Single transistor audio mixer
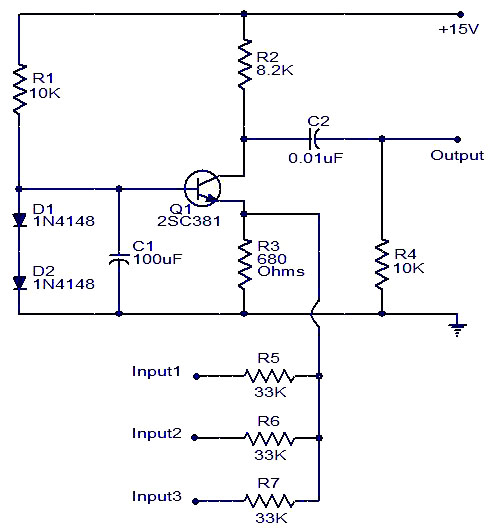
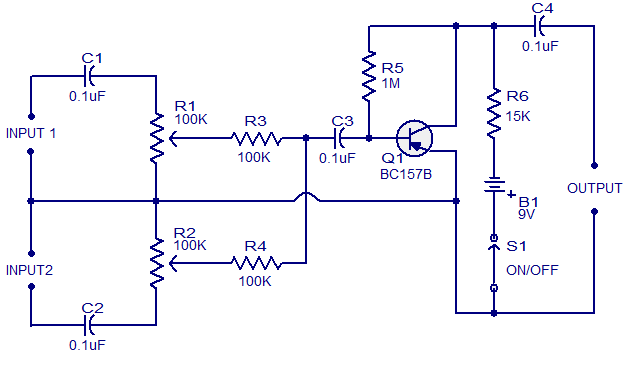
Numerous audio mixer circuits have been published; however, this particular design is among the simplest. This straightforward audio mixer circuit utilizes only a single transistor. The base-emitter junction of the transistor is biased with diodes D1 and D2. The signals intended for mixing are directly connected to the base of transistor Q1. Each input line is current-limited using a 33K resistor. With the specified component values, the collector current is approximately 1mA.
The described audio mixer circuit operates primarily through a single transistor, which simplifies its design and reduces component count. The transistor, designated as Q1, serves as the core element for mixing audio signals. The biasing of the base-emitter junction is achieved through the inclusion of diodes D1 and D2, which establish a stable operating point for the transistor, ensuring consistent performance across varying input signal levels.
The audio signals to be mixed are fed directly into the base of Q1. This direct coupling allows for minimal signal degradation and preserves the integrity of the audio signals. Each input line is equipped with a 33K resistor, which functions as a current limiter. This resistor is critical for preventing excessive current from flowing into the base of the transistor, thereby protecting it from potential damage and ensuring reliable operation.
The choice of a 33K resistor also influences the overall gain and mixing characteristics of the circuit. Given the component values used, the collector current is maintained at approximately 1mA, which is suitable for driving subsequent stages in an audio processing chain. This low current level indicates that the circuit is designed for low-power operation, making it ideal for battery-powered applications or compact audio devices.
Overall, this simple audio mixer circuit exemplifies effective design principles in electronics, utilizing minimal components while achieving functional audio mixing capabilities. The use of a single transistor, along with the biasing diodes and current-limiting resistors, creates a straightforward yet effective solution for audio mixing applications.Many audio mixer circuits have been published here. But I think, this one is the simplest of them. This very simple audio mixer circuit uses only one transistor. The base emitter junction of the transistor is biased by the diodes D1 and D2. The signals to be mixed are directly coupled to the base of Q1. Each input lines are current limited by using a 33K resistor. With the used component values the collector current is around 1mA. 🔗 External reference
The described audio mixer circuit operates primarily through a single transistor, which simplifies its design and reduces component count. The transistor, designated as Q1, serves as the core element for mixing audio signals. The biasing of the base-emitter junction is achieved through the inclusion of diodes D1 and D2, which establish a stable operating point for the transistor, ensuring consistent performance across varying input signal levels.
The audio signals to be mixed are fed directly into the base of Q1. This direct coupling allows for minimal signal degradation and preserves the integrity of the audio signals. Each input line is equipped with a 33K resistor, which functions as a current limiter. This resistor is critical for preventing excessive current from flowing into the base of the transistor, thereby protecting it from potential damage and ensuring reliable operation.
The choice of a 33K resistor also influences the overall gain and mixing characteristics of the circuit. Given the component values used, the collector current is maintained at approximately 1mA, which is suitable for driving subsequent stages in an audio processing chain. This low current level indicates that the circuit is designed for low-power operation, making it ideal for battery-powered applications or compact audio devices.
Overall, this simple audio mixer circuit exemplifies effective design principles in electronics, utilizing minimal components while achieving functional audio mixing capabilities. The use of a single transistor, along with the biasing diodes and current-limiting resistors, creates a straightforward yet effective solution for audio mixing applications.Many audio mixer circuits have been published here. But I think, this one is the simplest of them. This very simple audio mixer circuit uses only one transistor. The base emitter junction of the transistor is biased by the diodes D1 and D2. The signals to be mixed are directly coupled to the base of Q1. Each input lines are current limited by using a 33K resistor. With the used component values the collector current is around 1mA. 🔗 External reference