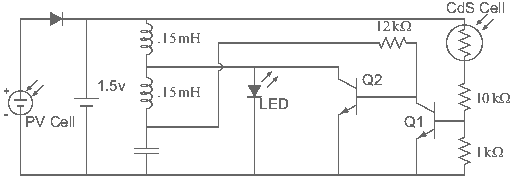
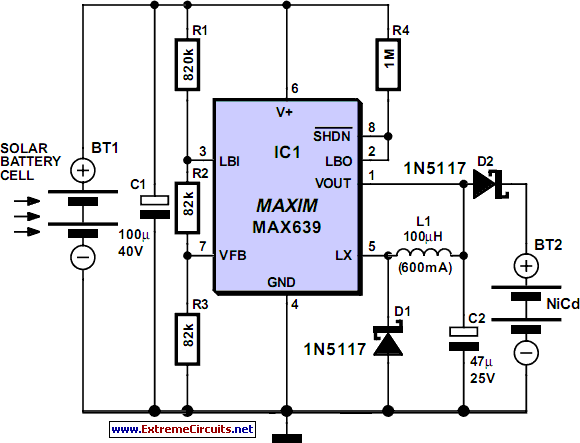
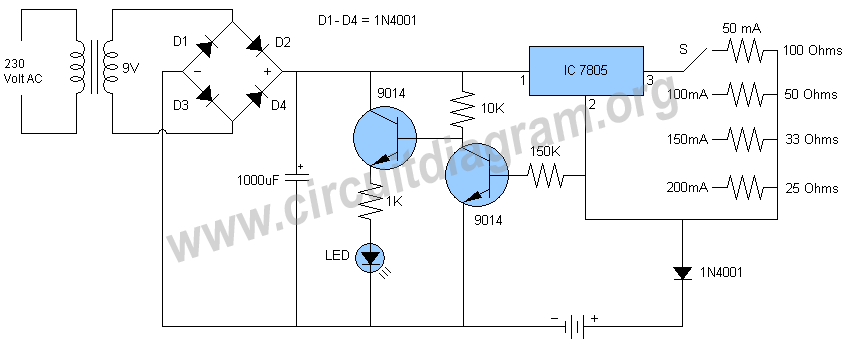
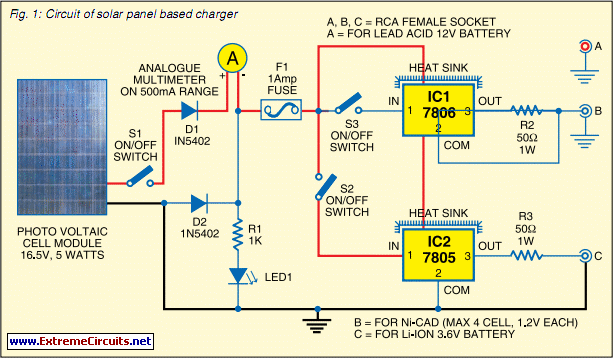
Solar charger for lead-acid batteries
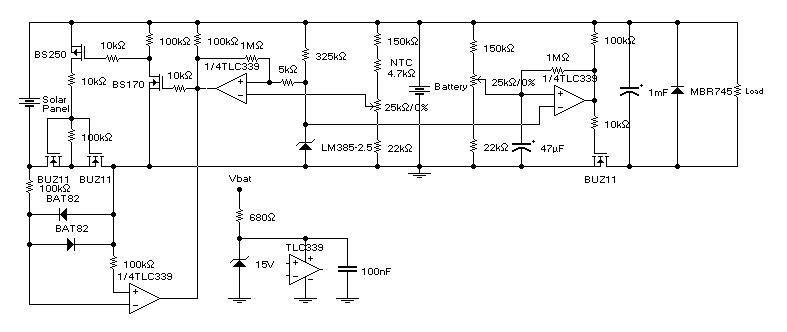
This circuit is intended for charging lead-acid batteries with a solar panel. The customary diode that prevents the battery from discharging through the solar panel has been replaced by a FET-comparator combination. The charger will stop charging once a pre-set voltage (temperature compensated) has been reached, and recommence charging when the voltage has dropped off sufficiently. The load is disconnected when the battery voltage drops below 11V and reconnected when it gets back to 12.5V. More: The circuit has the following features:
* Charges until Vbat = 13.8V (adjustable), then float charges;
* Shuts down load when Vbat < 11V (adjustable), resets at 12.5V;
* Temperature compensation;
* Will work with cheap and readily available components.
