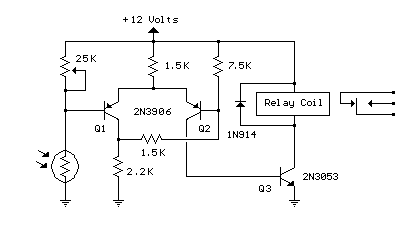
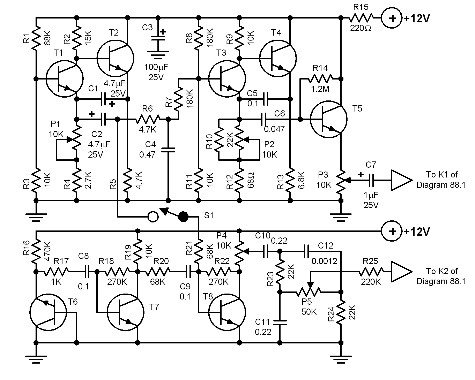
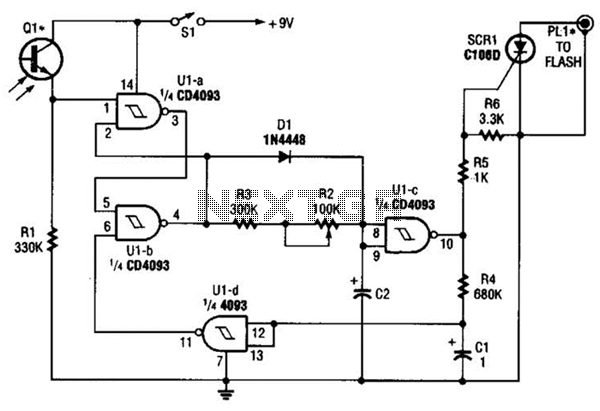
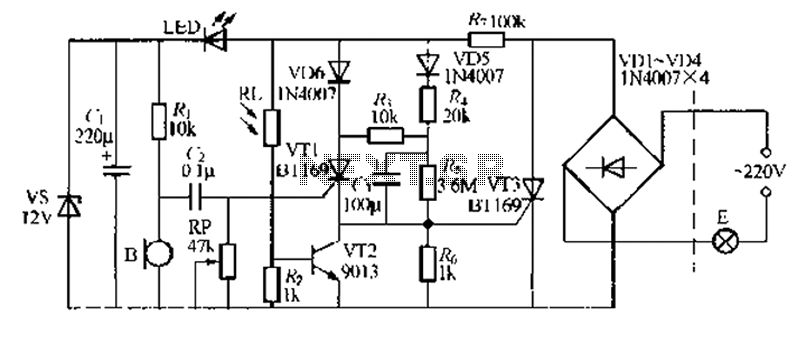
Sound light-flash trigger
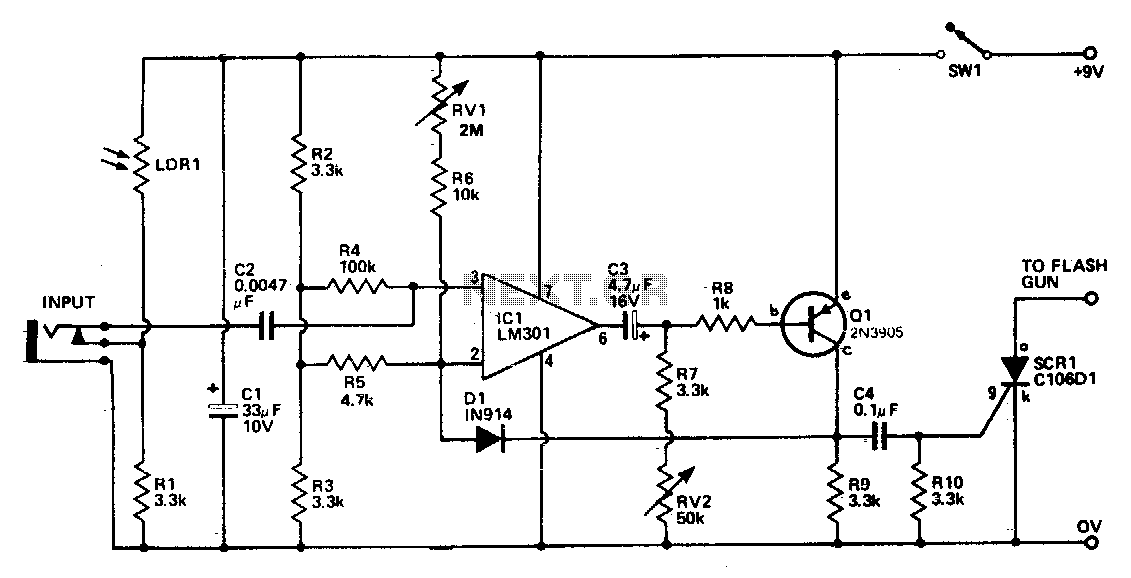
Sound input to the microphone triggers the IC monostable circuit, which subsequently triggers an SCR, and hence the flash, after a time delay. This delay is adjustable by varying the monostable on-time from 5 milliseconds to 200 milliseconds.
