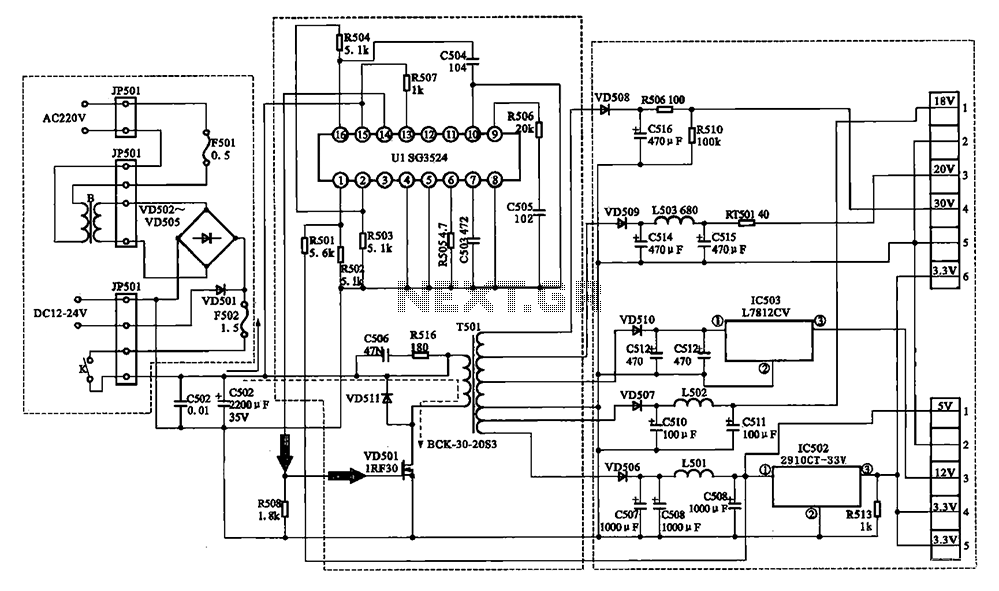
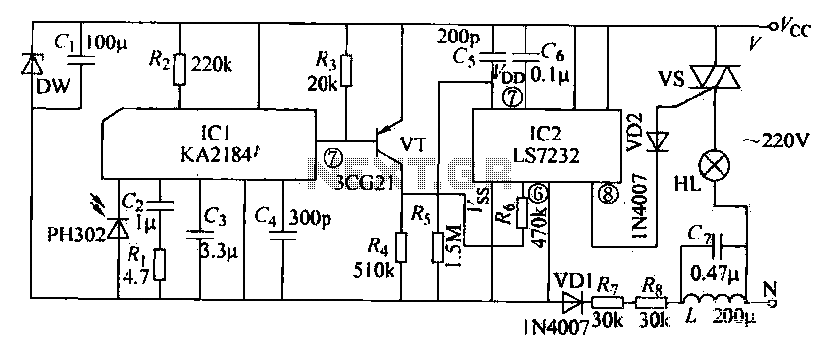
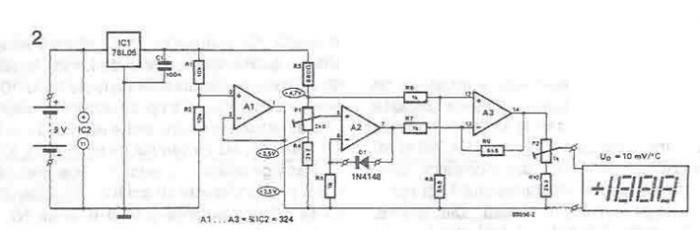
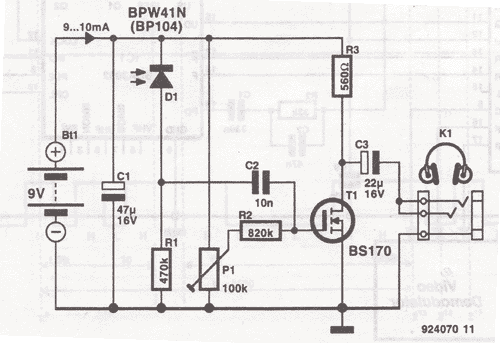
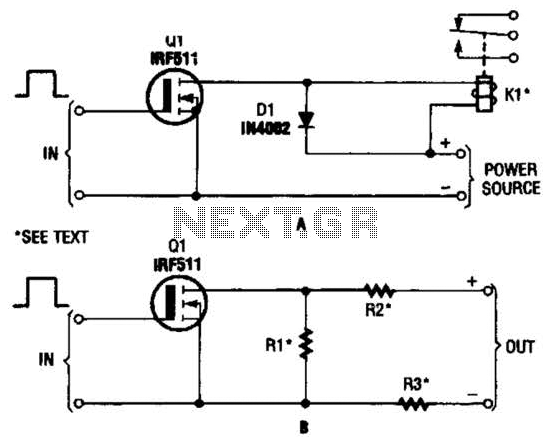
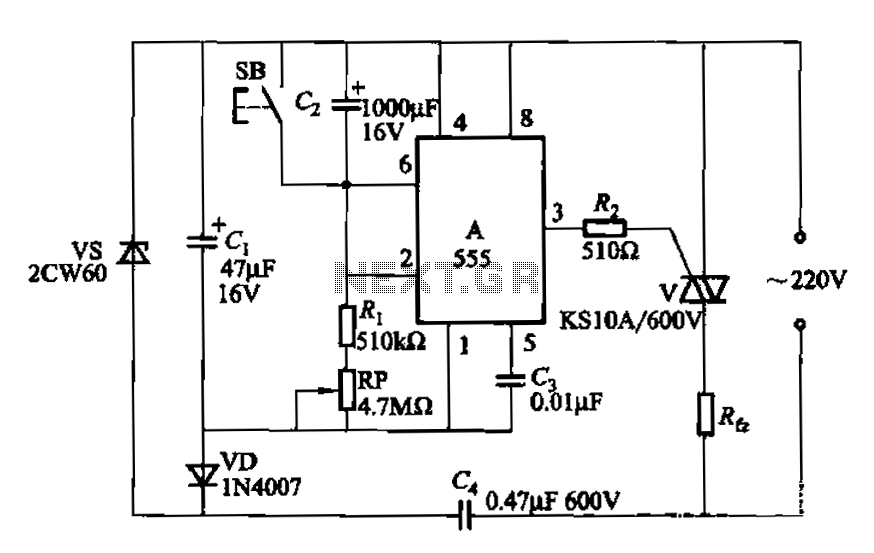
spi circuit
