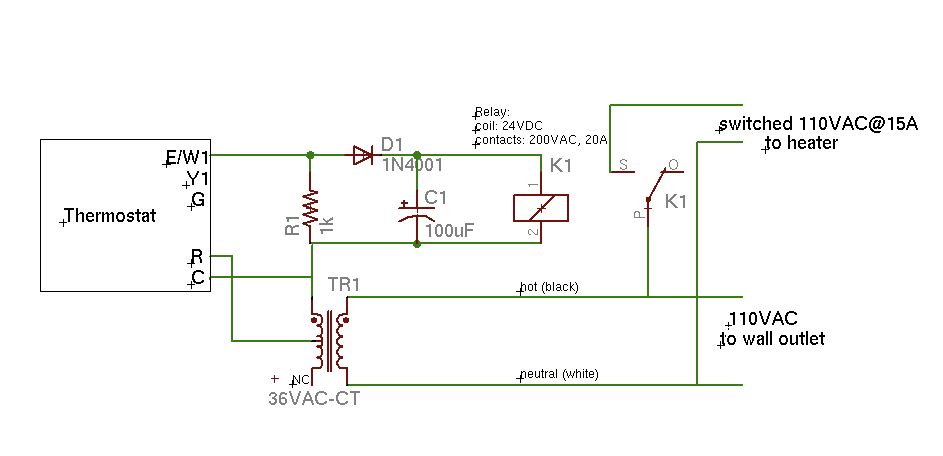
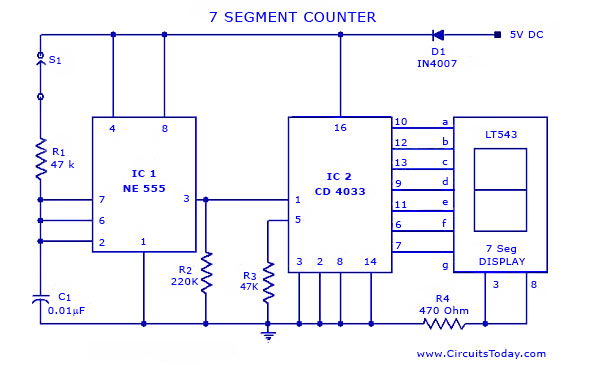
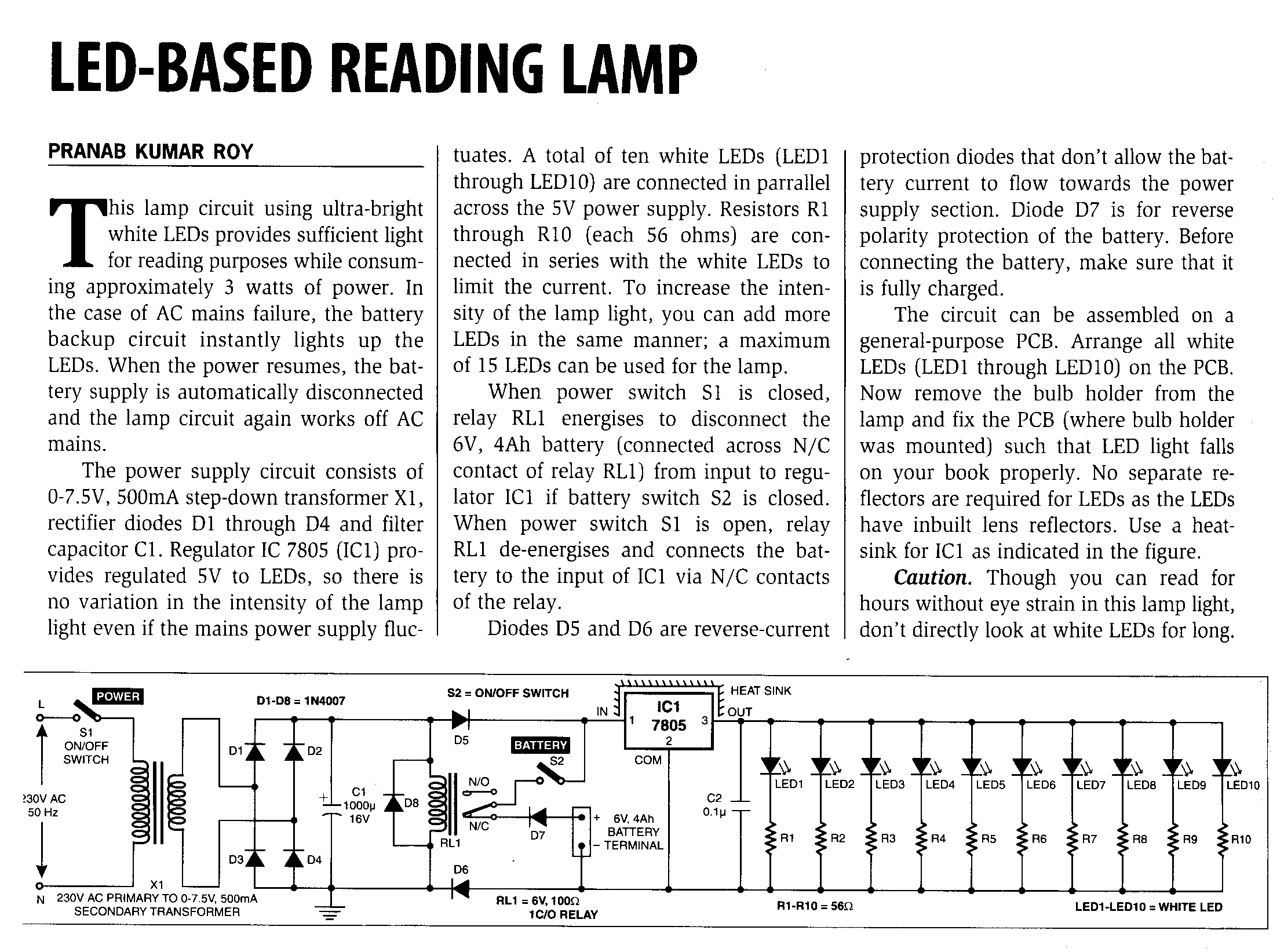
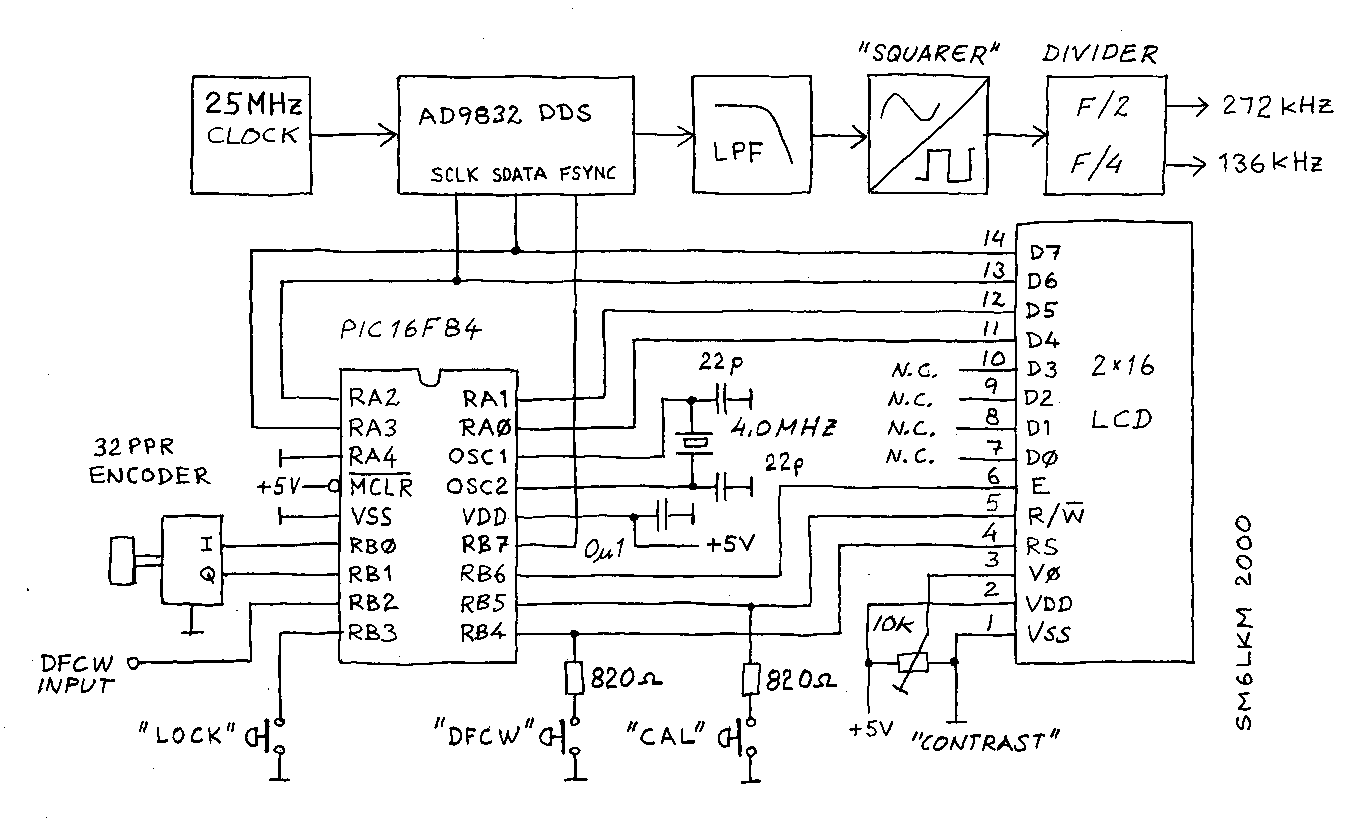
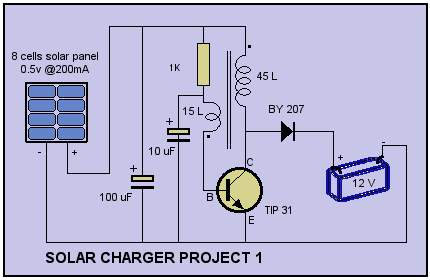
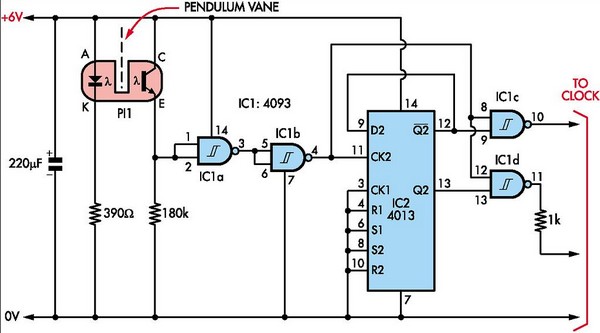
Single Cell LED Flashlight
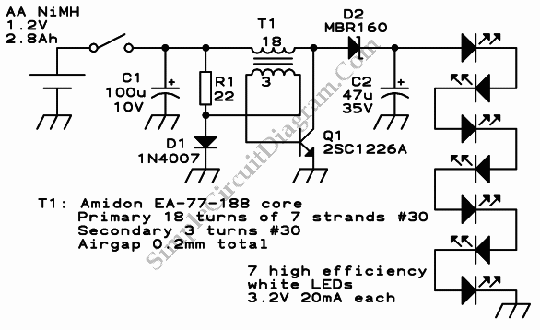
This is a single-cell LED flashlight circuit. This circuit utilizes a white LED that achieves optimal power efficiency at approximately 20 mA and requires about 3.3 V.
The single-cell LED flashlight circuit is designed to provide efficient illumination using a white LED. The circuit operates on a single-cell power source, typically a lithium-ion or alkaline battery, delivering a nominal voltage of around 3.3 V, which is ideal for the forward voltage requirement of the white LED. The LED is selected for its high luminous efficacy, which translates to more light output per unit of power consumed.
To ensure the LED operates at the optimal current of 20 mA, a current-limiting resistor is included in the circuit. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm’s Law, taking into account the supply voltage and the forward voltage drop of the LED. For instance, if the battery voltage is 3.3 V and the LED has a forward voltage of 3.0 V, the resistor value can be determined as follows:
