Simple structure hi-fi amplifier

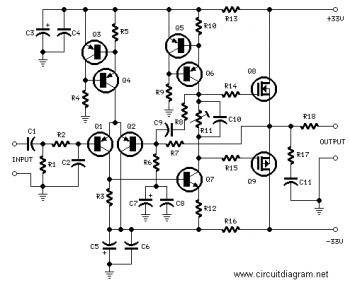
The circuit illustrated in Figure 240 is straightforward, utilizing only four transistors to process the input voltage, resulting in a large, inverted output. This configuration serves as a high-performance amplifier, delivering excellent high-fidelity power discharge capabilities. The input stage employs a PNP transistor (VT1), which functions as both the input stage and impedance matching component. The voltage amplification stage is handled by VT2, which operates in a common emitter configuration and provides an inverted push function. The output stage consists of a complementary push-pull arrangement formed by transistors VT3 and VT4. Resistor R7 and resistor R set up a negative feedback loop that determines the circuit gain, calculated as Av = R7 * (8 - 2.7) / 0.22, yielding a gain of approximately 21 dB. Capacitor C3 acts as a bootstrap capacitor, while resistor R6 serves as an isolation resistor.
The circuit described utilizes a minimalist approach with four transistors, which are strategically arranged to achieve a high-fidelity amplification of the input signal. The PNP transistor (VT1) at the input stage is crucial for matching the input impedance, ensuring that the circuit can effectively interface with various signal sources without significant signal loss or distortion. The voltage amplification stage, facilitated by VT2, is configured in a common emitter mode, which is well-known for providing substantial voltage gain while also inverting the phase of the input signal.
Transistors VT3 and VT4 form a complementary push-pull output stage, which is essential for driving loads efficiently. This configuration allows for improved linearity and reduced distortion in the output signal, making it suitable for high-quality audio applications. The negative feedback loop, established through resistors R7 and R, plays a vital role in stabilizing the gain of the amplifier. The gain equation provided indicates that the circuit can be fine-tuned by adjusting the values of R7 and R, thereby allowing for versatility in various applications.
The bootstrap capacitor C3 enhances the amplifier's performance by improving the frequency response and stability, particularly at higher frequencies. Additionally, the isolation resistor R6 helps to prevent unwanted interactions between different stages of the circuit, ensuring that each transistor operates within its optimal range. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a well-engineered amplifier capable of delivering high-fidelity audio output with minimal distortion, making it suitable for demanding audio applications. Circuit shown in Figure 240 of the circuit structure is very simple, with only four transistors to achieve circuit from input voltage put large, inverted, and promote the whole process of the amplifier, and a high technical indicators circuit, is an excellent high-fidelity power discharge path. VTi for the input stage, the use of a PNP transistor input stage and both impedance matching function, VTz voltage amplification stage and both CE and inverted push function, VT3 and VT4 constitute complementary push-pull amplifier output stage O R7, and R Pat negative feedback loop and determine the circuit gain: Av-R7 cuddle 8-2.7/0.22, together 21dBo bootstrap capacitor C3, R6 for the isolation resistance.
The circuit described utilizes a minimalist approach with four transistors, which are strategically arranged to achieve a high-fidelity amplification of the input signal. The PNP transistor (VT1) at the input stage is crucial for matching the input impedance, ensuring that the circuit can effectively interface with various signal sources without significant signal loss or distortion. The voltage amplification stage, facilitated by VT2, is configured in a common emitter mode, which is well-known for providing substantial voltage gain while also inverting the phase of the input signal.
Transistors VT3 and VT4 form a complementary push-pull output stage, which is essential for driving loads efficiently. This configuration allows for improved linearity and reduced distortion in the output signal, making it suitable for high-quality audio applications. The negative feedback loop, established through resistors R7 and R, plays a vital role in stabilizing the gain of the amplifier. The gain equation provided indicates that the circuit can be fine-tuned by adjusting the values of R7 and R, thereby allowing for versatility in various applications.
The bootstrap capacitor C3 enhances the amplifier's performance by improving the frequency response and stability, particularly at higher frequencies. Additionally, the isolation resistor R6 helps to prevent unwanted interactions between different stages of the circuit, ensuring that each transistor operates within its optimal range. Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a well-engineered amplifier capable of delivering high-fidelity audio output with minimal distortion, making it suitable for demanding audio applications. Circuit shown in Figure 240 of the circuit structure is very simple, with only four transistors to achieve circuit from input voltage put large, inverted, and promote the whole process of the amplifier, and a high technical indicators circuit, is an excellent high-fidelity power discharge path. VTi for the input stage, the use of a PNP transistor input stage and both impedance matching function, VTz voltage amplification stage and both CE and inverted push function, VT3 and VT4 constitute complementary push-pull amplifier output stage O R7, and R Pat negative feedback loop and determine the circuit gain: Av-R7 cuddle 8-2.7/0.22, together 21dBo bootstrap capacitor C3, R6 for the isolation resistance.