This circuit is designed to efficiently charge lead-acid batteries using solar energy while incorporating a FET-comparator arrangement to enhance performance compared to traditional diode-based systems. The charging process is initiated by the solar panel output, which is directed to the battery through the FET. The FET serves not only as a switch but also as a means to minimize energy loss, which is often associated with diodes due to their forward voltage drop.
The charging voltage is set to a maximum of 13.8V, which is a common float charging voltage for lead-acid batteries. This voltage can be adjusted to suit specific battery types or requirements. The circuit includes a temperature compensation feature, which adjusts the charging voltage based on the ambient temperature, ensuring that the battery is charged optimally without risk of overcharging in high-temperature conditions.
When the battery voltage falls below 11V, the FET disconnects the load to prevent further discharge, protecting the battery from damage due to over-discharge. This threshold is adjustable, allowing for customization based on the battery specifications. The load is automatically reconnected when the battery voltage rises back to 12.5V, ensuring that the battery remains operational without manual intervention.
The use of readily available and cost-effective components makes this circuit accessible for various applications, particularly in off-grid solar systems where efficient battery management is crucial. Overall, this circuit provides a reliable solution for solar charging of lead-acid batteries, integrating essential features for effective battery maintenance and longevity.This circuit is intended for charging lead-acid batteries with a solar panel. The customary diode that prevents the battery from discharging through the solar panel has been replaced by a FET-comparator combination. The charger will stop charging once a pre-set voltage (temperature compensated) has been reached, and recommence charging when the voltage has dropped off sufficiently.
The load is disconnected when the baterry voltage drops below 11V and reconnected when it gets back to 12.5V. The circuit has the following features: * Charges until Vbat = 13,8V (adjustable), then float charges; * Shuts down load when Vbat < 11V (adjustable), resets at 12,5V; * Temperature compensation; * Will work with cheap and readily 🔗 External reference
* Charges until Vbat = 13.8V (adjustable), then float charges;
* Shuts down load when Vbat < 11V (adjustable), resets at 12.5V;
* Temperature compensation;
* Will work with cheap and readily available components.
This circuit is designed to efficiently charge lead-acid batteries using solar energy while incorporating a FET-comparator arrangement to enhance performance compared to traditional diode-based systems. The charging process is initiated by the solar panel output, which is directed to the battery through the FET. The FET serves not only as a switch but also as a means to minimize energy loss, which is often associated with diodes due to their forward voltage drop.
The charging voltage is set to a maximum of 13.8V, which is a common float charging voltage for lead-acid batteries. This voltage can be adjusted to suit specific battery types or requirements. The circuit includes a temperature compensation feature, which adjusts the charging voltage based on the ambient temperature, ensuring that the battery is charged optimally without risk of overcharging in high-temperature conditions.
When the battery voltage falls below 11V, the FET disconnects the load to prevent further discharge, protecting the battery from damage due to over-discharge. This threshold is adjustable, allowing for customization based on the battery specifications. The load is automatically reconnected when the battery voltage rises back to 12.5V, ensuring that the battery remains operational without manual intervention.
The use of readily available and cost-effective components makes this circuit accessible for various applications, particularly in off-grid solar systems where efficient battery management is crucial. Overall, this circuit provides a reliable solution for solar charging of lead-acid batteries, integrating essential features for effective battery maintenance and longevity.This circuit is intended for charging lead-acid batteries with a solar panel. The customary diode that prevents the battery from discharging through the solar panel has been replaced by a FET-comparator combination. The charger will stop charging once a pre-set voltage (temperature compensated) has been reached, and recommence charging when the voltage has dropped off sufficiently.
The load is disconnected when the baterry voltage drops below 11V and reconnected when it gets back to 12.5V. The circuit has the following features: * Charges until Vbat = 13,8V (adjustable), then float charges; * Shuts down load when Vbat < 11V (adjustable), resets at 12,5V; * Temperature compensation; * Will work with cheap and readily 🔗 External reference