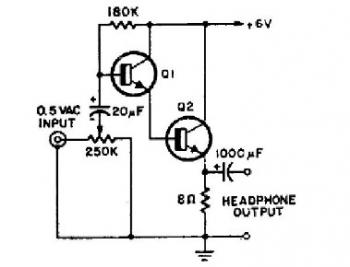
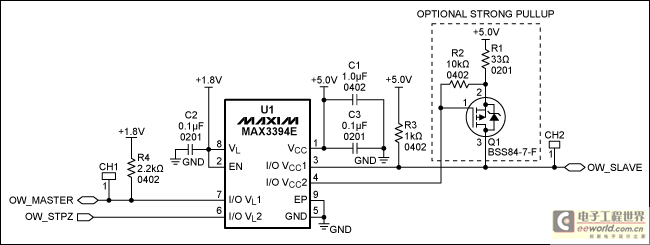
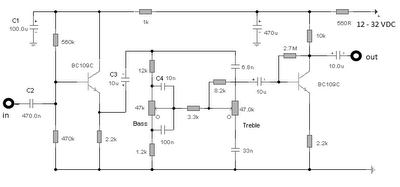
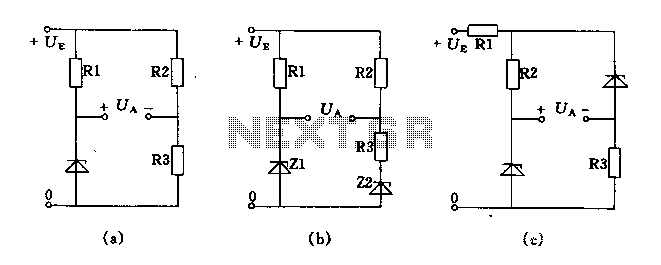
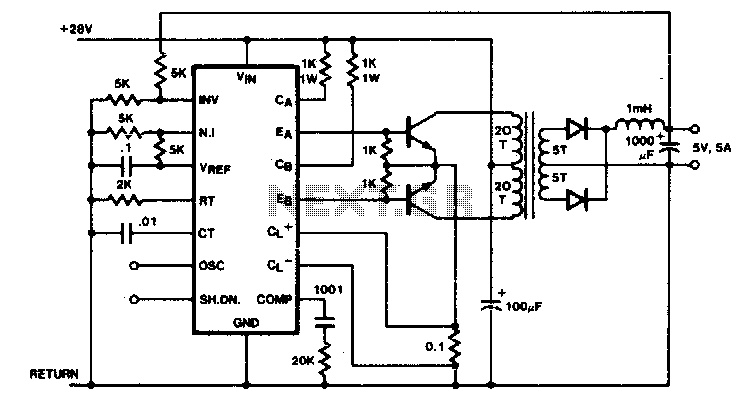
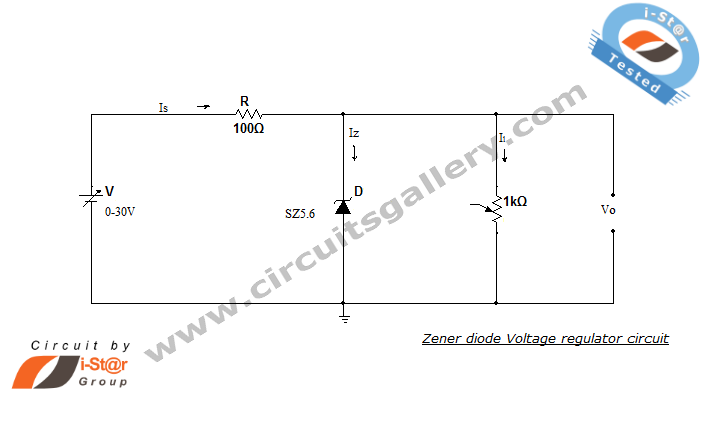
Step down voltage converter 5v with transistor BC337
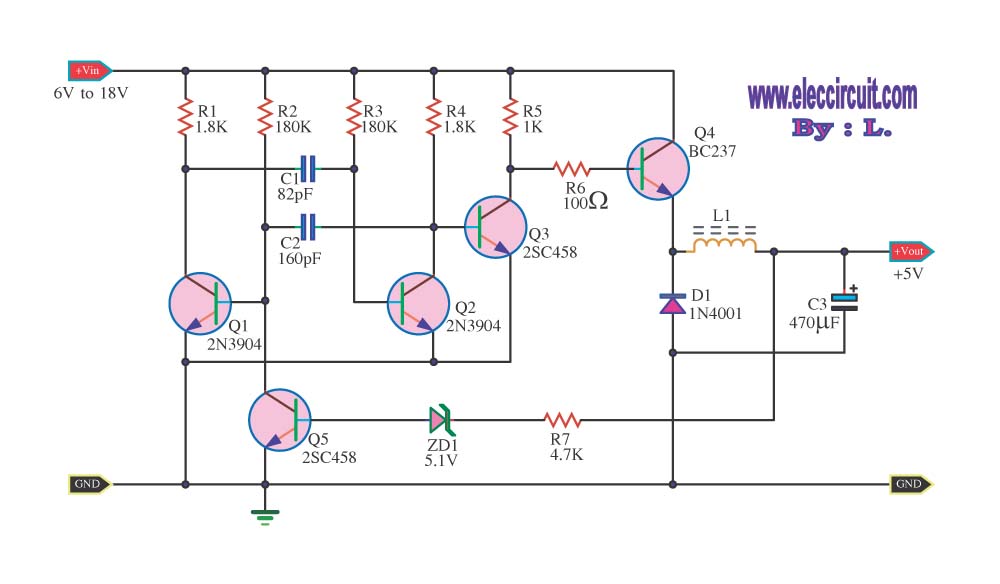
The circuit reduces voltage size or functions as a step-down voltage converter circuit, which is a DC regulated circuit model utilizing a switching converter. This design generates a specific voltage output.
The step-down voltage converter, also known as a buck converter, is an essential circuit in power electronics, allowing for efficient voltage regulation and conversion. This type of converter operates by switching elements, typically a transistor, on and off rapidly to control the energy transfer to the output. The fundamental components include an inductor, a diode, a capacitor, and a control circuit.
In operation, when the switching element is turned on, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch is turned off, the inductor releases the stored energy to the output load through the diode. The output voltage is regulated by adjusting the duty cycle of the switching signal, which is the ratio of the on-time to the total time of the switching cycle.
The design of the circuit must consider several factors, including the input voltage range, the desired output voltage, and the load current requirements. Additionally, the selection of the inductor and capacitor values is critical for ensuring stability and minimizing ripple voltage at the output.
The efficiency of the buck converter is typically high, often exceeding 90%, making it suitable for battery-powered applications where power conservation is essential. Proper thermal management and component selection are crucial to maintain performance and reliability in various operating conditions.
