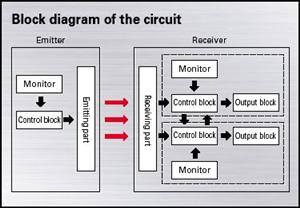
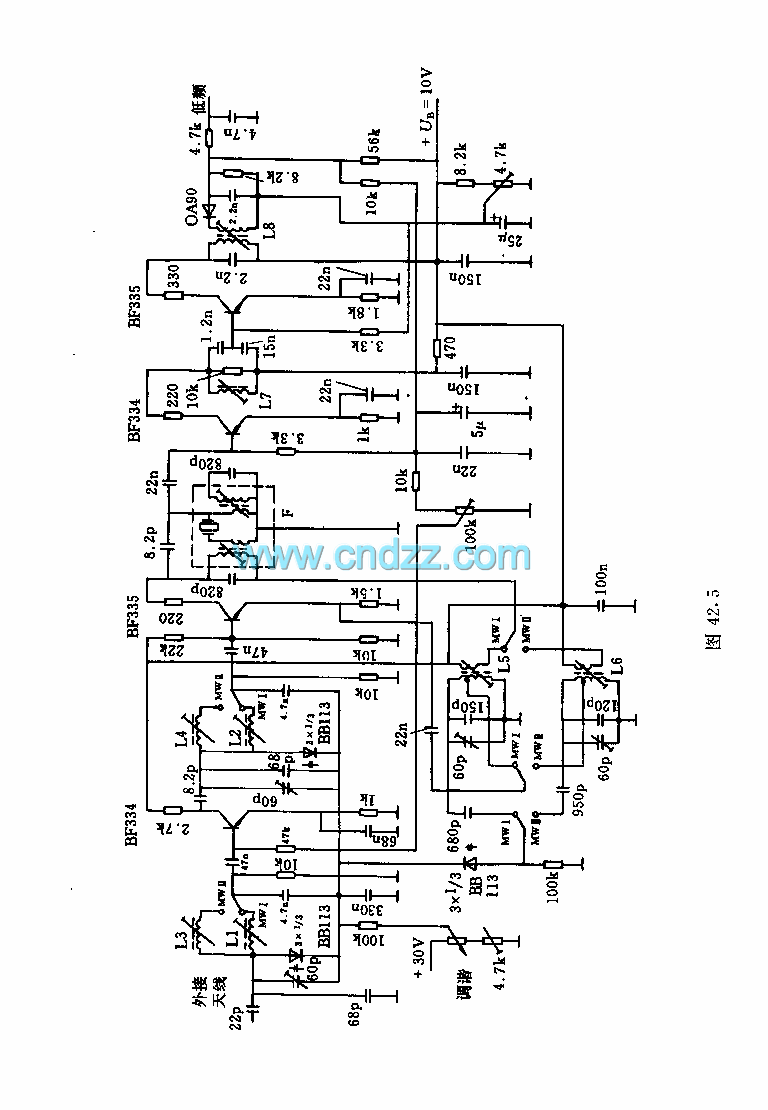
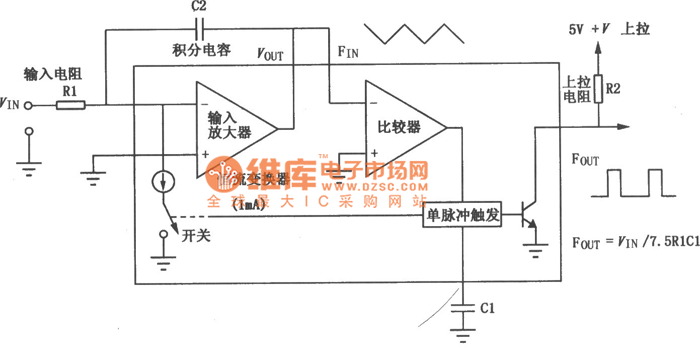
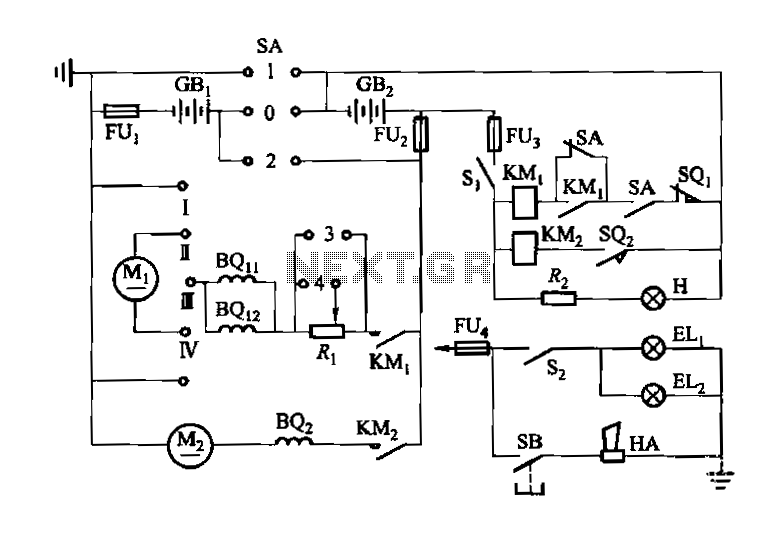
Speed differential negative feedback circuit
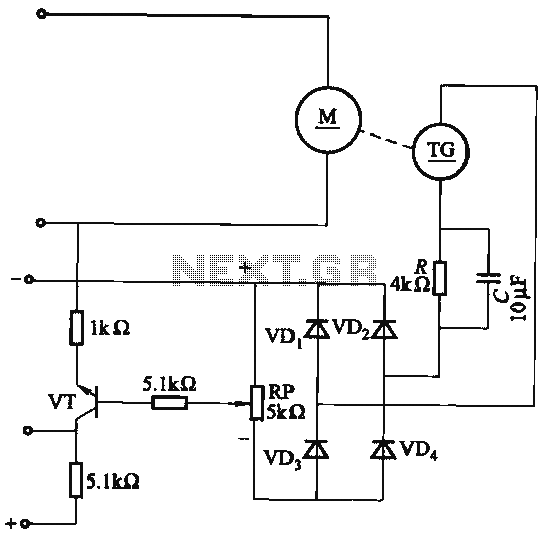
The capacitor C is part of the speed differential negative feedback system. The adjustment potentiometer RP allows for changing the amount of negative feedback. Both components can be utilized simultaneously within the circuit. The voltage (or speed) will only be affected when the negative feedback mechanism for speed fluctuation is not operational, impacting speed stability.
The circuit employs a capacitor (C) in conjunction with an adjustment potentiometer (RP) to establish a negative feedback loop that regulates speed differentials. The capacitor serves to filter or smooth out voltage fluctuations, thereby stabilizing the output voltage in response to changes in speed. The adjustment potentiometer provides a means to fine-tune the level of negative feedback applied to the system, allowing for precise control over the circuit's response characteristics.
In this configuration, the negative feedback mechanism is crucial for maintaining consistent speed and stability. When the system experiences speed fluctuations, the negative feedback loop works to counteract these changes by adjusting the output voltage accordingly. However, if the feedback mechanism is inactive, the circuit may not adequately respond to speed variations, leading to instability in the output.
The design allows for simultaneous operation of both the capacitor and the potentiometer, which enhances flexibility in circuit tuning. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can increase or decrease the feedback level, thus altering the circuit's responsiveness to speed changes. This capability is particularly important in applications where precise speed control is essential, such as in motor drive systems or automated machinery.
In summary, the integration of capacitor C and potentiometer RP in the speed differential negative feedback system plays a critical role in achieving stable and reliable operation. The careful adjustment of these components can significantly improve the overall performance of the circuit, ensuring that speed variations are effectively managed.Now the capacitor C from the speed differential negative feedback. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the amount of negative feedback. It can be used simultaneously both the necessary circuit. Voltage (or speed) only when negative feedback differential speed fluctuation function does not work when the speed and stability.
