Musical Instrument Digital Interface (Midi) Transmitter Circuit
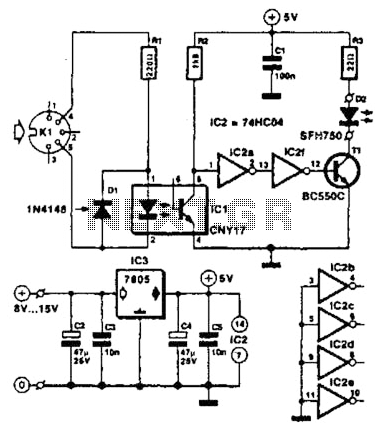
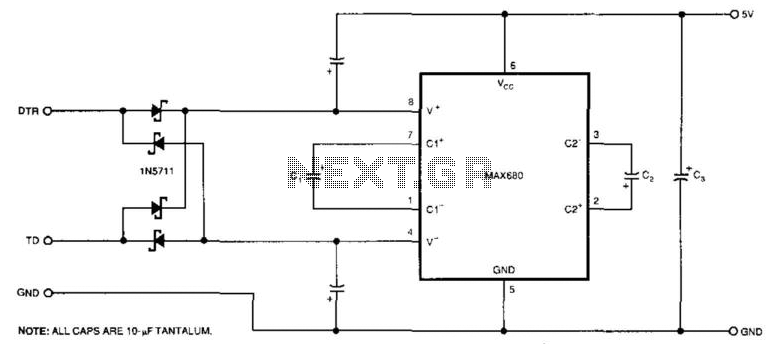
Used for digital control of musical instruments, this transmitter converts digital data signals into equivalent optical signals for a fiber optic cable interface. Optocoupler IC1 provides isolation, driving IC2-a and -b, and T1, ultimately providing a cable driver LED (SFH750).
This circuit is designed to facilitate the digital control of musical instruments through the conversion of digital signals into optical signals suitable for transmission via fiber optic cables. The use of an optocoupler (IC1) is essential for ensuring electrical isolation between the digital control circuitry and the optical transmission components. This isolation protects sensitive components from potential voltage spikes and noise that could be present in the control signals.
The optocoupler IC1 interfaces with two additional integrated circuits, IC2-a and IC2-b, which may serve various roles such as signal processing, amplification, or additional isolation. The outputs from these ICs are then directed to T1, which is likely a transformer or a similar component that helps in further conditioning the signal before it reaches the optical transmission stage.
The final stage of the circuit involves a cable driver LED, specifically the SFH750 model. This LED is designed to emit light when driven by the processed signals from T1, effectively converting the electrical signals into optical signals. The SFH750 is chosen for its efficiency and compatibility with fiber optic transmission, ensuring that the signals maintain integrity over long distances.
Overall, this circuit is a crucial component in modern digital musical instruments, providing reliable communication through optical means while maintaining isolation and signal integrity throughout the process. Used for digital control of musical instruments, this transmitter converts the digital data signals to equivalent optical signals for fiberoptic cable interface. Optocoupler IC1 provides isolation, and drives IC2-a and -b and Tl, and finally provides a cable driver LED (SFH750).
This circuit is designed to facilitate the digital control of musical instruments through the conversion of digital signals into optical signals suitable for transmission via fiber optic cables. The use of an optocoupler (IC1) is essential for ensuring electrical isolation between the digital control circuitry and the optical transmission components. This isolation protects sensitive components from potential voltage spikes and noise that could be present in the control signals.
The optocoupler IC1 interfaces with two additional integrated circuits, IC2-a and IC2-b, which may serve various roles such as signal processing, amplification, or additional isolation. The outputs from these ICs are then directed to T1, which is likely a transformer or a similar component that helps in further conditioning the signal before it reaches the optical transmission stage.
The final stage of the circuit involves a cable driver LED, specifically the SFH750 model. This LED is designed to emit light when driven by the processed signals from T1, effectively converting the electrical signals into optical signals. The SFH750 is chosen for its efficiency and compatibility with fiber optic transmission, ensuring that the signals maintain integrity over long distances.
Overall, this circuit is a crucial component in modern digital musical instruments, providing reliable communication through optical means while maintaining isolation and signal integrity throughout the process. Used for digital control of musical instruments, this transmitter converts the digital data signals to equivalent optical signals for fiberoptic cable interface. Optocoupler IC1 provides isolation, and drives IC2-a and -b and Tl, and finally provides a cable driver LED (SFH750).