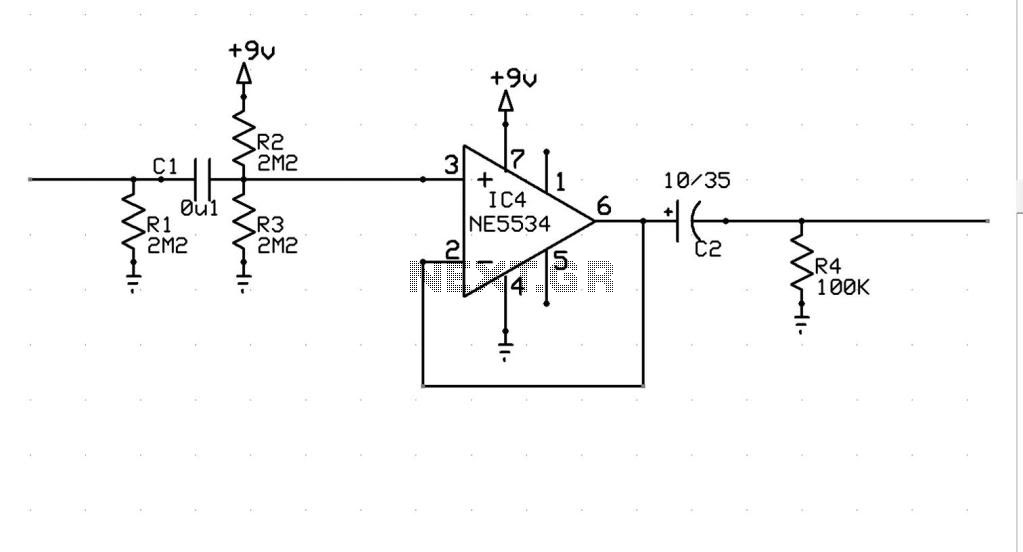
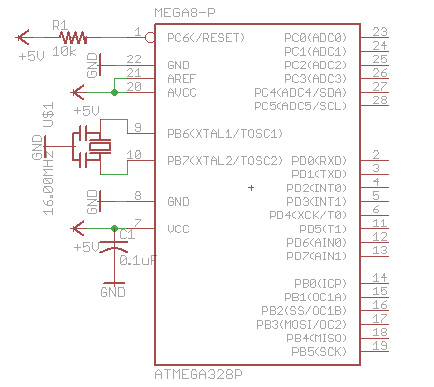
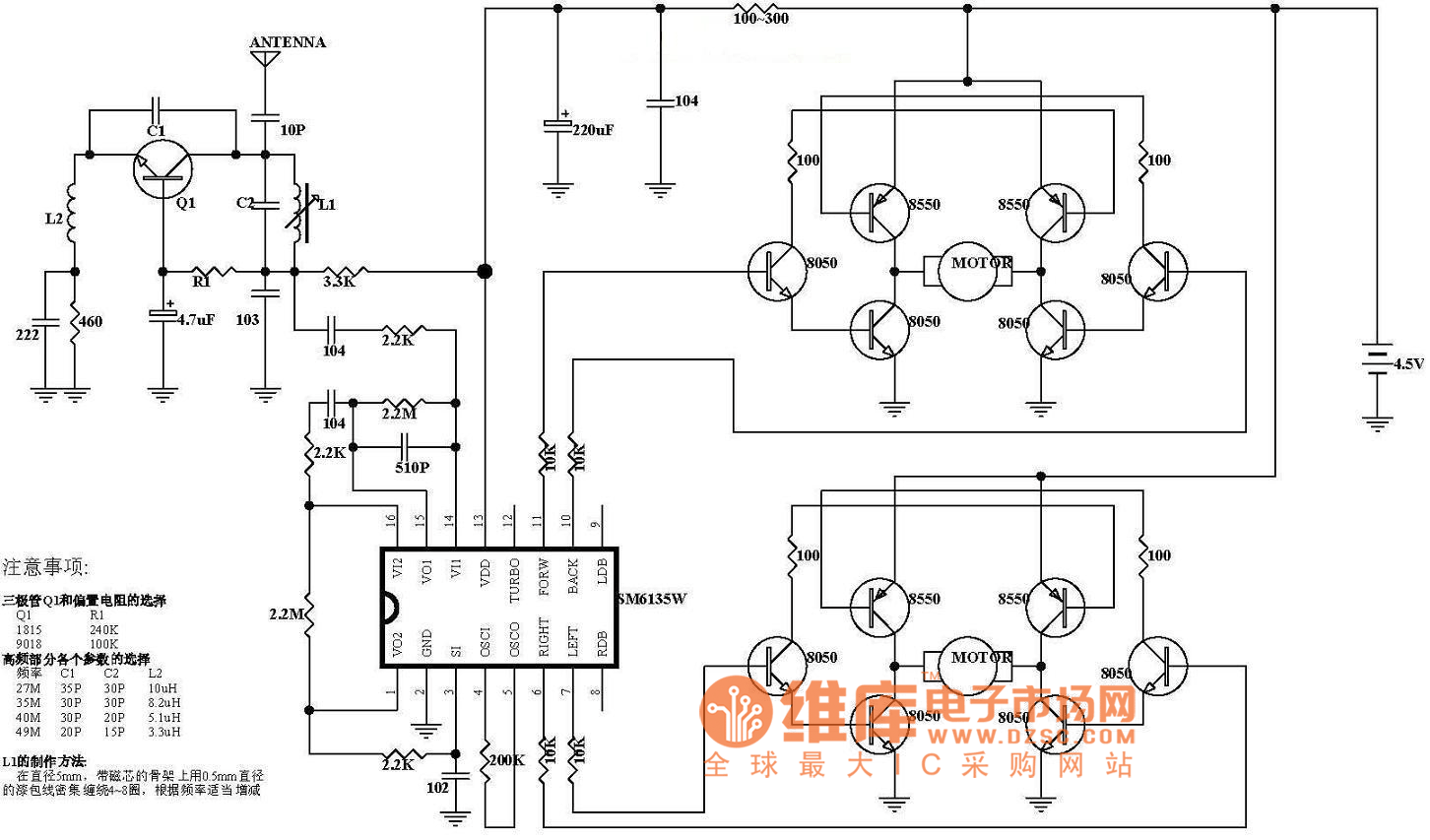
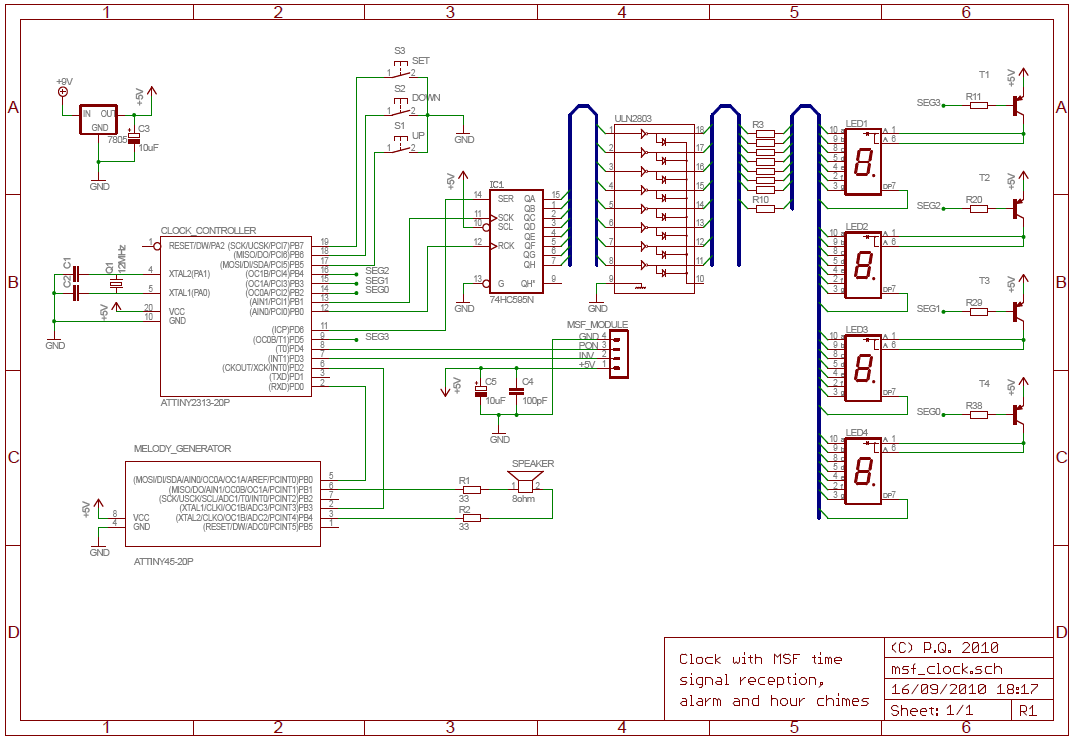
Small FM radio receiver
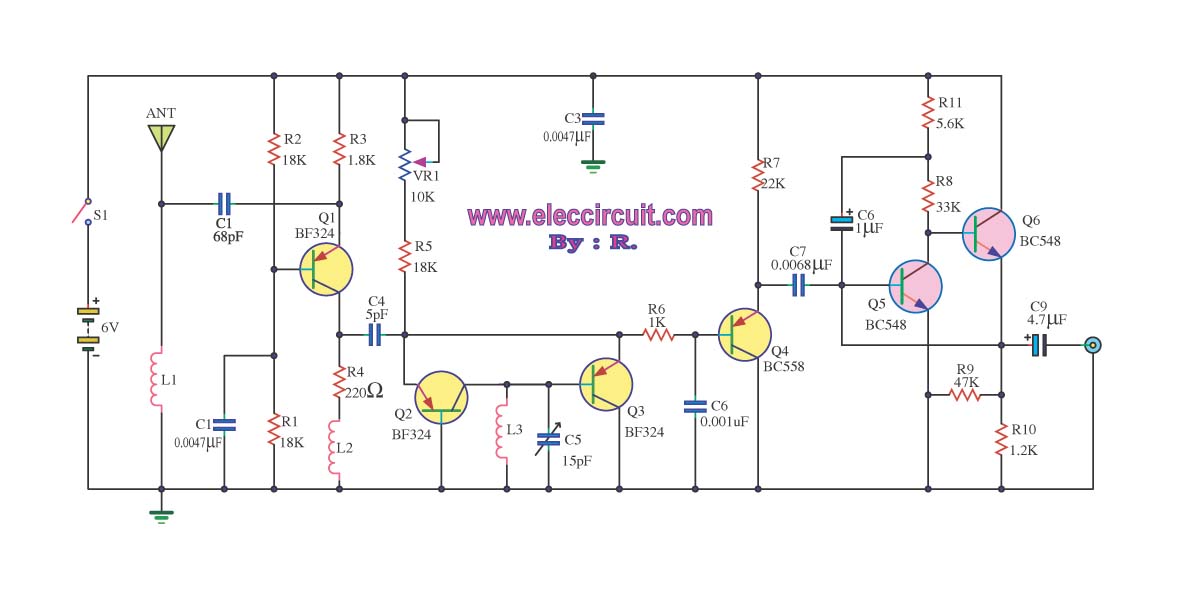
This circuit is an FM radio receiver that is very small in size and operates effectively, although its sensitivity is limited. The principle of this circuit is based on the use of a generator.
The FM radio receiver circuit typically consists of several key components, including an antenna, RF amplifier, mixer, local oscillator, demodulator, and audio amplifier. The antenna captures radio frequency signals, which are then amplified by the RF amplifier to improve signal strength. The mixer combines the amplified RF signal with a signal from the local oscillator to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This IF signal is then demodulated to extract the audio information, which is subsequently amplified by the audio amplifier for output to speakers or headphones.
In a compact design, the circuit may utilize integrated circuits (ICs) to minimize size and enhance performance. The generator mentioned in the description likely refers to the local oscillator, which is crucial for tuning the receiver to specific FM frequencies. The circuit may incorporate variable capacitors or inductors to allow for tuning across the FM band.
