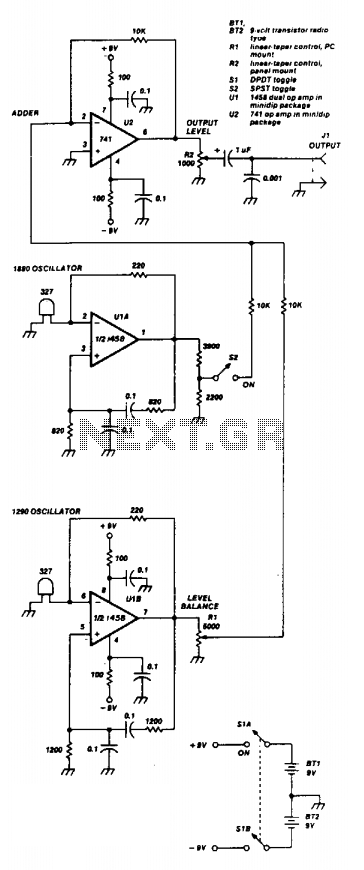
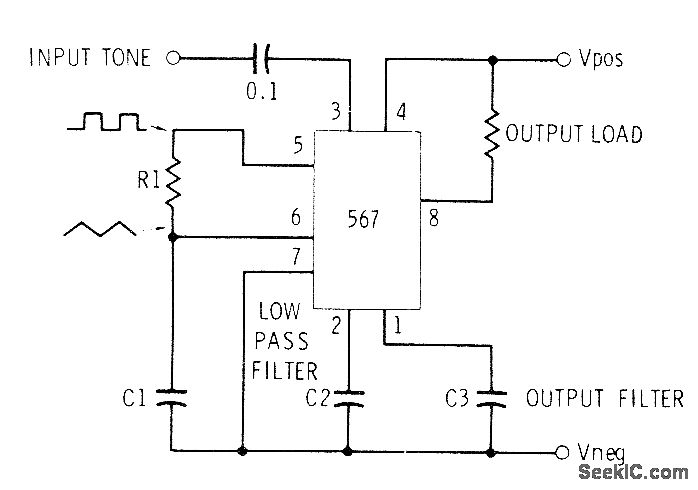
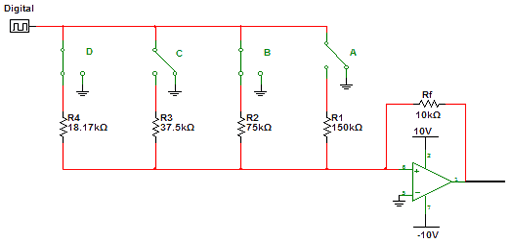
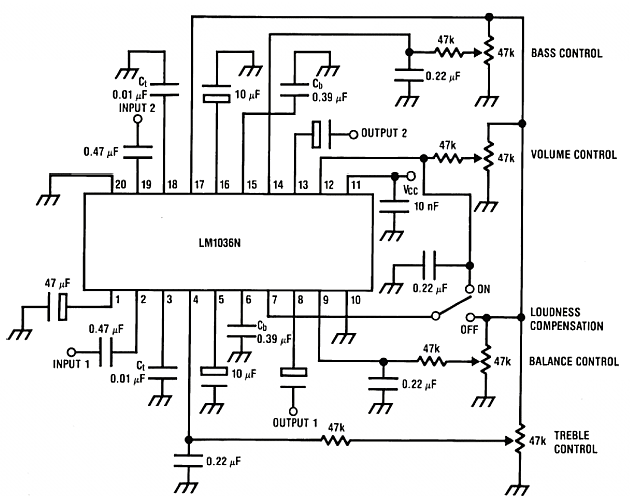
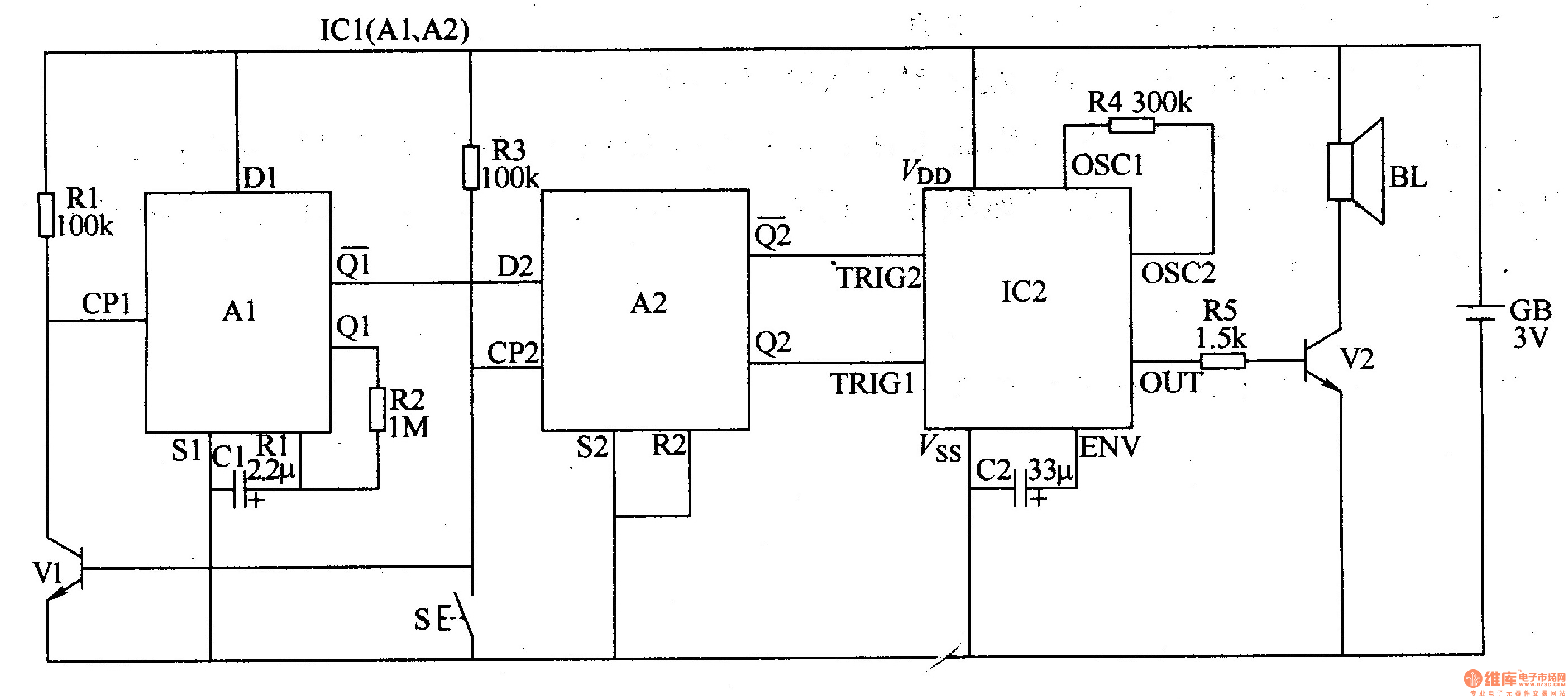
Subaudible tone encoder
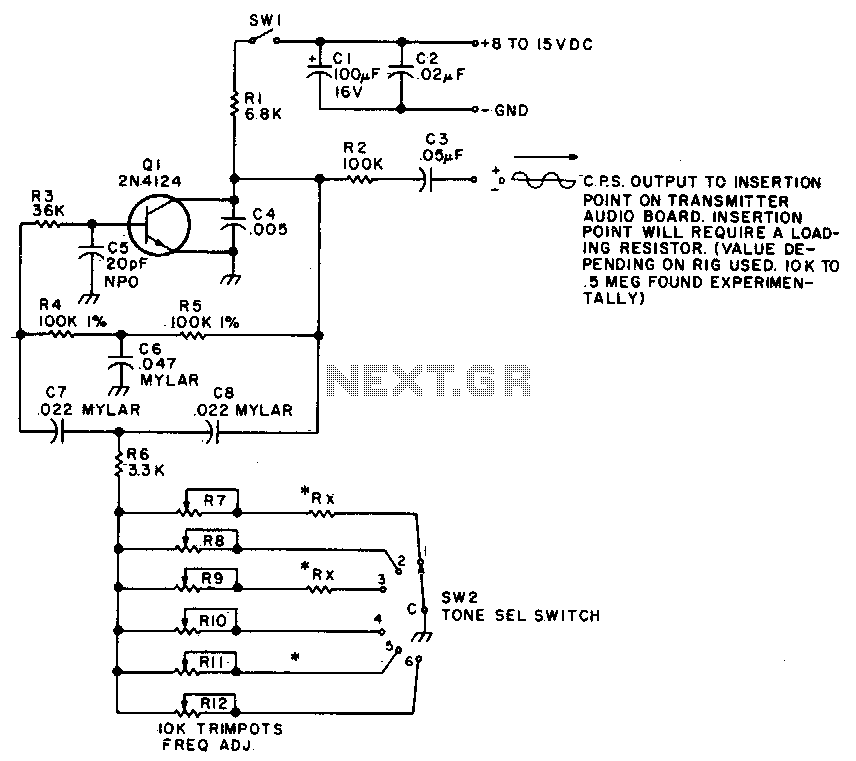
This twin-T oscillator generates six preset subaudible tones ranging from 93 to 170 Hz across three distinct frequency ranges.
The twin-T oscillator is a specific type of electronic oscillator that utilizes a twin-T network configuration to produce audio signals at subaudible frequencies. The circuit typically consists of two T-shaped networks composed of resistors and capacitors, which are configured to create phase shifts necessary for oscillation.
In this design, the oscillator is capable of producing six different frequencies, specifically within the range of 93 Hz to 170 Hz. The selection of these frequencies is achieved through the adjustment of component values or through the use of switches that alter the resistor and capacitor configurations, enabling the user to choose from three distinct frequency ranges.
