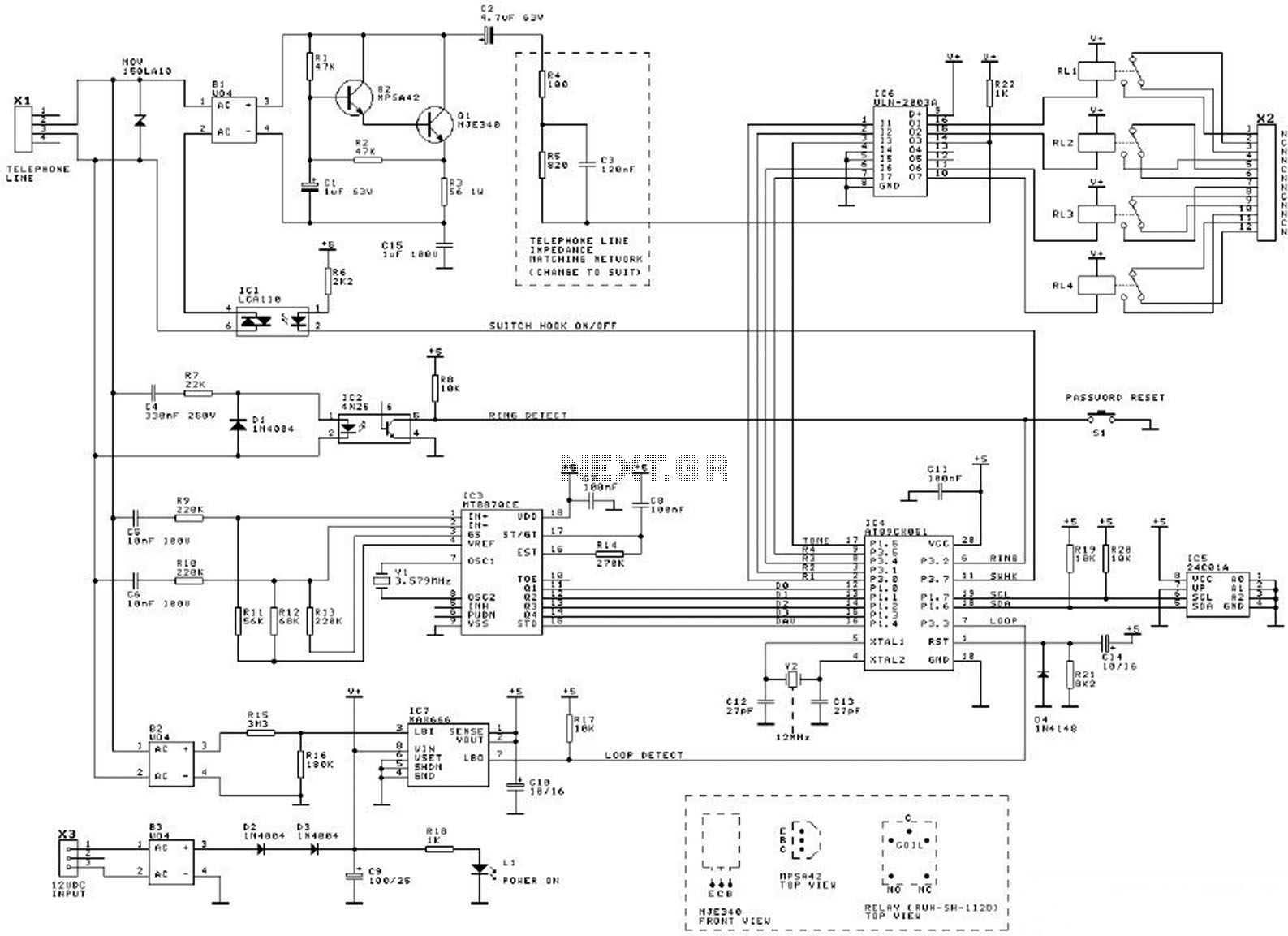
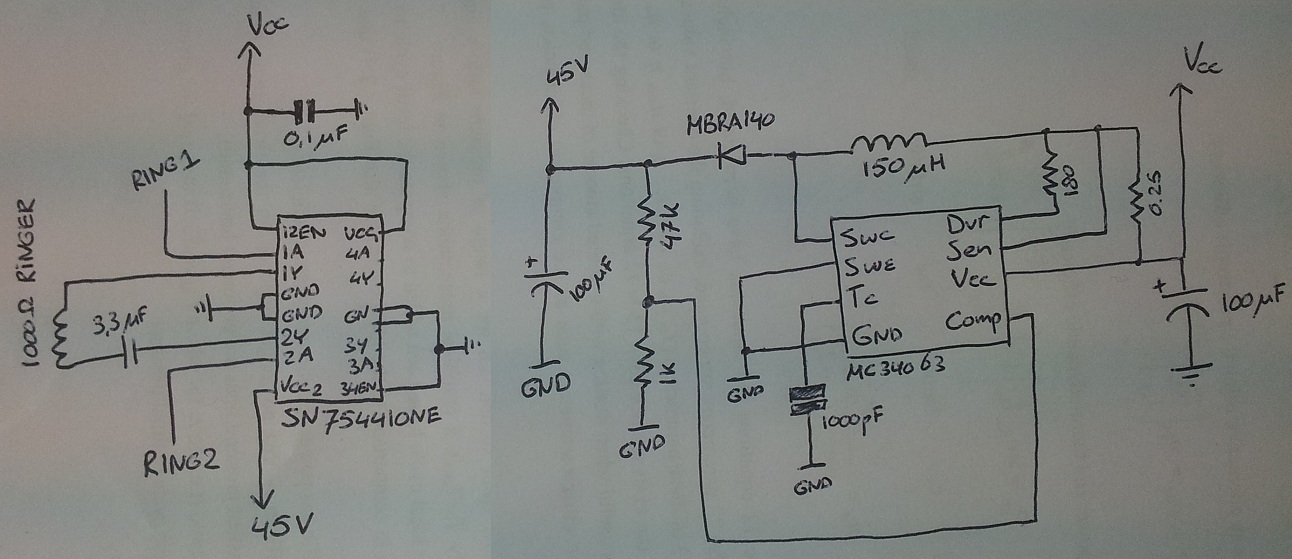
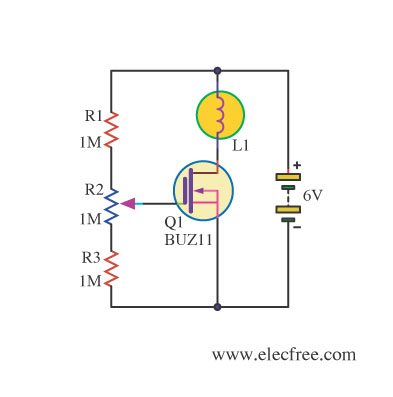
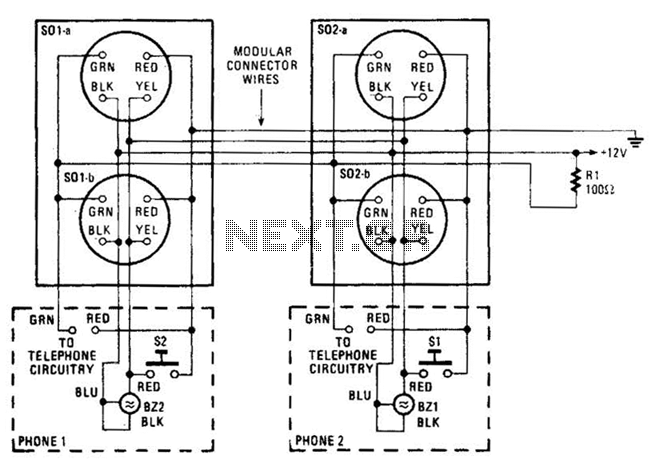
Telephone line monitors
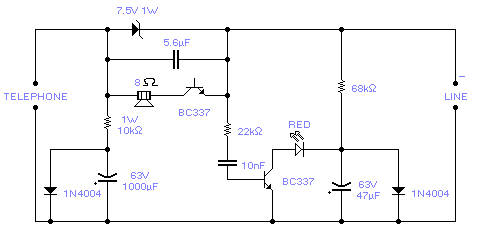
This circuit is designed to detect tampering with a telephone line. It identifies if another telephone is connected, if there is a short circuit, or if the line is open. An audio alert and a flashing LED indicate the current status. During normal conversations, the speaker is effectively muted to maintain privacy, with the LED flashing intermittently. The circuit operates without a battery, drawing power directly from the telephone line. The transistors are configured in a reverse-biased manner, functioning as oscillators. The 2N2222A transistor may be used as an alternative, although it has not been tested. This monitor is intended for use with analog telephone lines. Care should be taken regarding the input line's polarity; while the circuit is resistant to polarity reversal, incorrect polarity will prevent proper operation.