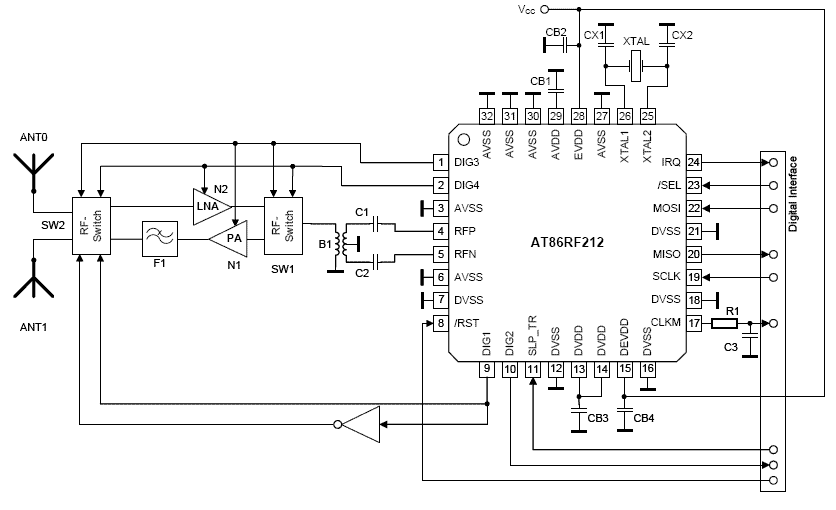
SPI Integrated Circuit Bus, IC Buses, an IC, Chip-to-Chip Bus Serial Peripheral Interface, Integrated Circuit Bus types, and IC Bus Electrical Interface Descriptions. The Peripheral Interface (SPI) circuit is a.
