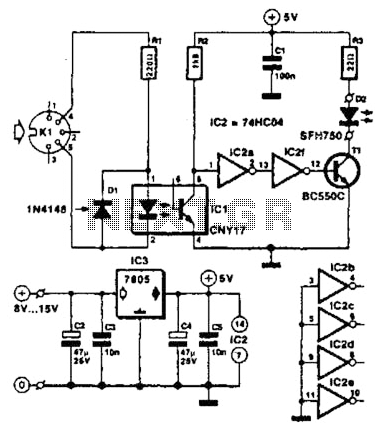
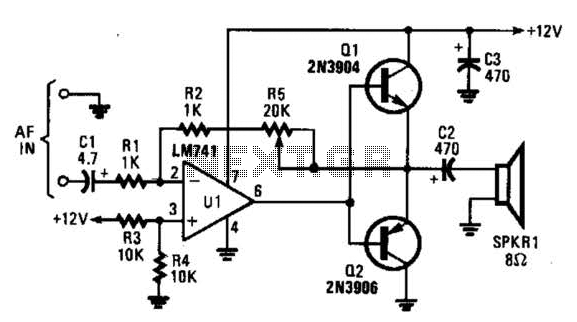
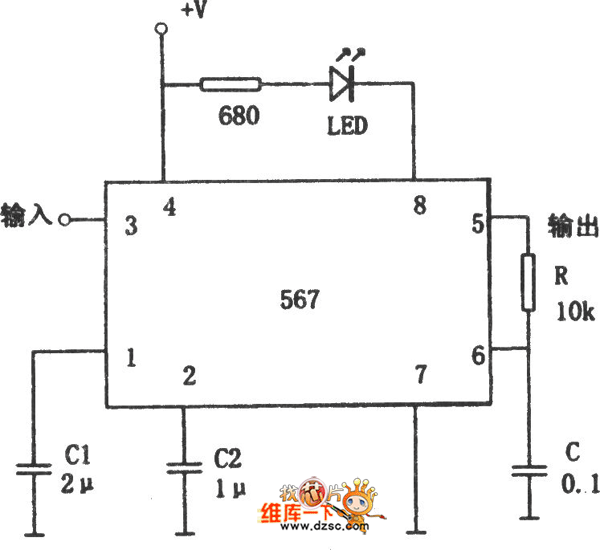
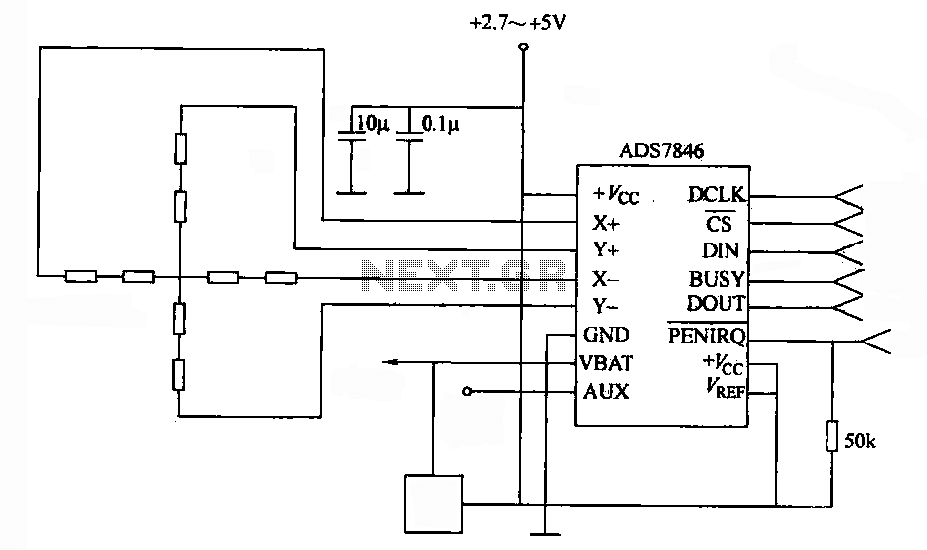
SK-IV with automatic voice-activated lights with music sounding circuit diagram
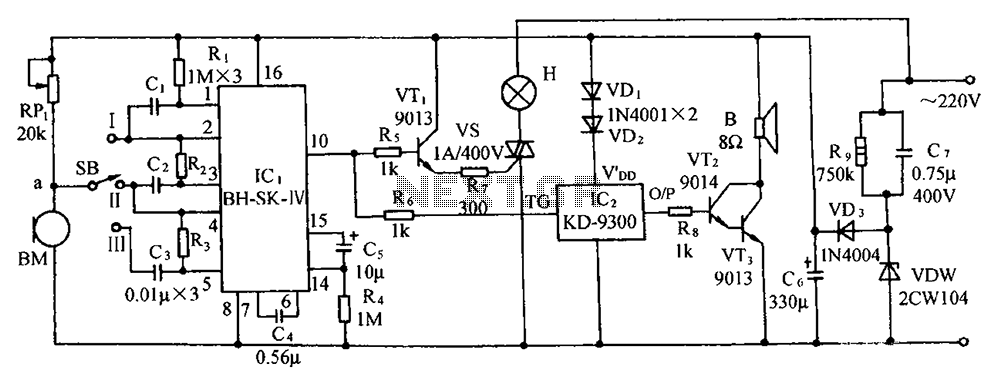
The circuit includes a microphone transducer, voice circuits, an SCR control circuit, a vocal music buck rectifier circuit, and an AC circuit. The BH-SK-IV serves as the core of the device.
The described circuit is a complex assembly designed to process audio signals, primarily focusing on vocal input. At the heart of the system is the BH-SK-IV, which acts as the main processing unit. The microphone transducer captures sound waves, converting them into electrical signals that can be manipulated by the subsequent circuitry.
The voice circuits are responsible for amplifying and filtering the audio signals to enhance clarity and quality. This stage may involve various components such as operational amplifiers and passive filters that work together to ensure that the output is suitable for further processing.
An SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) control circuit is integrated into the design to manage power flow within the system. This component allows for precise control of the electrical supply to the vocal music buck rectifier circuit, which is essential for converting the AC input into a usable DC output. The buck rectifier circuit is particularly important for reducing voltage levels while maintaining power efficiency, ensuring that the audio processing components receive the appropriate voltage levels.
The AC circuit serves as the power supply backbone for the entire system, providing the necessary energy for operation. It is designed to handle the input power requirements safely and efficiently, often incorporating transformers and rectifiers to convert high voltage AC to lower voltage levels suitable for the rest of the circuit.
Overall, this circuit is a sophisticated assembly that harmonizes various electronic components to achieve effective vocal signal processing, making it suitable for applications in audio equipment, communication devices, and other electronic systems requiring sound input and processing. Circuit as shown, including microphone transducer, voice circuits, SCR control circuit, vocal music buck rectifier circuit and the AC circuit. BH-SK-IV is the core of the devic e circuit.
