Switching power supply drive circuit
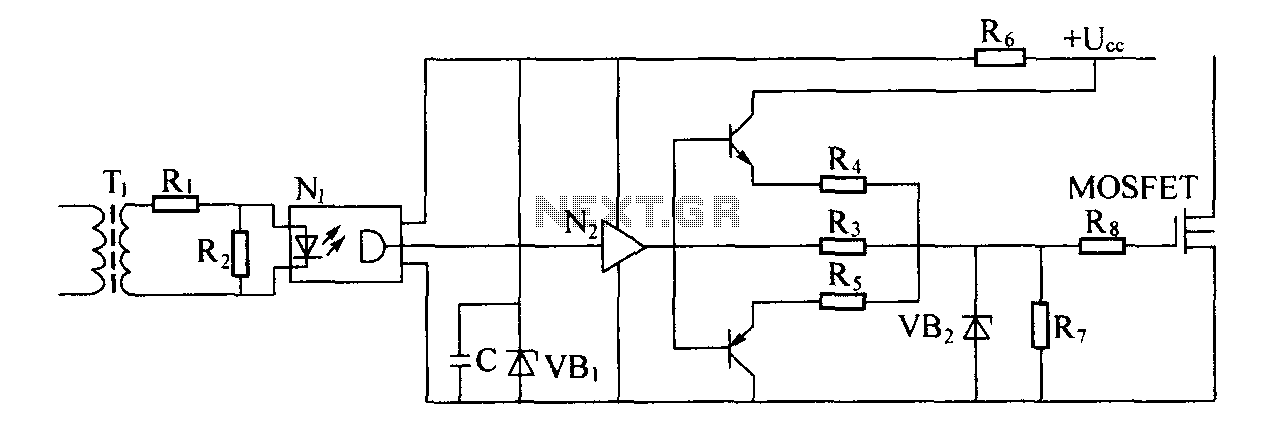
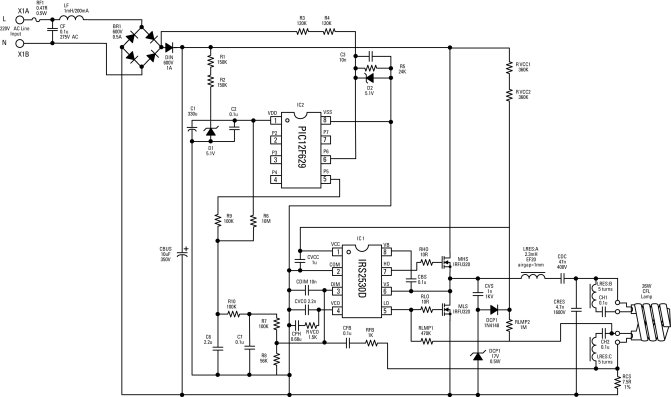
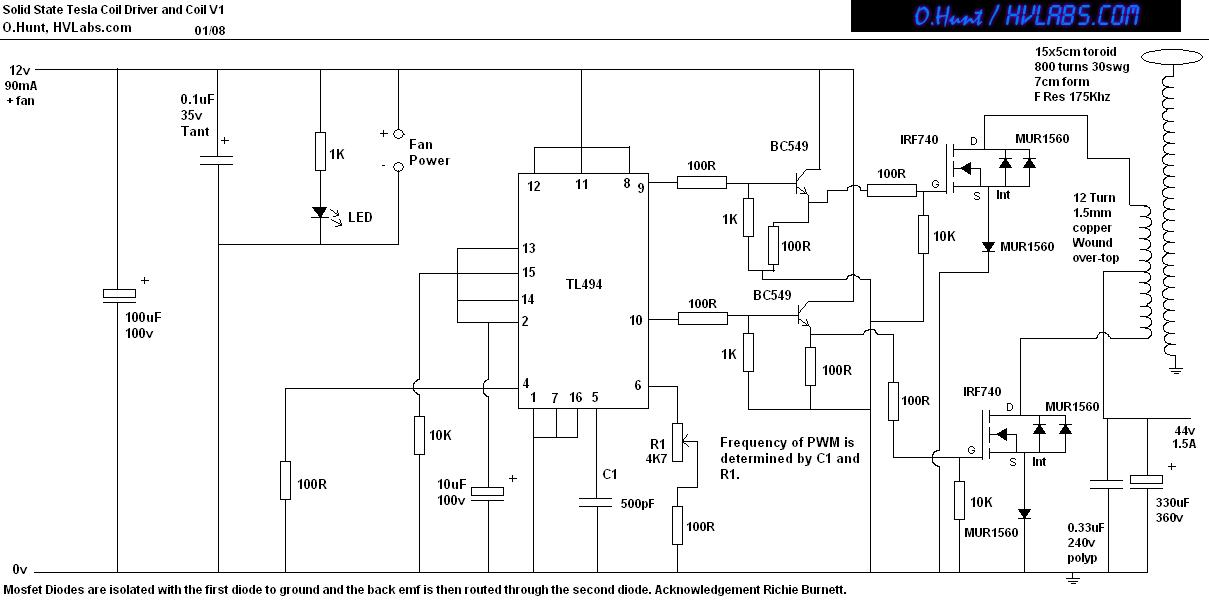
Driver circuit diagram: The primary function of the driver circuit is to serve as a variable width pulse width modulator output power amplifier, providing a drive signal to high voltage power switching devices. The driving circuit typically plays a role in isolation, often utilizing a coupling transformer to achieve isolation between the input and output stages of high-voltage power switching devices. When the power switching device is turned off, reverse bias is applied to facilitate the rapid switching of the device. In conventional applications, a transformer-driven circuit is used for driving MOSFET devices. Considering the effects of leakage inductance and lead inductance, the drive transformer must be designed to accommodate the main MOSFET's large gate-source capacitance (Cg-s), which can complicate high-speed charging and discharging. Therefore, it is common to employ a MOSFET driver that utilizes a transformer with a smaller Cg-s in a totem pole configuration to effectively drive the main MOSFET. The primary input of the drive transformer receives the output signal from the drive signal control circuit, which is then processed through a shaping circuit before being isolated by the transformer. Both transformer isolators and optocouplers provide isolation and anti-interference functions, and after shaping, the totem pole drive circuit activates the main MOSFET.