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication protocol used for connecting microcontrollers to various peripherals, such as sensors, memory devices, and other integrated circuits (ICs). SPI operates through a master-slave architecture, where one master device controls one or more slave devices. The communication is facilitated through four primary lines:
1. **MOSI (Master Out Slave In)** - This line carries data from the master to the slave.
2. **MISO (Master In Slave Out)** - This line carries data from the slave back to the master.
3. **SCK (Serial Clock)** - The clock signal generated by the master to synchronize data transmission.
4. **SS (Slave Select)** - This line is used by the master to select which slave device to communicate with.
The SPI bus supports full-duplex communication, allowing data to be sent and received simultaneously. This feature makes SPI particularly efficient for applications requiring high-speed data transfer. The protocol does not specify a maximum data rate, but it is commonly used in applications with speeds ranging from a few kilobits per second to tens of megabits per second.
In terms of electrical characteristics, SPI interfaces typically operate at standard logic levels (e.g., 3.3V or 5V), and the data lines are usually driven by push-pull outputs. The physical layout of the SPI bus can vary, with devices often arranged in a daisy chain or star configuration depending on the application requirements.
The SPI protocol is widely used in various applications, including but not limited to, digital signal processing, data acquisition systems, and interfacing with memory devices such as EEPROMs and flash memory. Its simplicity and speed make it a popular choice for embedded system designers seeking reliable and efficient communication between integrated circuits.SPI Integrated Circuit Bus , IC Buses, an IC, Chip-to-Chip Bus Serial Peripheral Interface, Integrated Circuit Bus types, and IC Bus Electrical Interface Descriptions, . Peripheral Interface (SPI) circuit is a . -> Integrated Circuit Bus Li.. 🔗 External reference
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication protocol used for connecting microcontrollers to various peripherals, such as sensors, memory devices, and other integrated circuits (ICs). SPI operates through a master-slave architecture, where one master device controls one or more slave devices. The communication is facilitated through four primary lines:
1. **MOSI (Master Out Slave In)** - This line carries data from the master to the slave.
2. **MISO (Master In Slave Out)** - This line carries data from the slave back to the master.
3. **SCK (Serial Clock)** - The clock signal generated by the master to synchronize data transmission.
4. **SS (Slave Select)** - This line is used by the master to select which slave device to communicate with.
The SPI bus supports full-duplex communication, allowing data to be sent and received simultaneously. This feature makes SPI particularly efficient for applications requiring high-speed data transfer. The protocol does not specify a maximum data rate, but it is commonly used in applications with speeds ranging from a few kilobits per second to tens of megabits per second.
In terms of electrical characteristics, SPI interfaces typically operate at standard logic levels (e.g., 3.3V or 5V), and the data lines are usually driven by push-pull outputs. The physical layout of the SPI bus can vary, with devices often arranged in a daisy chain or star configuration depending on the application requirements.
The SPI protocol is widely used in various applications, including but not limited to, digital signal processing, data acquisition systems, and interfacing with memory devices such as EEPROMs and flash memory. Its simplicity and speed make it a popular choice for embedded system designers seeking reliable and efficient communication between integrated circuits.SPI Integrated Circuit Bus , IC Buses, an IC, Chip-to-Chip Bus Serial Peripheral Interface, Integrated Circuit Bus types, and IC Bus Electrical Interface Descriptions, . Peripheral Interface (SPI) circuit is a . -> Integrated Circuit Bus Li.. 🔗 External reference