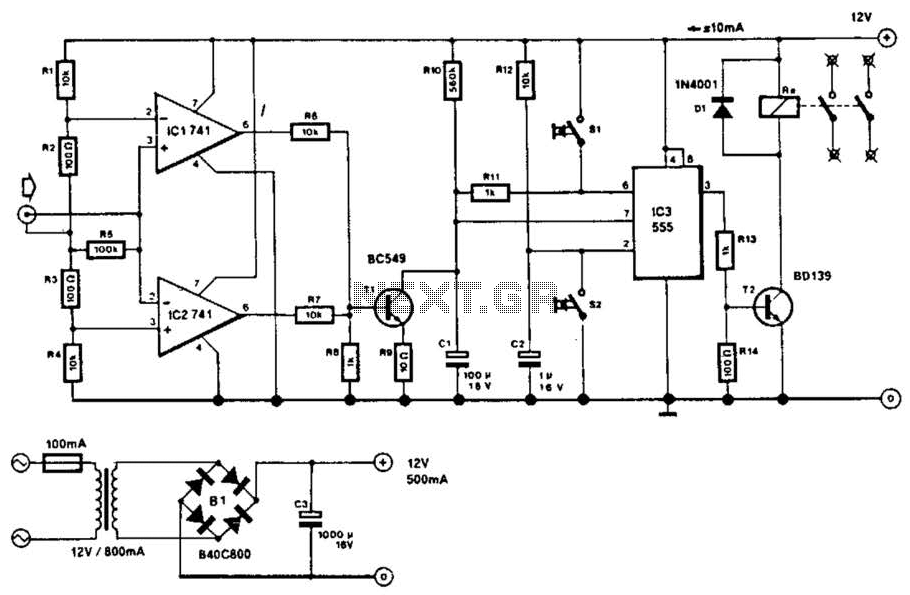
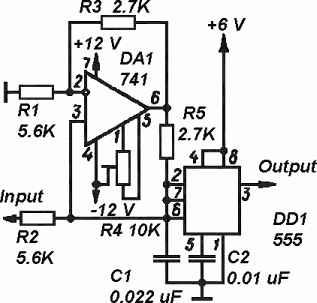
Table circuit voltage electric lines

A voltmeter operates through a measuring mechanism in a specified circuit, utilizing a moving coil in series with additional resistance. The fixed coil is denoted as N1, while the moving coil is designated as N2. The additional resistances are represented as R1 and R2, with U1 and U2 serving to limit the voltage levels. When the additional resistance R exceeds the fixed and moving coil's inductance, the effective current through the coil can be calculated using I = U / R, where U is the RMS measured voltage. The additional resistance is essential for the voltmeter's operation. The deflection angle of the voltmeter is determined by the formula a = KU / R2, where the angle is proportional to the square of the pointer deflection and the measured RMS voltage, resulting in a non-linear scale. This voltmeter can measure both DC and AC voltages, including sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal AC voltages, providing accurate readings.
The voltmeter described functions by integrating a moving coil mechanism within a circuit, allowing for precise voltage measurements. The fixed coil (N1) and the moving coil (N2) are configured in series with additional resistances (R1 and R2) to optimize the measurement range and accuracy. The additional resistance plays a crucial role in defining the current flowing through the moving coil, represented by the equation I = U / R, where U is the root mean square (RMS) voltage being measured.
The relationship between the deflection angle (a) of the voltmeter's pointer and the measured voltage is governed by the equation a = KU / R2, where K is a constant that relates to the design of the voltmeter. The pointer's deflection is not linear with respect to the voltage due to the square relationship, which necessitates a non-linear scale for accurate readings across a range of voltages.
This voltmeter is capable of measuring both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) voltages. It can accurately gauge sinusoidal AC voltages, as well as non-sinusoidal AC voltages, ensuring versatility in various applications. The design considerations include ensuring that the additional resistance is appropriately selected to accommodate the inductive properties of the coils, thus maintaining measurement integrity across different voltage levels. The voltmeter's construction requires careful calibration to ensure that the scale reflects the non-linear nature of the voltage-to-deflection relationship, allowing users to interpret readings accurately.Voltmeter by the measuring mechanism in a given circle and moving coil in series to configure certain additional resistance. Nl is constant circle, N2 for the moving coil, R., Rz is additional resistance, U1, U2 to limit the amount of voltage.
When the additional resistance R is greater than the fixed and movable solid inductance coil, the coil is fixed and moving coil current effective value I = U / R wherein U- RMS measured voltage; additional resistance Nepal a voltmeter. Voltmeter deflection angle using the formula a = KU / Rz obtained, visible, proportional to the square pointer deflection angle and the measured RMS voltage, so the scale is not uniform indexing.
Similarly, the electric line voltage meter can measure the DC voltage and AC voltage sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal AC voltage has a valid value. .
The voltmeter described functions by integrating a moving coil mechanism within a circuit, allowing for precise voltage measurements. The fixed coil (N1) and the moving coil (N2) are configured in series with additional resistances (R1 and R2) to optimize the measurement range and accuracy. The additional resistance plays a crucial role in defining the current flowing through the moving coil, represented by the equation I = U / R, where U is the root mean square (RMS) voltage being measured.
The relationship between the deflection angle (a) of the voltmeter's pointer and the measured voltage is governed by the equation a = KU / R2, where K is a constant that relates to the design of the voltmeter. The pointer's deflection is not linear with respect to the voltage due to the square relationship, which necessitates a non-linear scale for accurate readings across a range of voltages.
This voltmeter is capable of measuring both direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) voltages. It can accurately gauge sinusoidal AC voltages, as well as non-sinusoidal AC voltages, ensuring versatility in various applications. The design considerations include ensuring that the additional resistance is appropriately selected to accommodate the inductive properties of the coils, thus maintaining measurement integrity across different voltage levels. The voltmeter's construction requires careful calibration to ensure that the scale reflects the non-linear nature of the voltage-to-deflection relationship, allowing users to interpret readings accurately.Voltmeter by the measuring mechanism in a given circle and moving coil in series to configure certain additional resistance. Nl is constant circle, N2 for the moving coil, R., Rz is additional resistance, U1, U2 to limit the amount of voltage.
When the additional resistance R is greater than the fixed and movable solid inductance coil, the coil is fixed and moving coil current effective value I = U / R wherein U- RMS measured voltage; additional resistance Nepal a voltmeter. Voltmeter deflection angle using the formula a = KU / Rz obtained, visible, proportional to the square pointer deflection angle and the measured RMS voltage, so the scale is not uniform indexing.
Similarly, the electric line voltage meter can measure the DC voltage and AC voltage sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal AC voltage has a valid value. .