Simple Intercom Circuit Transistor
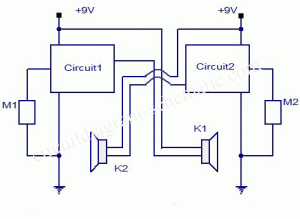
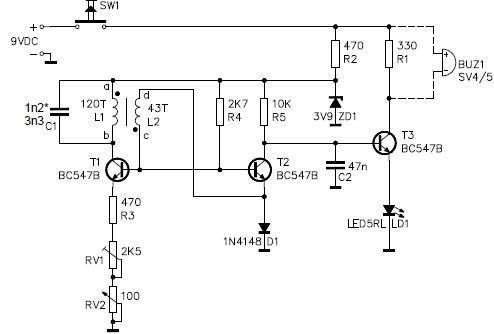
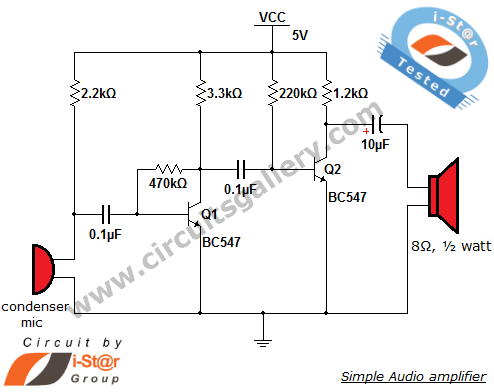
The circuit diagram represents a simple yet effective intercom system entirely based on transistors. It consists of three stages along with an RC amplifier. When the pushbutton S2 is pressed, the amplifier circuit around transistor T1 is activated.
The intercom circuit utilizes three transistor stages to amplify audio signals, ensuring clear communication between the stations. The first stage typically involves a microphone connected to the base of the first transistor (T1), which serves as a pre-amplifier. This stage is crucial for picking up the audio signals and converting them into electrical signals.
The second stage amplifies the signal further, using a second transistor (T2) configured in a common emitter arrangement. This configuration provides additional gain and helps to drive the next stage of the circuit. The output from T2 is then fed into an RC (resistor-capacitor) filter that smooths out the signal and eliminates any high-frequency noise that may interfere with audio clarity.
The final stage, which involves the third transistor (T3), acts as a driver stage to power the speaker or output device. This transistor also ensures that the audio signal is strong enough to be heard clearly at the receiving end of the intercom system. The pushbutton switch S2 serves as a control mechanism, allowing the user to activate the circuit and initiate communication.
In summary, this transistor-based intercom circuit design effectively amplifies audio signals through a three-stage amplification process, with the RC filter enhancing signal quality, making it suitable for reliable intercom applications.Circuit diagram is a simple but effective circuit intercom circuit is based entirely on transistors. Circuit diagram is based on three stages plus RC amplifier. When the pushbutton S2 is pressed, the amplifier cord around T1 . 🔗 External reference
The intercom circuit utilizes three transistor stages to amplify audio signals, ensuring clear communication between the stations. The first stage typically involves a microphone connected to the base of the first transistor (T1), which serves as a pre-amplifier. This stage is crucial for picking up the audio signals and converting them into electrical signals.
The second stage amplifies the signal further, using a second transistor (T2) configured in a common emitter arrangement. This configuration provides additional gain and helps to drive the next stage of the circuit. The output from T2 is then fed into an RC (resistor-capacitor) filter that smooths out the signal and eliminates any high-frequency noise that may interfere with audio clarity.
The final stage, which involves the third transistor (T3), acts as a driver stage to power the speaker or output device. This transistor also ensures that the audio signal is strong enough to be heard clearly at the receiving end of the intercom system. The pushbutton switch S2 serves as a control mechanism, allowing the user to activate the circuit and initiate communication.
In summary, this transistor-based intercom circuit design effectively amplifies audio signals through a three-stage amplification process, with the RC filter enhancing signal quality, making it suitable for reliable intercom applications.Circuit diagram is a simple but effective circuit intercom circuit is based entirely on transistors. Circuit diagram is based on three stages plus RC amplifier. When the pushbutton S2 is pressed, the amplifier cord around T1 . 🔗 External reference