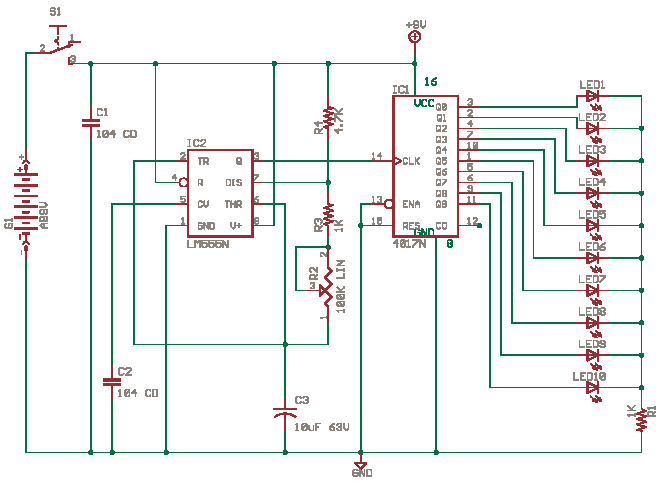
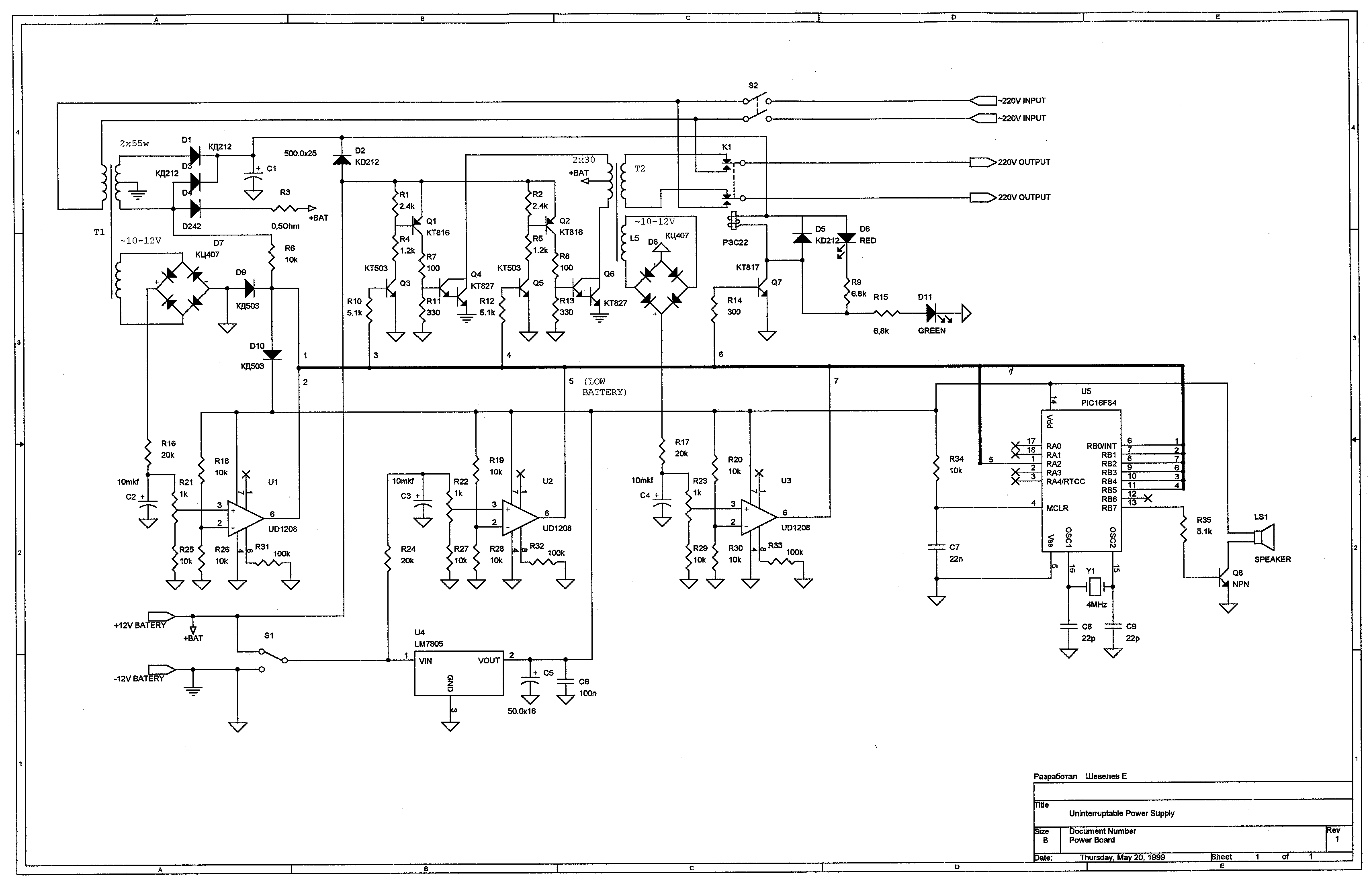
Small Metal detector schematic circuit
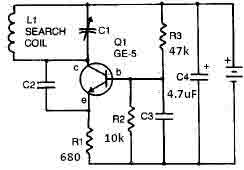
This metal detector circuit requires a power supply of 9 volts (DC) or a 9-volt battery. The circuit includes a variable capacitor C1 valued at 365 pF, a 100 pF silver mica capacitor C2, a 0.05 µF disc capacitor C3, and a 4.7 µF capacitor C4. The transistor Q1 can be an RCA SK3011 NPN transistor or an equivalent type, along with various resistors.
