SWR Protection Circuit
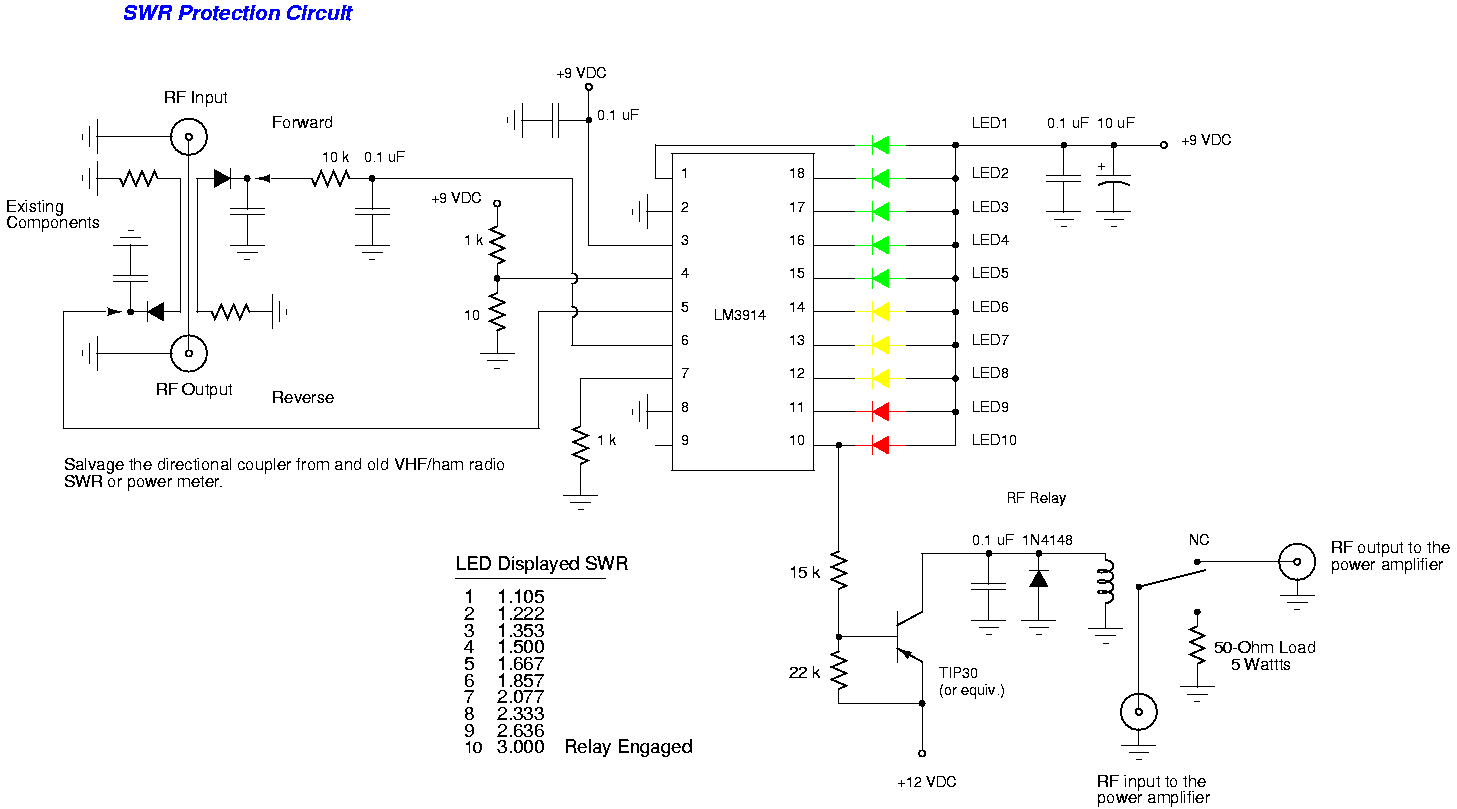
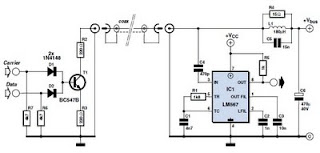
This scheme is a Standing Wave Ratio (SWR) meter, which is relatively simple and can be easily constructed. Once a directional coupler is created, the results will be indicated on the measuring LED meters as a ratio of SWR.
The SWR meter is an essential tool in RF (radio frequency) applications, used to measure the standing wave ratio of a transmission line. The SWR meter typically consists of a directional coupler, which samples the forward and reflected power in the transmission line. The directional coupler is usually constructed using a series of resistors and inductors that create a voltage divider, allowing for the measurement of both forward and reflected signals.
In operation, the SWR meter takes the voltage readings from the directional coupler and processes them to determine the SWR value. The SWR is calculated using the formula: SWR = (1 + |Γ|) / (1 - |Γ|), where |Γ| is the reflection coefficient derived from the measured voltages. The resulting SWR value is then displayed on LED meters, providing a visual representation of the efficiency of the antenna system.
To build the SWR meter, one must first design the directional coupler, ensuring that it can handle the expected power levels without distortion. The coupler should be calibrated to provide accurate readings across the frequency range of interest. Additionally, the LED meters should be selected based on their sensitivity and response time to ensure they accurately reflect the SWR in real-time.
Overall, the SWR meter is a straightforward yet effective device for monitoring antenna performance, helping to optimize transmission efficiency and minimize signal loss. Proper construction and calibration are key to ensuring accurate measurements, making it a valuable asset for amateur radio operators and professionals alike.This scheme is an SWR meter, which is quite simple and easily built. Once you make a directional coupler, the results will be displayed with the measure led meters as a ratio SWR. 🔗 External reference
The SWR meter is an essential tool in RF (radio frequency) applications, used to measure the standing wave ratio of a transmission line. The SWR meter typically consists of a directional coupler, which samples the forward and reflected power in the transmission line. The directional coupler is usually constructed using a series of resistors and inductors that create a voltage divider, allowing for the measurement of both forward and reflected signals.
In operation, the SWR meter takes the voltage readings from the directional coupler and processes them to determine the SWR value. The SWR is calculated using the formula: SWR = (1 + |Γ|) / (1 - |Γ|), where |Γ| is the reflection coefficient derived from the measured voltages. The resulting SWR value is then displayed on LED meters, providing a visual representation of the efficiency of the antenna system.
To build the SWR meter, one must first design the directional coupler, ensuring that it can handle the expected power levels without distortion. The coupler should be calibrated to provide accurate readings across the frequency range of interest. Additionally, the LED meters should be selected based on their sensitivity and response time to ensure they accurately reflect the SWR in real-time.
Overall, the SWR meter is a straightforward yet effective device for monitoring antenna performance, helping to optimize transmission efficiency and minimize signal loss. Proper construction and calibration are key to ensuring accurate measurements, making it a valuable asset for amateur radio operators and professionals alike.This scheme is an SWR meter, which is quite simple and easily built. Once you make a directional coupler, the results will be displayed with the measure led meters as a ratio SWR. 🔗 External reference