Simple transistor tester circuits
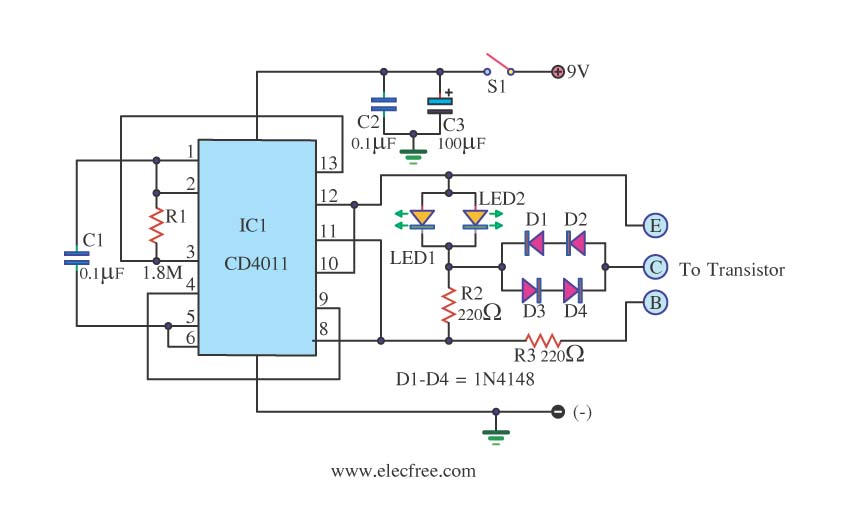
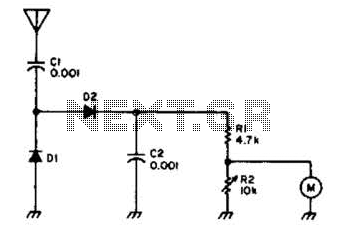
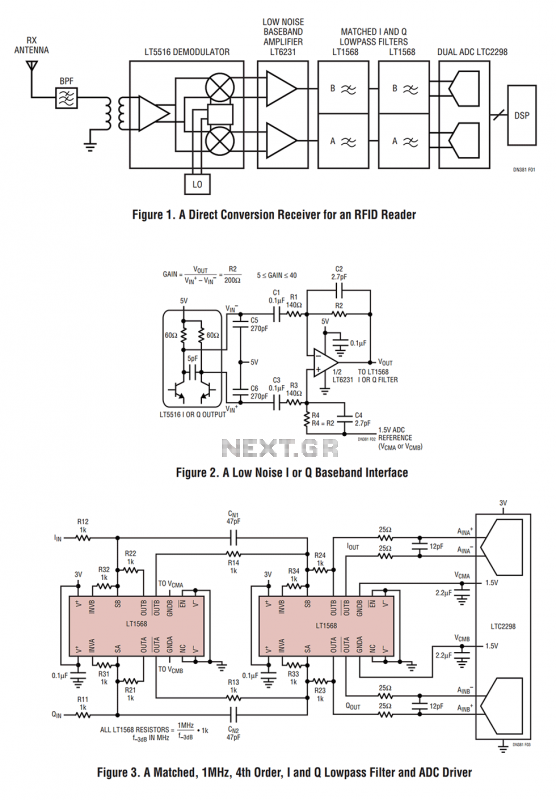
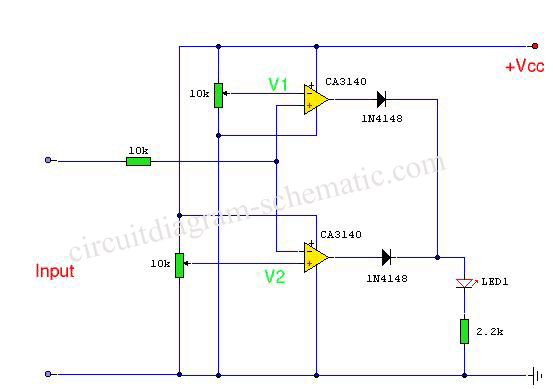
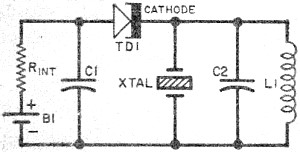
This is a transistor tester integrated into a circuit or printed circuit board (PCB). It is utilized when a project does not function correctly, allowing for the testing of electronic components.
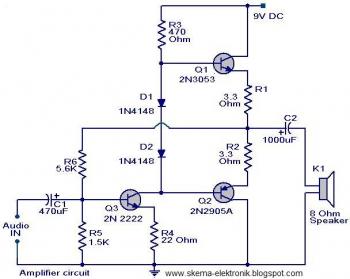
The transistor tester is a crucial tool in electronic diagnostics, designed to evaluate the functionality of transistors and other semiconductor devices. It typically operates by applying a small voltage to the transistor's terminals to determine its operational state. The tester can identify whether the transistor is functioning properly, whether it is open or shorted, and can also measure key parameters such as current gain (hFE), base-emitter threshold voltage, and collector-emitter breakdown voltage.
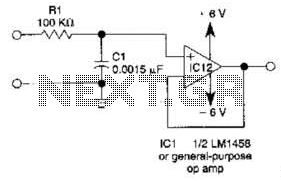
In a typical schematic, the transistor tester circuit may consist of a microcontroller or an operational amplifier that processes the signals from the transistor under test. The circuit often includes a display unit, such as an LCD or LED indicators, which provides real-time feedback on the test results. Additionally, resistors and capacitors may be incorporated to stabilize the circuit and filter out noise, ensuring accurate measurements.
The design of the PCB for the transistor tester should facilitate easy connections to the transistor leads, often through dedicated test probes or sockets. Proper layout considerations must be taken into account to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the accuracy of the measurements. Power supply requirements should also be addressed, with provisions for both battery and external power options.
Overall, the integration of a transistor tester into a circuit or PCB enhances troubleshooting capabilities, allowing engineers and technicians to quickly assess the health of transistors and ensure the reliability of electronic systems.This is the Transistor tester into the Circuit or PCB. When your project do not works, the tester electronic parts or.. 🔗 External reference
The transistor tester is a crucial tool in electronic diagnostics, designed to evaluate the functionality of transistors and other semiconductor devices. It typically operates by applying a small voltage to the transistor's terminals to determine its operational state. The tester can identify whether the transistor is functioning properly, whether it is open or shorted, and can also measure key parameters such as current gain (hFE), base-emitter threshold voltage, and collector-emitter breakdown voltage.
In a typical schematic, the transistor tester circuit may consist of a microcontroller or an operational amplifier that processes the signals from the transistor under test. The circuit often includes a display unit, such as an LCD or LED indicators, which provides real-time feedback on the test results. Additionally, resistors and capacitors may be incorporated to stabilize the circuit and filter out noise, ensuring accurate measurements.
The design of the PCB for the transistor tester should facilitate easy connections to the transistor leads, often through dedicated test probes or sockets. Proper layout considerations must be taken into account to minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the accuracy of the measurements. Power supply requirements should also be addressed, with provisions for both battery and external power options.
Overall, the integration of a transistor tester into a circuit or PCB enhances troubleshooting capabilities, allowing engineers and technicians to quickly assess the health of transistors and ensure the reliability of electronic systems.This is the Transistor tester into the Circuit or PCB. When your project do not works, the tester electronic parts or.. 🔗 External reference