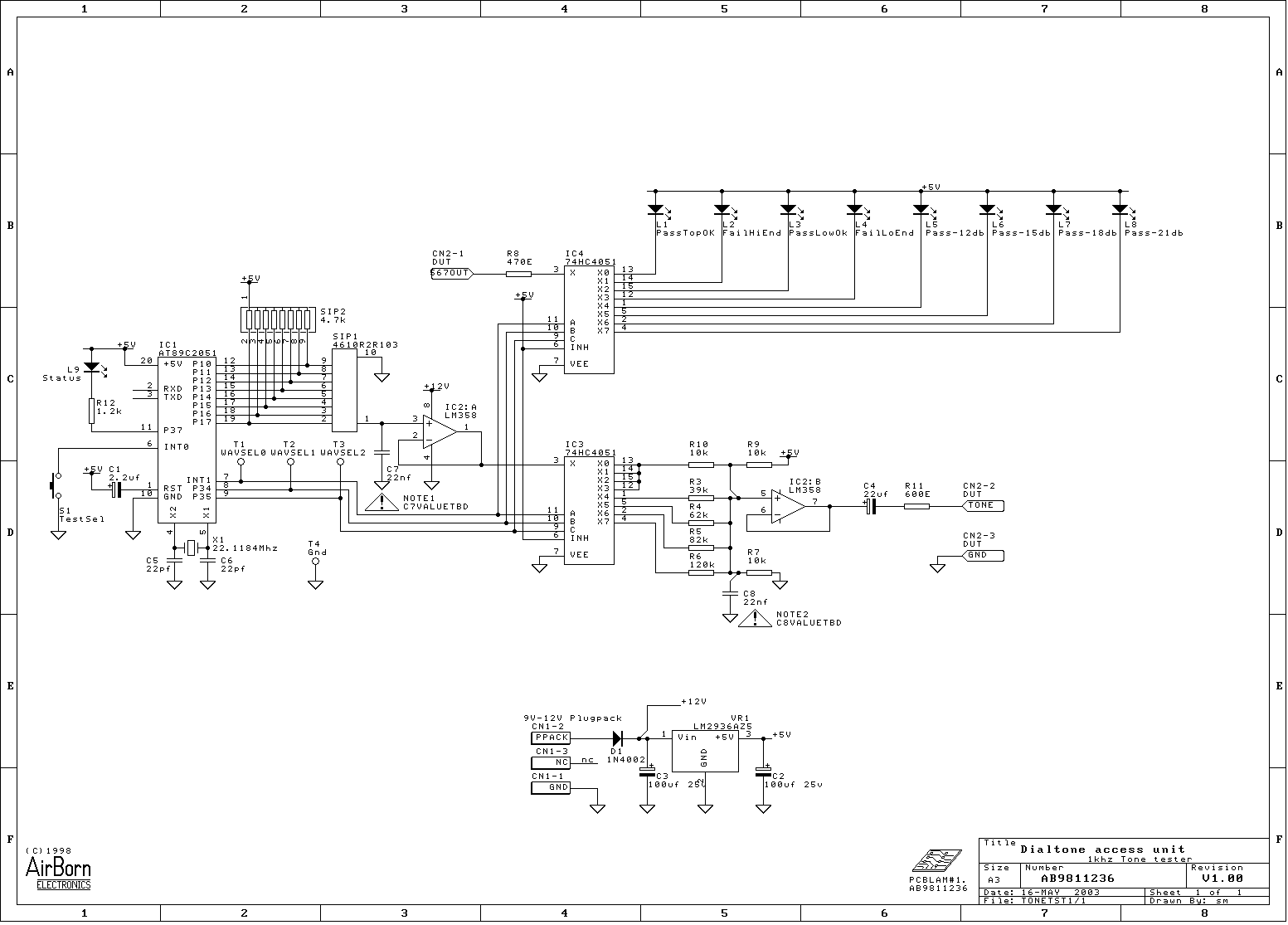
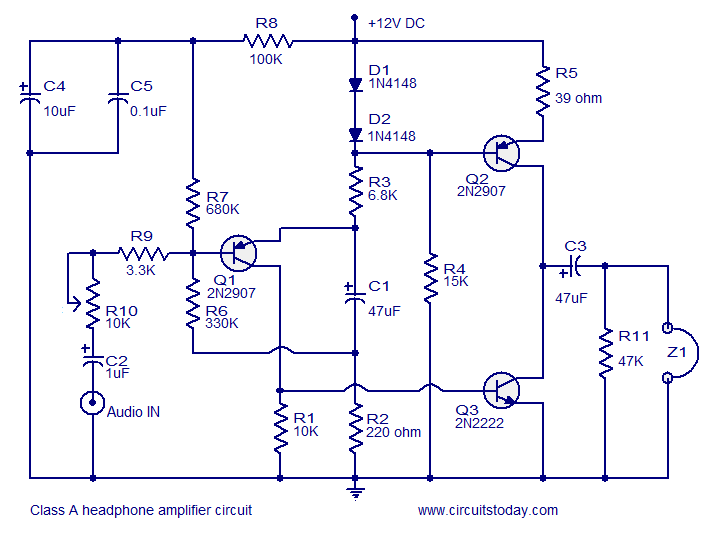
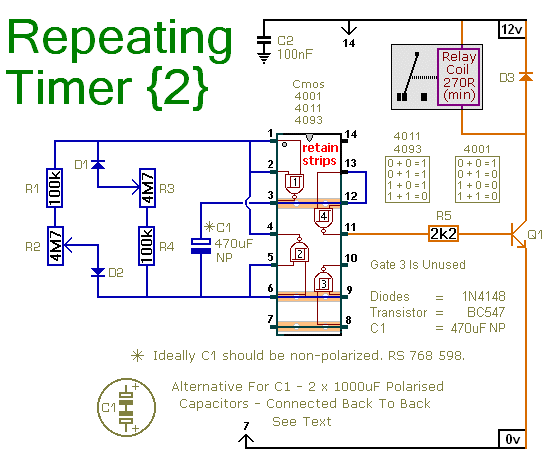
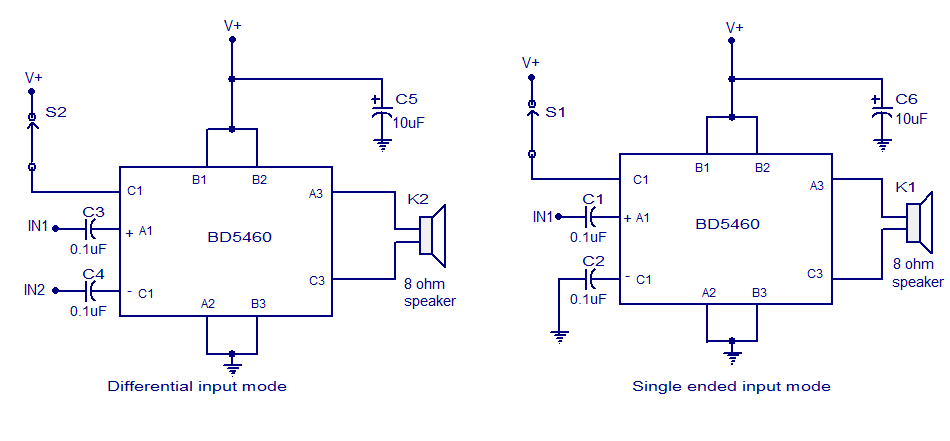
Stereo Balance Meter Circuit
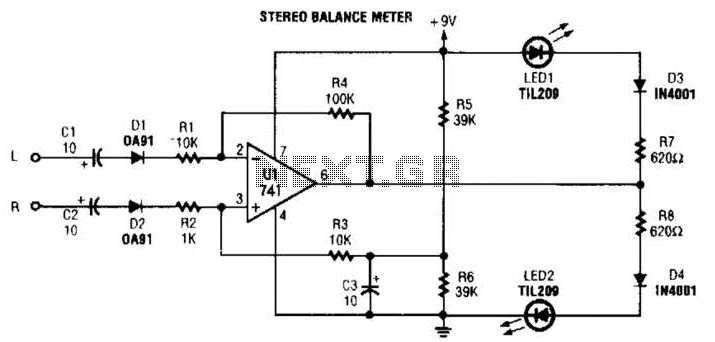
When the L and R signals are equal, no output is present from U1, and pin 6 is at a steady 4.5 V. Unbalanced audio causes the LEDs to vary in brightness, which indicates a difference that corresponds to the imbalance between channels.
The described circuit operates as a signal balance indicator, typically used in audio applications to monitor the equality of left (L) and right (R) audio signals. The operational amplifier U1 plays a crucial role in this setup. When the L and R signals are equal, the output from U1 remains inactive, resulting in no output signal. Under these conditions, pin 6 of the operational amplifier stabilizes at 4.5 V, indicating a balanced state.
In scenarios where the audio signals are unbalanced, the circuit responds by varying the brightness of connected LEDs. This variation in brightness serves as a visual representation of the degree of imbalance between the left and right audio channels. A greater disparity in signal levels will lead to a more pronounced difference in LED brightness, allowing users to easily identify issues in audio balance.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to filter noise and stabilize the voltage levels. Proper selection of these components is essential to ensure the circuit's responsiveness and accuracy in detecting signal imbalances. Furthermore, the use of a dual power supply may be necessary to provide the required voltage levels for optimal operation of the operational amplifier.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective tool for audio engineers and technicians to maintain proper audio balance, enhancing the listening experience by ensuring that both channels are equally represented. When L R signals are equal, no output is present from Ul, and pin 6 is at a steady 4.5 V. Unbalanced audio causes the LEDs to vary in brightness, which causes a difference that corresponds to unbalance between channels.
The described circuit operates as a signal balance indicator, typically used in audio applications to monitor the equality of left (L) and right (R) audio signals. The operational amplifier U1 plays a crucial role in this setup. When the L and R signals are equal, the output from U1 remains inactive, resulting in no output signal. Under these conditions, pin 6 of the operational amplifier stabilizes at 4.5 V, indicating a balanced state.
In scenarios where the audio signals are unbalanced, the circuit responds by varying the brightness of connected LEDs. This variation in brightness serves as a visual representation of the degree of imbalance between the left and right audio channels. A greater disparity in signal levels will lead to a more pronounced difference in LED brightness, allowing users to easily identify issues in audio balance.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to filter noise and stabilize the voltage levels. Proper selection of these components is essential to ensure the circuit's responsiveness and accuracy in detecting signal imbalances. Furthermore, the use of a dual power supply may be necessary to provide the required voltage levels for optimal operation of the operational amplifier.
Overall, this circuit serves as an effective tool for audio engineers and technicians to maintain proper audio balance, enhancing the listening experience by ensuring that both channels are equally represented. When L R signals are equal, no output is present from Ul, and pin 6 is at a steady 4.5 V. Unbalanced audio causes the LEDs to vary in brightness, which causes a difference that corresponds to unbalance between channels.