The circuit employs a capacitor (C) in conjunction with an adjustment potentiometer (RP) to establish a negative feedback loop that regulates speed differentials. The capacitor serves to filter or smooth out voltage fluctuations, thereby stabilizing the output voltage in response to changes in speed. The adjustment potentiometer provides a means to fine-tune the level of negative feedback applied to the system, allowing for precise control over the circuit's response characteristics.
In this configuration, the negative feedback mechanism is crucial for maintaining consistent speed and stability. When the system experiences speed fluctuations, the negative feedback loop works to counteract these changes by adjusting the output voltage accordingly. However, if the feedback mechanism is inactive, the circuit may not adequately respond to speed variations, leading to instability in the output.
The design allows for simultaneous operation of both the capacitor and the potentiometer, which enhances flexibility in circuit tuning. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can increase or decrease the feedback level, thus altering the circuit's responsiveness to speed changes. This capability is particularly important in applications where precise speed control is essential, such as in motor drive systems or automated machinery.
In summary, the integration of capacitor C and potentiometer RP in the speed differential negative feedback system plays a critical role in achieving stable and reliable operation. The careful adjustment of these components can significantly improve the overall performance of the circuit, ensuring that speed variations are effectively managed.Now the capacitor C from the speed differential negative feedback. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change the amount of negative feedback. It can be used simultaneously both the necessary circuit. Voltage (or speed) only when negative feedback differential speed fluctuation function does not work when the speed and stability.