Despite its small size, the sensitivity of the receiver can be affected by various factors, including the quality of components, circuit layout, and the design of the antenna. Proper shielding and grounding techniques can help mitigate interference and improve overall performance. Additionally, the use of a better-quality RF amplifier can enhance sensitivity, allowing the receiver to pick up weaker signals more effectively.
Overall, this FM radio receiver circuit is a practical solution for compact radio applications, providing a balance between size and functionality, albeit with some limitations in sensitivity.This circuit is FM radio receiver that very small size and works well, although the sensitivity is poor. The principle of this circuit is to use the generator.. 🔗 External reference
The FM radio receiver circuit typically consists of several key components, including an antenna, RF amplifier, mixer, local oscillator, demodulator, and audio amplifier. The antenna captures radio frequency signals, which are then amplified by the RF amplifier to improve signal strength. The mixer combines the amplified RF signal with a signal from the local oscillator to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This IF signal is then demodulated to extract the audio information, which is subsequently amplified by the audio amplifier for output to speakers or headphones.
In a compact design, the circuit may utilize integrated circuits (ICs) to minimize size and enhance performance. The generator mentioned in the description likely refers to the local oscillator, which is crucial for tuning the receiver to specific FM frequencies. The circuit may incorporate variable capacitors or inductors to allow for tuning across the FM band.
Despite its small size, the sensitivity of the receiver can be affected by various factors, including the quality of components, circuit layout, and the design of the antenna. Proper shielding and grounding techniques can help mitigate interference and improve overall performance. Additionally, the use of a better-quality RF amplifier can enhance sensitivity, allowing the receiver to pick up weaker signals more effectively.
Overall, this FM radio receiver circuit is a practical solution for compact radio applications, providing a balance between size and functionality, albeit with some limitations in sensitivity.This circuit is FM radio receiver that very small size and works well, although the sensitivity is poor. The principle of this circuit is to use the generator.. 🔗 External reference