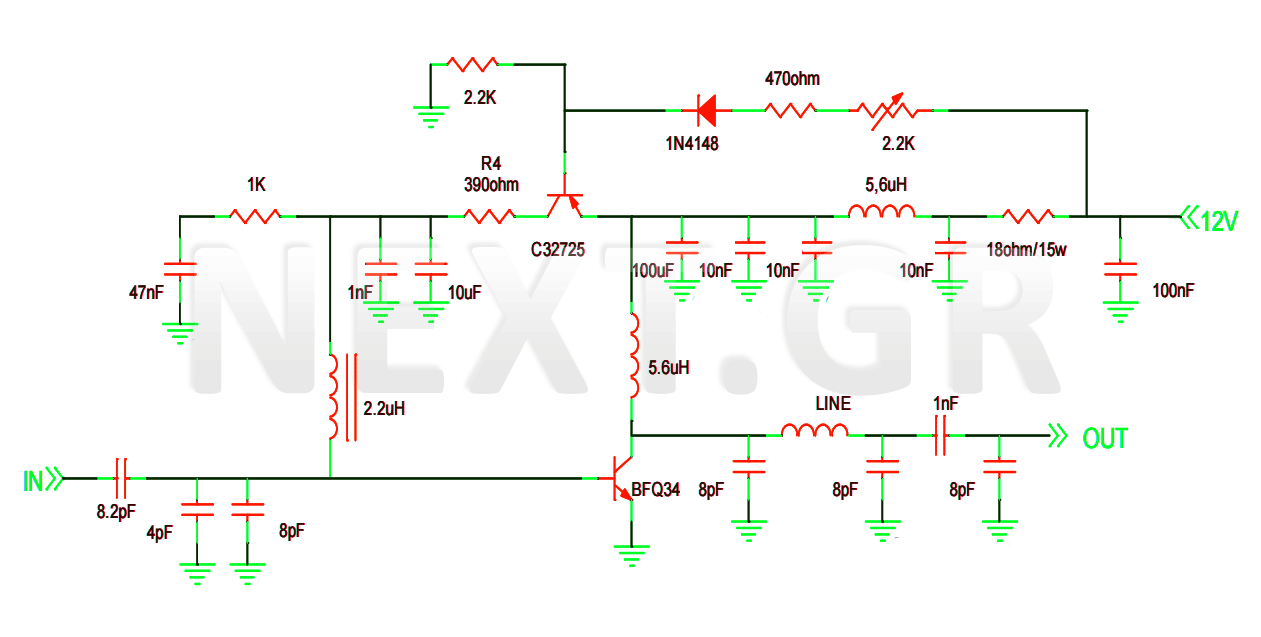
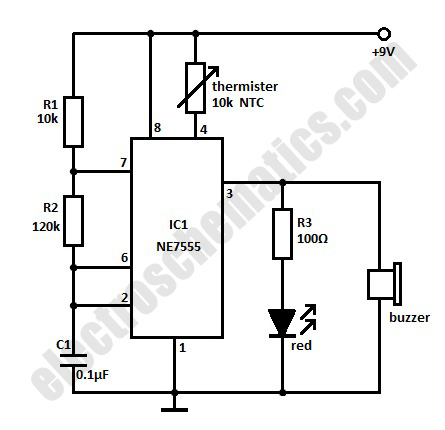
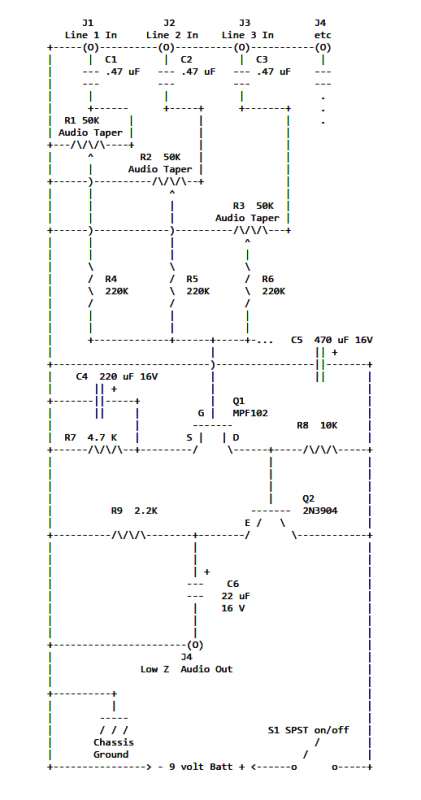
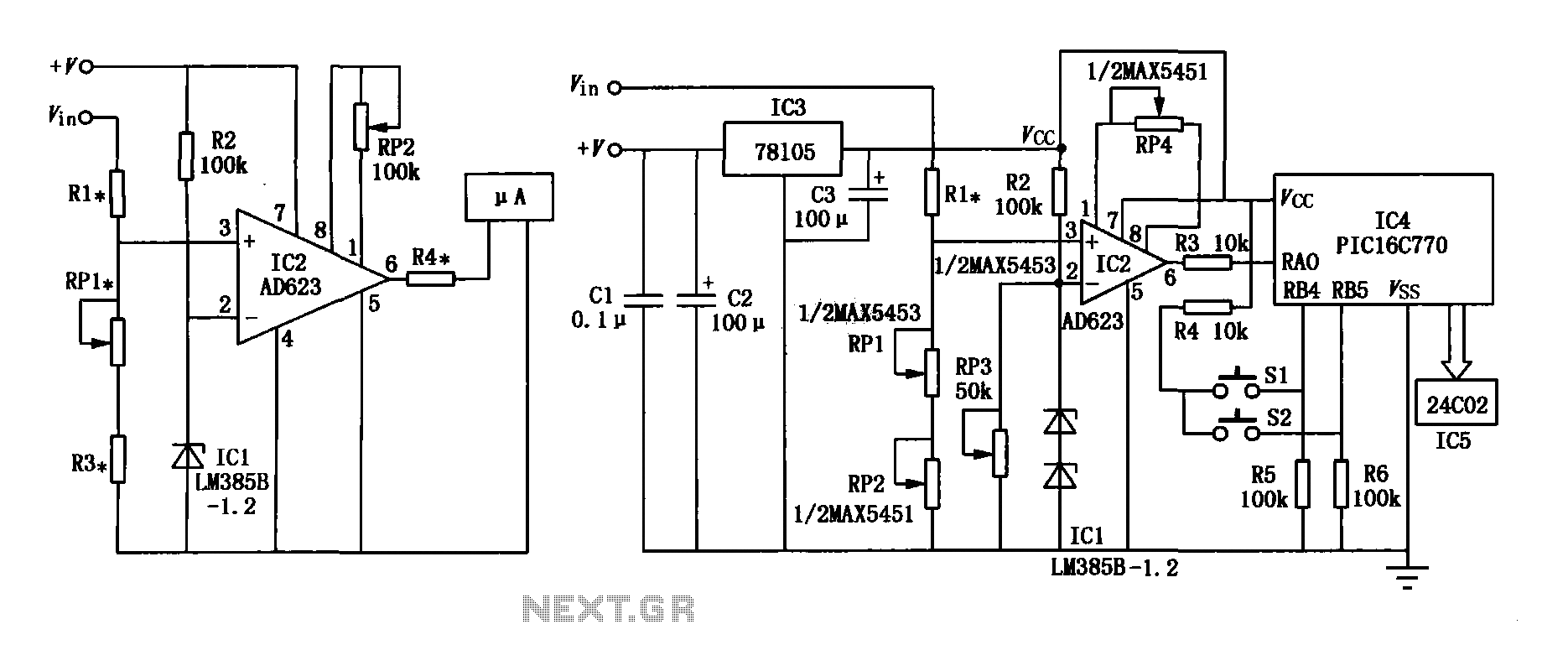
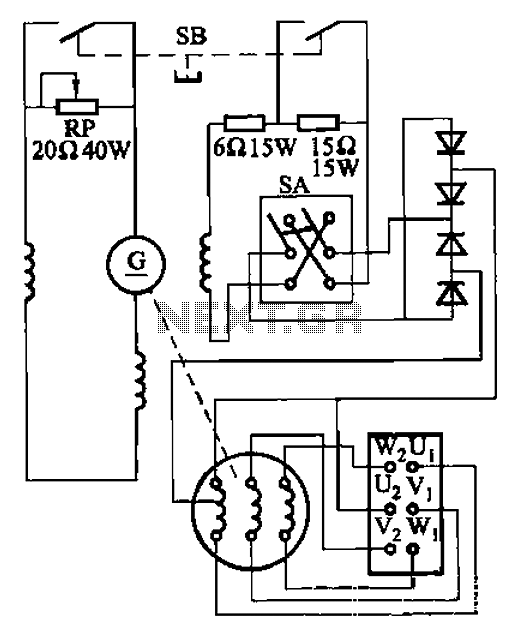
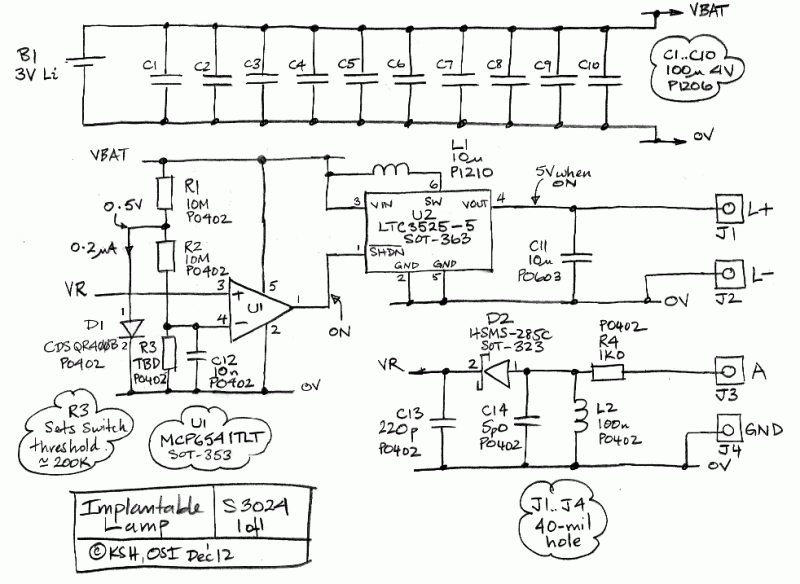
Structure and working principles of various protective circuit diagram e
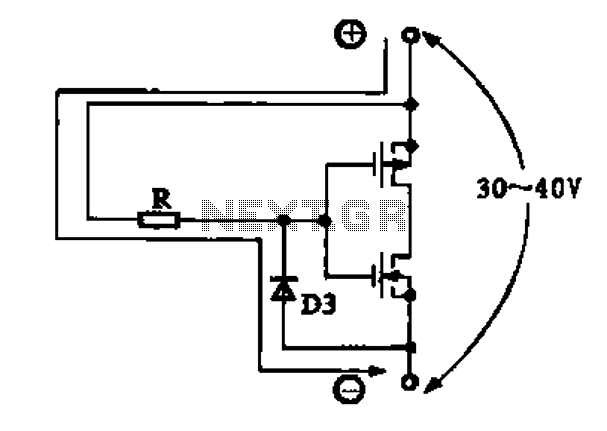
Due to the varying conditions of different input signals, when an abnormal voltage is applied to the pin, protection circuits are established to create a circuit path from the LSI (large scale integration) circuits for internal protection. The structure and principles of this protection circuit are illustrated.
The protection circuit for large scale integration (LSI) devices is essential to safeguard against abnormal voltage levels that can occur due to various input signal conditions. The circuit typically includes a combination of diodes, resistors, and capacitors designed to redirect excess voltage away from sensitive components within the LSI.
When an abnormal voltage is detected at the input pin, the protection circuit activates, providing a low-resistance path to ground or to the power supply rail, thereby preventing damage to the internal circuitry. The diodes are often configured in a clamping arrangement, allowing them to conduct when the voltage exceeds a certain threshold, effectively shunting the excess voltage.