The described circuit is a complex assembly designed to process audio signals, primarily focusing on vocal input. At the heart of the system is the BH-SK-IV, which acts as the main processing unit. The microphone transducer captures sound waves, converting them into electrical signals that can be manipulated by the subsequent circuitry.
The voice circuits are responsible for amplifying and filtering the audio signals to enhance clarity and quality. This stage may involve various components such as operational amplifiers and passive filters that work together to ensure that the output is suitable for further processing.
An SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier) control circuit is integrated into the design to manage power flow within the system. This component allows for precise control of the electrical supply to the vocal music buck rectifier circuit, which is essential for converting the AC input into a usable DC output. The buck rectifier circuit is particularly important for reducing voltage levels while maintaining power efficiency, ensuring that the audio processing components receive the appropriate voltage levels.
The AC circuit serves as the power supply backbone for the entire system, providing the necessary energy for operation. It is designed to handle the input power requirements safely and efficiently, often incorporating transformers and rectifiers to convert high voltage AC to lower voltage levels suitable for the rest of the circuit.
Overall, this circuit is a sophisticated assembly that harmonizes various electronic components to achieve effective vocal signal processing, making it suitable for applications in audio equipment, communication devices, and other electronic systems requiring sound input and processing. Circuit as shown, including microphone transducer, voice circuits, SCR control circuit, vocal music buck rectifier circuit and the AC circuit. BH-SK-IV is the core of the devic e circuit.