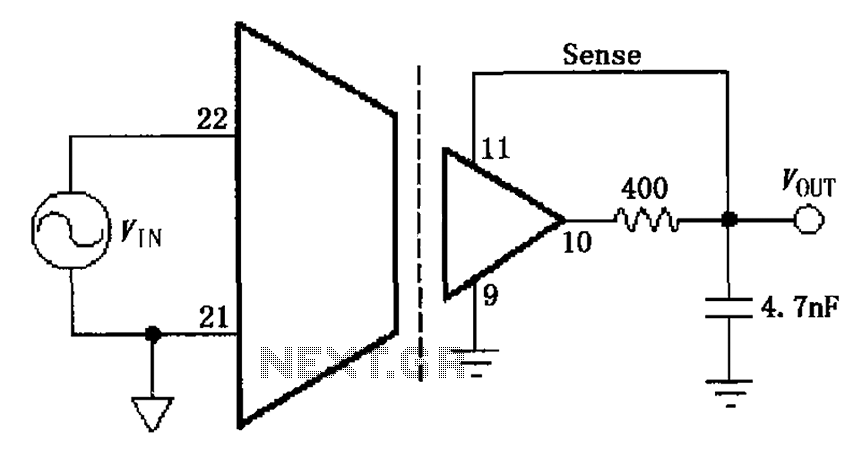
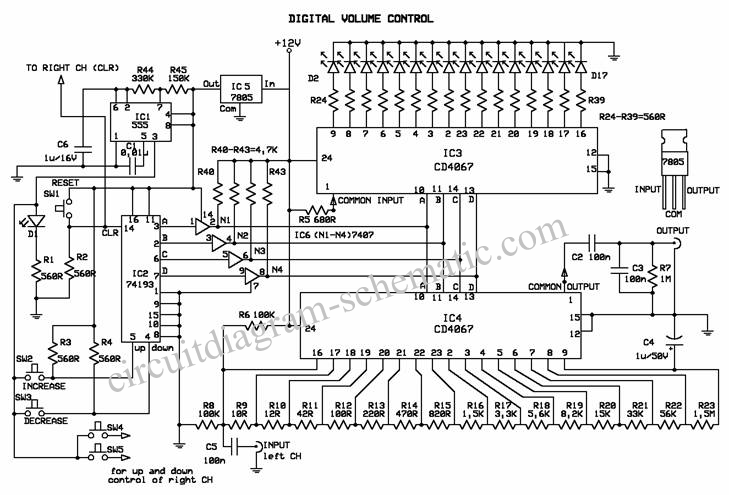
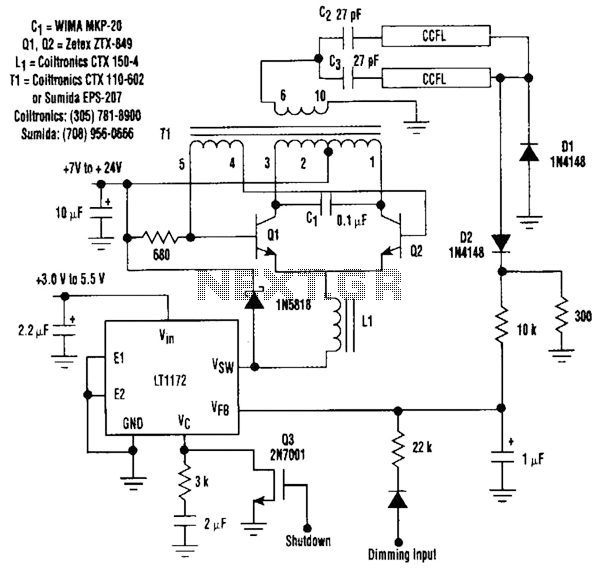
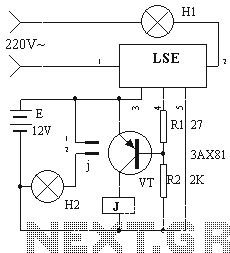
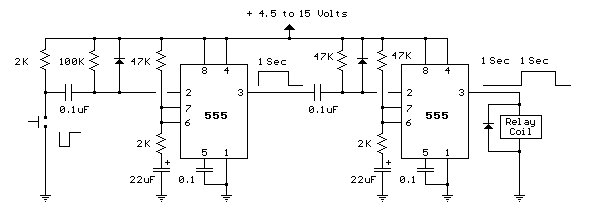
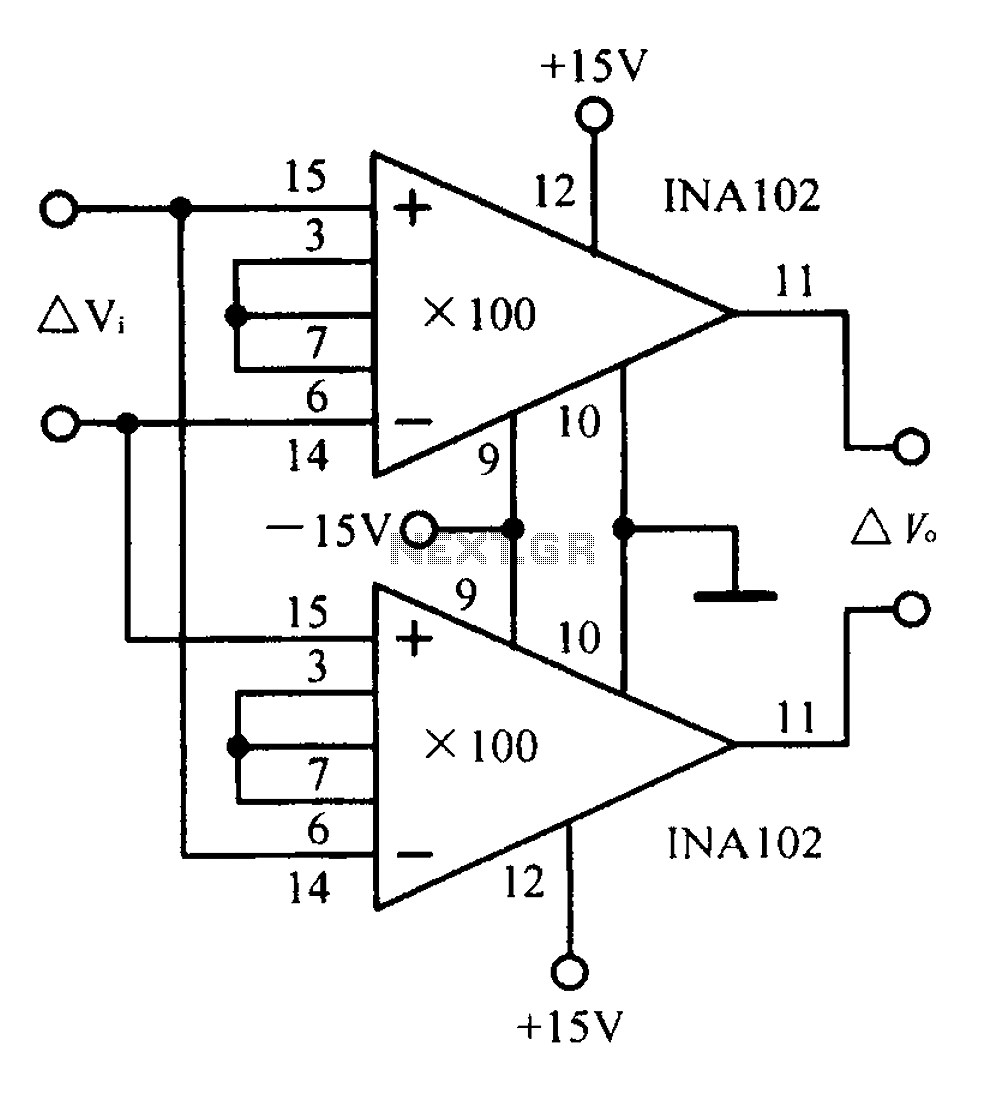
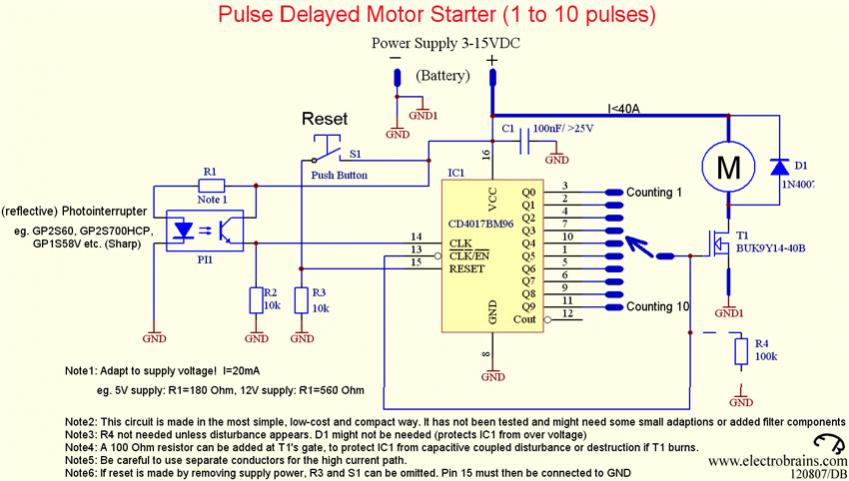
transistor circuit for counting wheel rotations
A new user has joined the forum and is seeking assistance with circuit design. They express a desire for guidance and acknowledge their inexperience in the subject.
In circuit design, it is crucial to understand the fundamental components and their interactions. A basic circuit typically includes resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, and transistors, each serving specific functions. Resistors limit current flow, capacitors store and release electrical energy, inductors oppose changes in current, diodes allow current to flow in one direction, and transistors act as switches or amplifiers.