Furthermore, the design of the protection circuit must consider the response time and the maximum voltage levels that the LSI can tolerate. Capacitors may be employed to filter out high-frequency noise, ensuring that transient spikes do not reach the internal circuits. The choice of components is critical; for instance, fast-switching diodes are preferred to minimize delay in response to voltage surges.
In summary, the protection circuit serves as a crucial line of defense for LSI circuits, ensuring their reliability and longevity by managing abnormal voltage conditions effectively. The principles of operation are based on well-established electronic components and configurations that work together to maintain the integrity of the LSI's functionality.Due to the different circumstances of the various input signals, when the pin is applied between the abnormal voltage, protection circuits to form a circuit path from while LSI (large scale integration) circuits internal protection. Structure and principles of its protection circuit is shown
The protection circuit for large scale integration (LSI) devices is essential to safeguard against abnormal voltage levels that can occur due to various input signal conditions. The circuit typically includes a combination of diodes, resistors, and capacitors designed to redirect excess voltage away from sensitive components within the LSI.
When an abnormal voltage is detected at the input pin, the protection circuit activates, providing a low-resistance path to ground or to the power supply rail, thereby preventing damage to the internal circuitry. The diodes are often configured in a clamping arrangement, allowing them to conduct when the voltage exceeds a certain threshold, effectively shunting the excess voltage.
Furthermore, the design of the protection circuit must consider the response time and the maximum voltage levels that the LSI can tolerate. Capacitors may be employed to filter out high-frequency noise, ensuring that transient spikes do not reach the internal circuits. The choice of components is critical; for instance, fast-switching diodes are preferred to minimize delay in response to voltage surges.
In summary, the protection circuit serves as a crucial line of defense for LSI circuits, ensuring their reliability and longevity by managing abnormal voltage conditions effectively. The principles of operation are based on well-established electronic components and configurations that work together to maintain the integrity of the LSI's functionality.Due to the different circumstances of the various input signals, when the pin is applied between the abnormal voltage, protection circuits to form a circuit path from while LSI (large scale integration) circuits internal protection. Structure and principles of its protection circuit is shown