Speaker Protector Circuit
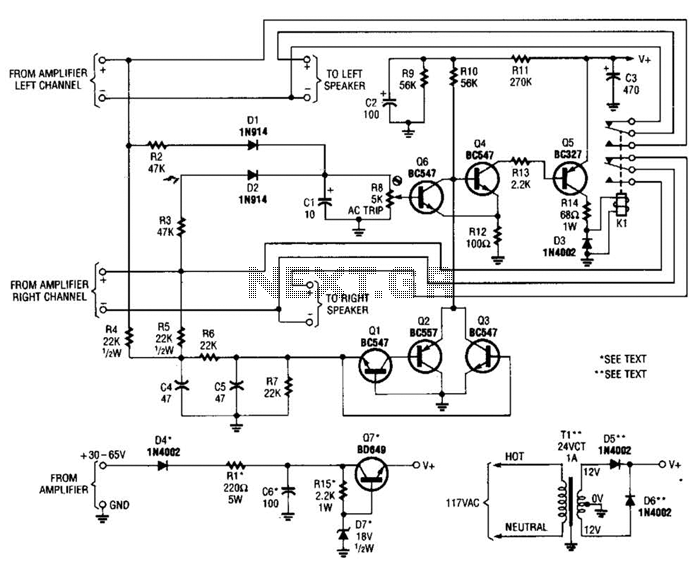
Most of the transistors in this speaker protector operate as switches. Normally, Q4, Q5, and K1 are activated, allowing the speakers to connect to the amplifier. However, if a significant DC voltage is detected at the amplifier output, either Q3 or the combination of Q1 and Q2 will activate, which biases Q4 off. This action subsequently turns off Q5, de-energizing the relay and disconnecting the speakers from the amplifier. Additionally, components D1, D2, and Q6 constitute the overdrive protection circuit.
The speaker protector circuit is designed to safeguard speakers from potential damage caused by excessive DC voltage from the amplifier. The primary components involved in this protection mechanism include transistors Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, and Q5, along with relay K1, and diodes D1, D2, and Q6.
In normal operation, Q4 and Q5 remain in the conducting state, which keeps K1 energized. This configuration allows the speakers to remain connected to the amplifier, ensuring proper audio output. The activation of Q4 is crucial, as it controls the state of Q5 and ultimately the relay K1.
When a large DC voltage is detected at the output of the amplifier, it triggers either Q3 or the combination of Q1 and Q2. The activation of these transistors biases Q4 into the off state. As Q4 turns off, Q5 also ceases to conduct, leading to the de-energization of relay K1. This disconnection is vital for protecting the speakers from the harmful effects of DC voltage, which can cause overheating and damage.
The overdrive protection circuit, formed by components D1, D2, and Q6, plays a critical role in monitoring the output voltage. Diodes D1 and D2 are typically configured to clamp the voltage levels, ensuring that any overvoltage conditions are detected promptly. Q6 serves as an additional control element that responds to the signals from the diodes, further enhancing the reliability of the protection circuit.
Overall, this speaker protection circuit is an essential component in audio amplification systems, ensuring that speakers are protected from damage due to overvoltage conditions while allowing for normal operation under safe conditions. The use of transistors and relays facilitates a quick response to potential threats, ensuring the longevity and performance of the audio equipment. Most of the transistors in this speaker protector function as switches. Normally, Q4, Q5, and K1 are on and the speakers are connected to the amplifier. However, if a large dc voltage appears at an amplifier output, either Q3, or Ql and Q2 turn on, biasing Q4 off. That action turns Q5 off, de-energizes the relay, and disconnects the speakers from the amplifier. Components Dl, D2, and Q6 form the overdrive-protection circuit.
The speaker protector circuit is designed to safeguard speakers from potential damage caused by excessive DC voltage from the amplifier. The primary components involved in this protection mechanism include transistors Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, and Q5, along with relay K1, and diodes D1, D2, and Q6.
In normal operation, Q4 and Q5 remain in the conducting state, which keeps K1 energized. This configuration allows the speakers to remain connected to the amplifier, ensuring proper audio output. The activation of Q4 is crucial, as it controls the state of Q5 and ultimately the relay K1.
When a large DC voltage is detected at the output of the amplifier, it triggers either Q3 or the combination of Q1 and Q2. The activation of these transistors biases Q4 into the off state. As Q4 turns off, Q5 also ceases to conduct, leading to the de-energization of relay K1. This disconnection is vital for protecting the speakers from the harmful effects of DC voltage, which can cause overheating and damage.
The overdrive protection circuit, formed by components D1, D2, and Q6, plays a critical role in monitoring the output voltage. Diodes D1 and D2 are typically configured to clamp the voltage levels, ensuring that any overvoltage conditions are detected promptly. Q6 serves as an additional control element that responds to the signals from the diodes, further enhancing the reliability of the protection circuit.
Overall, this speaker protection circuit is an essential component in audio amplification systems, ensuring that speakers are protected from damage due to overvoltage conditions while allowing for normal operation under safe conditions. The use of transistors and relays facilitates a quick response to potential threats, ensuring the longevity and performance of the audio equipment. Most of the transistors in this speaker protector function as switches. Normally, Q4, Q5, and K1 are on and the speakers are connected to the amplifier. However, if a large dc voltage appears at an amplifier output, either Q3, or Ql and Q2 turn on, biasing Q4 off. That action turns Q5 off, de-energizes the relay, and disconnects the speakers from the amplifier. Components Dl, D2, and Q6 form the overdrive-protection circuit.