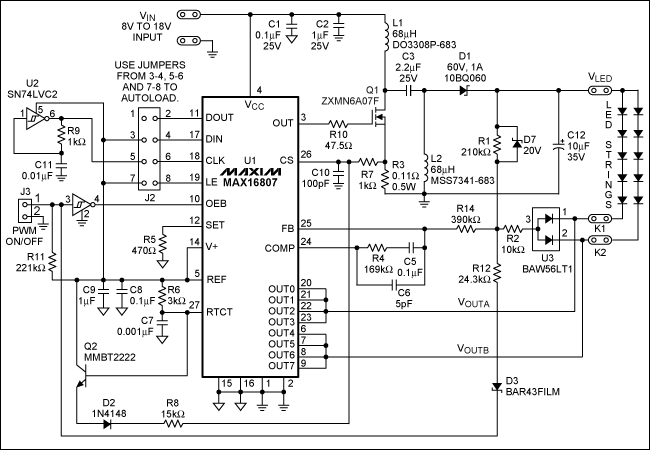
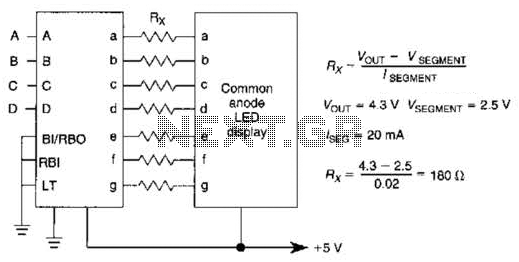
simplest led flasher

The schematic below illustrates a simple LED flasher circuit. This circuit utilizes three LEDs that begin to blink or flash upon receiving a 9-volt supply. It is straightforward in design, employing a self-flashing LED (LED 1) to trigger the flashing of all LEDs. Self-flashing LEDs contain an integrated circuit that enables them to flash and are generally inexpensive. Most self-blinking LEDs operate within a voltage range of 3.5V to 9V; however, it is advisable to verify the specifications with the seller or manufacturer. LED 2 and LED 3 can be any color of general-purpose LEDs.
The described LED flasher circuit is a basic yet effective design that illustrates the principles of LED operation and flashing mechanisms. The circuit is powered by a 9-volt battery, which is connected to the anode of the self-flashing LED (LED 1). This LED is designed with an internal oscillator that controls its flashing frequency. As LED 1 flashes, it generates a pulsing signal that is also applied to the other two general-purpose LEDs (LED 2 and LED 3).
The self-flashing LED typically incorporates a small integrated circuit (IC) that modulates the current flowing through it, causing it to turn on and off at a predetermined rate. This built-in circuitry simplifies the design, as it eliminates the need for external components such as resistors or capacitors that are commonly used in other flashing LED circuits.
LED 2 and LED 3 are connected in parallel with LED 1, allowing them to share the same voltage and current. The choice of colors for these LEDs can vary based on user preference, and their arrangement can create visually appealing light patterns. The circuit's simplicity makes it ideal for educational purposes, providing a clear demonstration of how LEDs function and how they can be used in various applications, such as decorative lighting or indicators.
To ensure optimal performance, it is crucial to select self-flashing LEDs that meet the voltage and current requirements of the circuit. Operating outside the specified voltage range may lead to suboptimal performance or damage to the LEDs. Therefore, confirming specifications with the manufacturer is essential for ensuring reliability and longevity in operation.Here`s The schematic shown below is a simplest LED flasher circuit. The circuit is using three LEDs which will start blinking or flashing when we provide 9 volt to the circuit. The circuit is so simple it uses a self flashing LED (LED 1) to make all LEDs flash. Self flashing LEDs have a built in circuit to make them flash and they are also very ch eap now a days. Most self blinking LEDs operate from 3. 5V to 9V but it is better to confirm from the seller or manufacturer to be sure. LED 2 and LED 3 are general LEDs of any colour. 🔗 External reference
The described LED flasher circuit is a basic yet effective design that illustrates the principles of LED operation and flashing mechanisms. The circuit is powered by a 9-volt battery, which is connected to the anode of the self-flashing LED (LED 1). This LED is designed with an internal oscillator that controls its flashing frequency. As LED 1 flashes, it generates a pulsing signal that is also applied to the other two general-purpose LEDs (LED 2 and LED 3).
The self-flashing LED typically incorporates a small integrated circuit (IC) that modulates the current flowing through it, causing it to turn on and off at a predetermined rate. This built-in circuitry simplifies the design, as it eliminates the need for external components such as resistors or capacitors that are commonly used in other flashing LED circuits.
LED 2 and LED 3 are connected in parallel with LED 1, allowing them to share the same voltage and current. The choice of colors for these LEDs can vary based on user preference, and their arrangement can create visually appealing light patterns. The circuit's simplicity makes it ideal for educational purposes, providing a clear demonstration of how LEDs function and how they can be used in various applications, such as decorative lighting or indicators.
To ensure optimal performance, it is crucial to select self-flashing LEDs that meet the voltage and current requirements of the circuit. Operating outside the specified voltage range may lead to suboptimal performance or damage to the LEDs. Therefore, confirming specifications with the manufacturer is essential for ensuring reliability and longevity in operation.Here`s The schematic shown below is a simplest LED flasher circuit. The circuit is using three LEDs which will start blinking or flashing when we provide 9 volt to the circuit. The circuit is so simple it uses a self flashing LED (LED 1) to make all LEDs flash. Self flashing LEDs have a built in circuit to make them flash and they are also very ch eap now a days. Most self blinking LEDs operate from 3. 5V to 9V but it is better to confirm from the seller or manufacturer to be sure. LED 2 and LED 3 are general LEDs of any colour. 🔗 External reference