This telephone line monitoring circuit serves as a practical tool for detecting unauthorized connections or faults in an analog telephone system. The core functionality hinges on the use of transistors configured as oscillators, which are sensitive to changes in the line's electrical characteristics. When another device is connected to the line, or if a fault occurs, the circuit's output changes, triggering an audio alert and an LED indicator.
The circuit can be implemented using a basic transistor configuration, where the transistors are arranged in a way that allows them to oscillate when the line is in a normal state. When a fault or an unauthorized connection is detected, the oscillation frequency changes, which can be translated into a sound signal via a small speaker. The LED is connected in such a way that it flashes in response to these changes, providing a visual indication of the line's status.
Powering the circuit directly from the telephone line eliminates the need for an external power source, making it a convenient solution for monitoring telephone line integrity. The design should ensure that the components used can handle the voltage and current levels present in standard telephone lines. Additionally, the circuit should incorporate protection mechanisms to safeguard the components from voltage spikes or other anomalies that may occur on the line.
For implementation, it is crucial to ensure that the polarity of the telephone line is correctly observed, as reversing the connections may lead to malfunction. The circuit can be housed in a compact enclosure, allowing for easy installation and accessibility. Overall, this monitoring circuit provides an effective means of ensuring the security and reliability of telephone communications.If you feel that somebody is tampering with your telephone line you might find this little circuit useful. It detects if there is another telephone connected to the line, if there is a short or an open line. Sound and a flashing light will tell you which is the current situation. The speaker is practically cut out during a normal conversation thus preserving privacy, only the LED will
flash occasionally. The circuit does not require any battery and takes the supply from the telephone line itself. The transistors used are wired in a reversed biased fashion thus behaving as oscillators. You might try the 2N2222A as an alternative (not tested). This monitor is, of course, suitable only for analogue lines. Watch the polarity of the input line: the circuit will not be damaged by a polarity reversal but it will not operate correctly. 🔗 External reference
This telephone line monitoring circuit serves as a practical tool for detecting unauthorized connections or faults in an analog telephone system. The core functionality hinges on the use of transistors configured as oscillators, which are sensitive to changes in the line's electrical characteristics. When another device is connected to the line, or if a fault occurs, the circuit's output changes, triggering an audio alert and an LED indicator.
The circuit can be implemented using a basic transistor configuration, where the transistors are arranged in a way that allows them to oscillate when the line is in a normal state. When a fault or an unauthorized connection is detected, the oscillation frequency changes, which can be translated into a sound signal via a small speaker. The LED is connected in such a way that it flashes in response to these changes, providing a visual indication of the line's status.
Powering the circuit directly from the telephone line eliminates the need for an external power source, making it a convenient solution for monitoring telephone line integrity. The design should ensure that the components used can handle the voltage and current levels present in standard telephone lines. Additionally, the circuit should incorporate protection mechanisms to safeguard the components from voltage spikes or other anomalies that may occur on the line.
For implementation, it is crucial to ensure that the polarity of the telephone line is correctly observed, as reversing the connections may lead to malfunction. The circuit can be housed in a compact enclosure, allowing for easy installation and accessibility. Overall, this monitoring circuit provides an effective means of ensuring the security and reliability of telephone communications.If you feel that somebody is tampering with your telephone line you might find this little circuit useful. It detects if there is another telephone connected to the line, if there is a short or an open line. Sound and a flashing light will tell you which is the current situation. The speaker is practically cut out during a normal conversation thus preserving privacy, only the LED will
flash occasionally. The circuit does not require any battery and takes the supply from the telephone line itself. The transistors used are wired in a reversed biased fashion thus behaving as oscillators. You might try the 2N2222A as an alternative (not tested). This monitor is, of course, suitable only for analogue lines. Watch the polarity of the input line: the circuit will not be damaged by a polarity reversal but it will not operate correctly. 🔗 External reference