When designing a circuit, one must start with a clear objective, such as creating a power supply, amplifier, or oscillator. The schematic diagram serves as a blueprint, illustrating how components are connected. Proper labeling of each component and adherence to standard symbols is essential for clarity.
Additionally, understanding Ohm's Law (V = IR) and Kirchhoff's Laws is fundamental for analyzing circuit behavior. Simulation tools can be utilized to test designs before physical implementation, allowing for adjustments and troubleshooting without the risk of damaging components.
In summary, effective circuit design requires a solid grasp of electronic principles, careful planning, and thorough testing to ensure functionality and reliability.Hey guys, I am new to the forum. I hope this is the right section. Sorry if I ask some dumb questions, I am new to circuit design. This is for my.. 🔗 External reference
In circuit design, it is crucial to understand the fundamental components and their interactions. A basic circuit typically includes resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, and transistors, each serving specific functions. Resistors limit current flow, capacitors store and release electrical energy, inductors oppose changes in current, diodes allow current to flow in one direction, and transistors act as switches or amplifiers.
When designing a circuit, one must start with a clear objective, such as creating a power supply, amplifier, or oscillator. The schematic diagram serves as a blueprint, illustrating how components are connected. Proper labeling of each component and adherence to standard symbols is essential for clarity.
Additionally, understanding Ohm's Law (V = IR) and Kirchhoff's Laws is fundamental for analyzing circuit behavior. Simulation tools can be utilized to test designs before physical implementation, allowing for adjustments and troubleshooting without the risk of damaging components.
In summary, effective circuit design requires a solid grasp of electronic principles, careful planning, and thorough testing to ensure functionality and reliability.Hey guys, I am new to the forum. I hope this is the right section. Sorry if I ask some dumb questions, I am new to circuit design. This is for my.. 🔗 External reference