The operation of the twin-T oscillator is based on the principle of feedback, where a portion of the output signal is fed back into the input in a manner that sustains oscillation. The stability and accuracy of the generated frequencies are influenced by the tolerance of the components used, particularly the resistors and capacitors, as well as the quality of the power supply.
In practical applications, such oscillators can be utilized in sound synthesis, alarm systems, and various audio applications where low-frequency tones are required. The ability to produce multiple preset tones makes this oscillator versatile for different uses, including experimental sound design and audio testing. Proper grounding and shielding are essential in the circuit design to minimize unwanted noise and ensure signal integrity.This twin-T oscillator produces six preset subaudible tones from 93 to 170 Hz in three ranges.
The twin-T oscillator is a specific type of electronic oscillator that utilizes a twin-T network configuration to produce audio signals at subaudible frequencies. The circuit typically consists of two T-shaped networks composed of resistors and capacitors, which are configured to create phase shifts necessary for oscillation.
In this design, the oscillator is capable of producing six different frequencies, specifically within the range of 93 Hz to 170 Hz. The selection of these frequencies is achieved through the adjustment of component values or through the use of switches that alter the resistor and capacitor configurations, enabling the user to choose from three distinct frequency ranges.
The operation of the twin-T oscillator is based on the principle of feedback, where a portion of the output signal is fed back into the input in a manner that sustains oscillation. The stability and accuracy of the generated frequencies are influenced by the tolerance of the components used, particularly the resistors and capacitors, as well as the quality of the power supply.
In practical applications, such oscillators can be utilized in sound synthesis, alarm systems, and various audio applications where low-frequency tones are required. The ability to produce multiple preset tones makes this oscillator versatile for different uses, including experimental sound design and audio testing. Proper grounding and shielding are essential in the circuit design to minimize unwanted noise and ensure signal integrity.This twin-T oscillator produces six preset subaudible tones from 93 to 170 Hz in three ranges.