The driver circuit is integral to high-voltage applications where precise control of power switching is necessary. The variable width pulse width modulation (PWM) allows for fine-tuning of the output power, which is crucial in applications such as motor control, power supplies, and RF amplifiers. The isolation provided by the coupling transformer is essential for protecting the low-voltage control circuitry from high-voltage transients and noise that can occur during switching events.
The design of the drive transformer is critical; it must be optimized for low leakage inductance to ensure that the drive signals maintain their integrity and speed. The transformer should also be capable of handling the required current without saturating, which could lead to distortion in the output signal. Additionally, the choice of MOSFET driver is pivotal; it needs to be capable of delivering the necessary gate drive current quickly to minimize switching losses and ensure that the MOSFET operates efficiently.
In applications where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a concern, the use of optocouplers can provide an additional layer of isolation while also helping to suppress noise. The shaping circuit preceding the transformer ensures that the output signal is clean and well-defined, which is vital for reliable operation of the MOSFET. The totem pole configuration allows for rapid switching by providing both sourcing and sinking capabilities, thus enabling fast transitions that are essential for high-frequency applications.
Overall, this driver circuit design exemplifies the integration of various electronic components to achieve a robust and efficient solution for controlling high-voltage power devices, ensuring performance reliability and safety in demanding operational environments.Driver circuit diagram: The main function of the driving circuit is variable width pulse width controller output power amplifier, as a drive signal to high voltage power switch ing device. Driving circuit generally have a role in isolation, often coupling transformer to achieve the high-voltage power switching devices incentive isolation between the input and output stages and, while both when the power switching device is turned off, reverse bias is applied, to accelerate the device on and off. When the drive MOSFET device, a conventional drive circuit is driven by a transformer to achieve. Taking into account the leakage inductance and lead inductance drive transformer to the main MOSFET having a large Cg-s high-speed charging and discharging cause difficulties, therefore, the usual way is to use a MOSFET driver drive transformer having a smaller Cg-S of the totem type driving circuit then this circuit driven by the main MOSFET.
As shown, the drive transformer primary input is the output signal of the drive signal control circuit, the output after shaping circuit shaping process after isolation transformer. Transformer isolators, optocouplers isolate both have anti-interference function, after shaping by Totem drive circuit drives the main MOSFET tube.
The driver circuit is integral to high-voltage applications where precise control of power switching is necessary. The variable width pulse width modulation (PWM) allows for fine-tuning of the output power, which is crucial in applications such as motor control, power supplies, and RF amplifiers. The isolation provided by the coupling transformer is essential for protecting the low-voltage control circuitry from high-voltage transients and noise that can occur during switching events.
The design of the drive transformer is critical; it must be optimized for low leakage inductance to ensure that the drive signals maintain their integrity and speed. The transformer should also be capable of handling the required current without saturating, which could lead to distortion in the output signal. Additionally, the choice of MOSFET driver is pivotal; it needs to be capable of delivering the necessary gate drive current quickly to minimize switching losses and ensure that the MOSFET operates efficiently.
In applications where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a concern, the use of optocouplers can provide an additional layer of isolation while also helping to suppress noise. The shaping circuit preceding the transformer ensures that the output signal is clean and well-defined, which is vital for reliable operation of the MOSFET. The totem pole configuration allows for rapid switching by providing both sourcing and sinking capabilities, thus enabling fast transitions that are essential for high-frequency applications.
Overall, this driver circuit design exemplifies the integration of various electronic components to achieve a robust and efficient solution for controlling high-voltage power devices, ensuring performance reliability and safety in demanding operational environments.Driver circuit diagram: The main function of the driving circuit is variable width pulse width controller output power amplifier, as a drive signal to high voltage power switch ing device. Driving circuit generally have a role in isolation, often coupling transformer to achieve the high-voltage power switching devices incentive isolation between the input and output stages and, while both when the power switching device is turned off, reverse bias is applied, to accelerate the device on and off. When the drive MOSFET device, a conventional drive circuit is driven by a transformer to achieve. Taking into account the leakage inductance and lead inductance drive transformer to the main MOSFET having a large Cg-s high-speed charging and discharging cause difficulties, therefore, the usual way is to use a MOSFET driver drive transformer having a smaller Cg-S of the totem type driving circuit then this circuit driven by the main MOSFET.
As shown, the drive transformer primary input is the output signal of the drive signal control circuit, the output after shaping circuit shaping process after isolation transformer. Transformer isolators, optocouplers isolate both have anti-interference function, after shaping by Totem drive circuit drives the main MOSFET tube.