The circuit described involves a microphone that detects sound input, which serves as the triggering mechanism for a monostable multivibrator integrated circuit (IC). When the microphone picks up sound, it sends a signal to the monostable circuit, causing it to output a pulse of a specific duration. This pulse duration is adjustable, allowing the user to set it anywhere between 5 milliseconds and 200 milliseconds by altering the timing components associated with the monostable configuration, typically a resistor-capacitor (RC) network.
Once the monostable circuit generates the output pulse, it activates a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR). The SCR is a semiconductor device that acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current to a connected load, in this case, a flash unit. The activation of the SCR allows current to flow through the flash circuit, resulting in the flash being triggered.
The adjustable delay feature is particularly useful in applications where the timing of the flash needs to be synchronized with specific sound events, such as in photography or signaling systems. The monostable circuit can be designed using various ICs, like the 555 timer, which is popular for its ease of use and flexibility in timing applications.
To implement this circuit effectively, one must carefully select the values of the resistor and capacitor to achieve the desired delay range. The SCR should also be chosen based on the load requirements of the flash unit to ensure it can handle the necessary current and voltage levels. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms may be needed to prevent overheating during operation, especially if the flash unit is activated frequently.
Overall, this circuit provides a versatile solution for sound-activated flash triggering, with adjustable timing capabilities that enhance its functionality across various applications.Sound input to the microphone triggers the IC monostable circuit which subsequently triggers an SCR, and hence the flash, after a time delay This delay is adjustable—by varying the monostable on-time—from from 5 milliseconds to 200 milliseconds.
The circuit described involves a microphone that detects sound input, which serves as the triggering mechanism for a monostable multivibrator integrated circuit (IC). When the microphone picks up sound, it sends a signal to the monostable circuit, causing it to output a pulse of a specific duration. This pulse duration is adjustable, allowing the user to set it anywhere between 5 milliseconds and 200 milliseconds by altering the timing components associated with the monostable configuration, typically a resistor-capacitor (RC) network.
Once the monostable circuit generates the output pulse, it activates a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR). The SCR is a semiconductor device that acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current to a connected load, in this case, a flash unit. The activation of the SCR allows current to flow through the flash circuit, resulting in the flash being triggered.
The adjustable delay feature is particularly useful in applications where the timing of the flash needs to be synchronized with specific sound events, such as in photography or signaling systems. The monostable circuit can be designed using various ICs, like the 555 timer, which is popular for its ease of use and flexibility in timing applications.
To implement this circuit effectively, one must carefully select the values of the resistor and capacitor to achieve the desired delay range. The SCR should also be chosen based on the load requirements of the flash unit to ensure it can handle the necessary current and voltage levels. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms may be needed to prevent overheating during operation, especially if the flash unit is activated frequently.
Overall, this circuit provides a versatile solution for sound-activated flash triggering, with adjustable timing capabilities that enhance its functionality across various applications.Sound input to the microphone triggers the IC monostable circuit which subsequently triggers an SCR, and hence the flash, after a time delay This delay is adjustable—by varying the monostable on-time—from from 5 milliseconds to 200 milliseconds.