R = (V_supply - V_LED) / I_LED
R = (3.3 V - 3.0 V) / 0.020 A
R = 15 Ohms
Additionally, a switch may be integrated into the design to allow for easy operation of the flashlight. The switch can be placed in series with the battery and LED to control the on/off function.
The circuit design may also incorporate a small PCB (printed circuit board) layout to facilitate compactness and ease of assembly. Proper thermal management should be considered, as excessive current can lead to overheating of the LED, reducing its lifespan.
In summary, this single-cell LED flashlight circuit is a straightforward yet effective design that balances power efficiency and light output, making it suitable for portable lighting applications.This is Single Cell LED Flashlight circuit. This circuit uses white LED that has best power-efficiency combination at about 20mA and requires abut 3.3V. Each.. 🔗 External reference
The single-cell LED flashlight circuit is designed to provide efficient illumination using a white LED. The circuit operates on a single-cell power source, typically a lithium-ion or alkaline battery, delivering a nominal voltage of around 3.3 V, which is ideal for the forward voltage requirement of the white LED. The LED is selected for its high luminous efficacy, which translates to more light output per unit of power consumed.
To ensure the LED operates at the optimal current of 20 mA, a current-limiting resistor is included in the circuit. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm’s Law, taking into account the supply voltage and the forward voltage drop of the LED. For instance, if the battery voltage is 3.3 V and the LED has a forward voltage of 3.0 V, the resistor value can be determined as follows:
R = (V_supply - V_LED) / I_LED
R = (3.3 V - 3.0 V) / 0.020 A
R = 15 Ohms
Additionally, a switch may be integrated into the design to allow for easy operation of the flashlight. The switch can be placed in series with the battery and LED to control the on/off function.
The circuit design may also incorporate a small PCB (printed circuit board) layout to facilitate compactness and ease of assembly. Proper thermal management should be considered, as excessive current can lead to overheating of the LED, reducing its lifespan.
In summary, this single-cell LED flashlight circuit is a straightforward yet effective design that balances power efficiency and light output, making it suitable for portable lighting applications.This is Single Cell LED Flashlight circuit. This circuit uses white LED that has best power-efficiency combination at about 20mA and requires abut 3.3V. Each.. 🔗 External reference