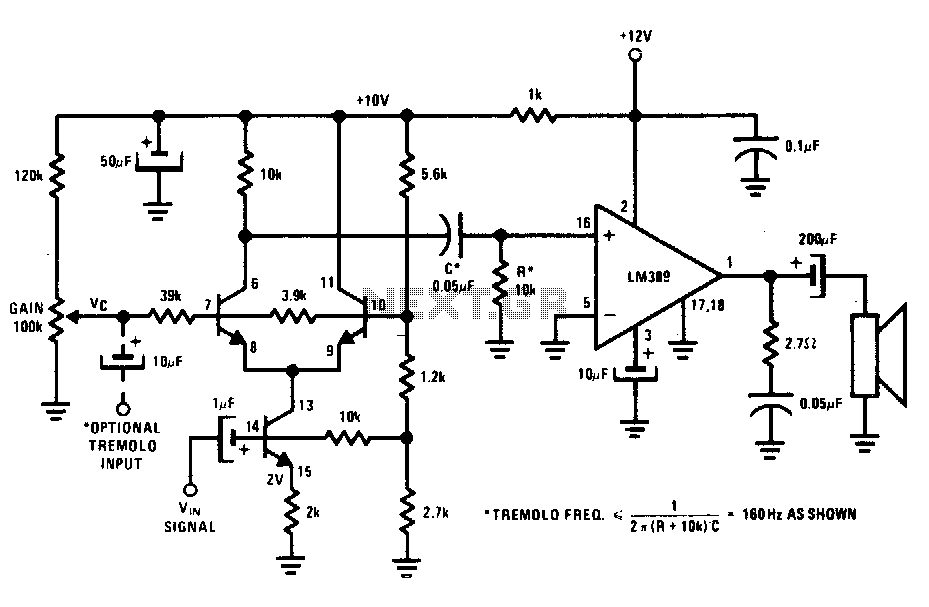
Single-device 80 w 50 ohm vhf amplifier

The amplifier utilizes a single MRF245 transistor and delivers 80 W of output power with a gain of 9.4 dB across the frequency range of 143 to 156 MHz.
The circuit design for the amplifier featuring the MRF245 transistor is intended for applications requiring significant RF output power within the specified frequency band. The MRF245 is a high-power RF transistor known for its efficiency and linearity, making it suitable for use in various communication systems.
The amplifier circuit typically consists of the MRF245 connected in a common-emitter configuration, which enhances its voltage gain. The input stage may include a matching network designed to optimize the impedance seen by the transistor's input, ensuring maximum power transfer and minimizing reflections. This network can be composed of inductors and capacitors, which are carefully selected based on the frequency characteristics of the MRF245.
The output stage is similarly equipped with a matching network to ensure that the output impedance of the amplifier aligns with the load impedance, often 50 ohms, which is standard in RF applications. This matching network is crucial for maximizing power delivery to the antenna or subsequent stages in the transmission line.
Power supply considerations are also important in the design. The MRF245 typically operates with a DC supply voltage that must be regulated to maintain consistent performance. Bypass capacitors are employed at the power supply pins to filter out any noise that could affect the amplifier's operation.
Thermal management is another key aspect of the design. The MRF245 can generate substantial heat during operation, especially at higher output levels. Therefore, an appropriate heat sink should be used to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring the transistor operates within safe temperature limits.
Overall, the amplifier circuit utilizing the MRF245 transistor is designed to provide reliable performance with high output power and gain across the specified frequency range, making it suitable for various RF applications.The amplifier uses a single MRF245 and provides 80 W with 9.4 dB gain across the 143 to 156 MHz band.
The circuit design for the amplifier featuring the MRF245 transistor is intended for applications requiring significant RF output power within the specified frequency band. The MRF245 is a high-power RF transistor known for its efficiency and linearity, making it suitable for use in various communication systems.
The amplifier circuit typically consists of the MRF245 connected in a common-emitter configuration, which enhances its voltage gain. The input stage may include a matching network designed to optimize the impedance seen by the transistor's input, ensuring maximum power transfer and minimizing reflections. This network can be composed of inductors and capacitors, which are carefully selected based on the frequency characteristics of the MRF245.
The output stage is similarly equipped with a matching network to ensure that the output impedance of the amplifier aligns with the load impedance, often 50 ohms, which is standard in RF applications. This matching network is crucial for maximizing power delivery to the antenna or subsequent stages in the transmission line.
Power supply considerations are also important in the design. The MRF245 typically operates with a DC supply voltage that must be regulated to maintain consistent performance. Bypass capacitors are employed at the power supply pins to filter out any noise that could affect the amplifier's operation.
Thermal management is another key aspect of the design. The MRF245 can generate substantial heat during operation, especially at higher output levels. Therefore, an appropriate heat sink should be used to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring the transistor operates within safe temperature limits.
Overall, the amplifier circuit utilizing the MRF245 transistor is designed to provide reliable performance with high output power and gain across the specified frequency range, making it suitable for various RF applications.The amplifier uses a single MRF245 and provides 80 W with 9.4 dB gain across the 143 to 156 MHz band.