The metal detector circuit operates by generating an electromagnetic field through the use of capacitors and transistors, which are essential components for signal processing. The variable capacitor C1 allows for tuning the circuit to different frequencies, optimizing the detection capability based on the metal's properties being searched. The use of a 365 pF variable capacitor is crucial as it can be adjusted to change the resonant frequency of the circuit, thus enhancing sensitivity to specific types of metals.
Capacitor C2, a 100 pF silver mica capacitor, is known for its stability and low loss characteristics, making it suitable for RF applications. This capacitor plays a significant role in maintaining the integrity of the signal being processed. Capacitor C3, with a value of 0.05 µF, serves to filter high-frequency noise, ensuring that the output remains clear and reliable. Meanwhile, capacitor C4, rated at 4.7 µF, may be used for coupling or bypassing applications, aiding in the stabilization of the power supply voltage across the circuit.
The transistor Q1, which can be an RCA SK3011 or an equivalent NPN transistor, acts as a switching or amplifying device. Its role is to control the current flow through the circuit, allowing for the detection of metal objects by amplifying the signal generated by the electromagnetic field. The choice of an NPN transistor is critical, as it provides the necessary gain and switching capabilities required for efficient operation.
The resistors in the circuit, while not specified in detail, are integral to setting the biasing conditions for the transistor, controlling current flow, and ensuring stable operation of the metal detector. Proper selection and configuration of these resistors are essential for achieving optimal performance and sensitivity in detecting metallic objects.
Overall, this metal detector circuit design emphasizes the importance of component selection and configuration, ensuring reliable operation and effective metal detection capabilities.This metal detector circuit needs to be powered using a 9 volts power supply ( DC) or a 9 volts battery. The C1 capacitor is a variable capacitor with a value of 365 pF, C2 is a 100pF silver mica capacitor, C3 is a 0.05 uF disc capacitor and the C4 is a 4.7 uF capacitor.
The Q1 transistor can be RCA SK3011 npn transistor or equivalent type and all resist.. 🔗 External reference
The metal detector circuit operates by generating an electromagnetic field through the use of capacitors and transistors, which are essential components for signal processing. The variable capacitor C1 allows for tuning the circuit to different frequencies, optimizing the detection capability based on the metal's properties being searched. The use of a 365 pF variable capacitor is crucial as it can be adjusted to change the resonant frequency of the circuit, thus enhancing sensitivity to specific types of metals.
Capacitor C2, a 100 pF silver mica capacitor, is known for its stability and low loss characteristics, making it suitable for RF applications. This capacitor plays a significant role in maintaining the integrity of the signal being processed. Capacitor C3, with a value of 0.05 µF, serves to filter high-frequency noise, ensuring that the output remains clear and reliable. Meanwhile, capacitor C4, rated at 4.7 µF, may be used for coupling or bypassing applications, aiding in the stabilization of the power supply voltage across the circuit.
The transistor Q1, which can be an RCA SK3011 or an equivalent NPN transistor, acts as a switching or amplifying device. Its role is to control the current flow through the circuit, allowing for the detection of metal objects by amplifying the signal generated by the electromagnetic field. The choice of an NPN transistor is critical, as it provides the necessary gain and switching capabilities required for efficient operation.
The resistors in the circuit, while not specified in detail, are integral to setting the biasing conditions for the transistor, controlling current flow, and ensuring stable operation of the metal detector. Proper selection and configuration of these resistors are essential for achieving optimal performance and sensitivity in detecting metallic objects.
Overall, this metal detector circuit design emphasizes the importance of component selection and configuration, ensuring reliable operation and effective metal detection capabilities.This metal detector circuit needs to be powered using a 9 volts power supply ( DC) or a 9 volts battery. The C1 capacitor is a variable capacitor with a value of 365 pF, C2 is a 100pF silver mica capacitor, C3 is a 0.05 uF disc capacitor and the C4 is a 4.7 uF capacitor.
The Q1 transistor can be RCA SK3011 npn transistor or equivalent type and all resist.. 🔗 External reference