Overall, the step-down voltage converter circuit is a versatile solution for providing regulated DC voltage outputs in a wide range of electronic applications, from consumer electronics to industrial power supplies.The circuit decreases the size voltage or Stepdown Voltage converter circuit be dc regulated circuit model switching converter. The that make voltage output.. 🔗 External reference
The step-down voltage converter, also known as a buck converter, is an essential circuit in power electronics, allowing for efficient voltage regulation and conversion. This type of converter operates by switching elements, typically a transistor, on and off rapidly to control the energy transfer to the output. The fundamental components include an inductor, a diode, a capacitor, and a control circuit.
In operation, when the switching element is turned on, current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch is turned off, the inductor releases the stored energy to the output load through the diode. The output voltage is regulated by adjusting the duty cycle of the switching signal, which is the ratio of the on-time to the total time of the switching cycle.
The design of the circuit must consider several factors, including the input voltage range, the desired output voltage, and the load current requirements. Additionally, the selection of the inductor and capacitor values is critical for ensuring stability and minimizing ripple voltage at the output.
The efficiency of the buck converter is typically high, often exceeding 90%, making it suitable for battery-powered applications where power conservation is essential. Proper thermal management and component selection are crucial to maintain performance and reliability in various operating conditions.
Overall, the step-down voltage converter circuit is a versatile solution for providing regulated DC voltage outputs in a wide range of electronic applications, from consumer electronics to industrial power supplies.The circuit decreases the size voltage or Stepdown Voltage converter circuit be dc regulated circuit model switching converter. The that make voltage output.. 🔗 External reference