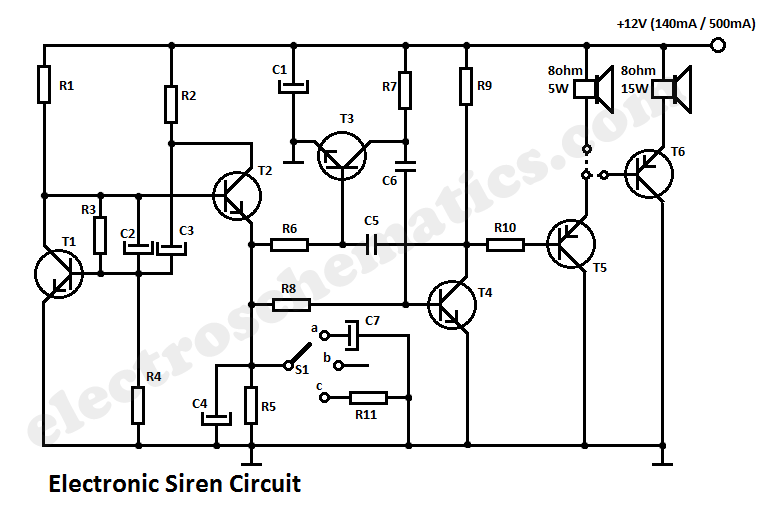
Simple RS 232 Level Converter
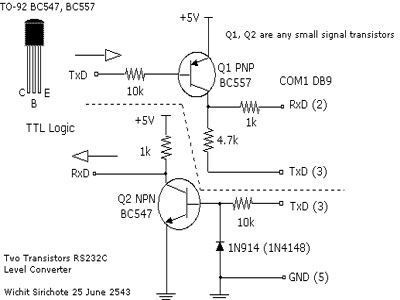
To connect a microcontroller project to the COM port of a PC, an RS-232 converter is required. Various chips are available to address this need, such as the MAX232 and DS275.
The RS-232 standard is widely used for serial communication between devices, including microcontrollers and computers. The voltage levels of RS-232 signals are typically between -15V and +15V, which are incompatible with the TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) levels of most microcontrollers, typically ranging from 0V to 5V or 0V to 3.3V. Therefore, an RS-232 converter is essential for level shifting and ensuring proper communication.
The MAX232 is a popular choice for this application. It contains dual voltage level translators that convert TTL logic levels to RS-232 levels and vice versa. The device usually requires a dual power supply of +5V for the TTL side and a -10V to -15V supply for the RS-232 side, which can be generated using external capacitors and charge pumps integrated within the chip.
The DS275 is another option that functions similarly to the MAX232, providing a bidirectional level translation. It is designed to operate at lower power levels, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The DS275 also includes features such as built-in protection against over-voltage and short-circuit conditions.
In designing a circuit with either of these chips, it is crucial to connect the microcontroller’s TX (transmit) pin to the RX (receive) pin of the RS-232 converter and the RX pin of the microcontroller to the TX pin of the converter. Additionally, proper decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the chips to ensure stable operation.
Overall, incorporating an RS-232 converter like the MAX232 or DS275 into a microcontroller project facilitates reliable communication with a PC's COM port, enabling data exchange for various applications.When you need connect your Microcontroller Project to COM port in PC you need RS 232 converter. There are many chip to solve the problem like MAX232, DS275 etc.. 🔗 External reference
The RS-232 standard is widely used for serial communication between devices, including microcontrollers and computers. The voltage levels of RS-232 signals are typically between -15V and +15V, which are incompatible with the TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) levels of most microcontrollers, typically ranging from 0V to 5V or 0V to 3.3V. Therefore, an RS-232 converter is essential for level shifting and ensuring proper communication.
The MAX232 is a popular choice for this application. It contains dual voltage level translators that convert TTL logic levels to RS-232 levels and vice versa. The device usually requires a dual power supply of +5V for the TTL side and a -10V to -15V supply for the RS-232 side, which can be generated using external capacitors and charge pumps integrated within the chip.
The DS275 is another option that functions similarly to the MAX232, providing a bidirectional level translation. It is designed to operate at lower power levels, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The DS275 also includes features such as built-in protection against over-voltage and short-circuit conditions.
In designing a circuit with either of these chips, it is crucial to connect the microcontroller’s TX (transmit) pin to the RX (receive) pin of the RS-232 converter and the RX pin of the microcontroller to the TX pin of the converter. Additionally, proper decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the chips to ensure stable operation.
Overall, incorporating an RS-232 converter like the MAX232 or DS275 into a microcontroller project facilitates reliable communication with a PC's COM port, enabling data exchange for various applications.When you need connect your Microcontroller Project to COM port in PC you need RS 232 converter. There are many chip to solve the problem like MAX232, DS275 etc.. 🔗 External reference