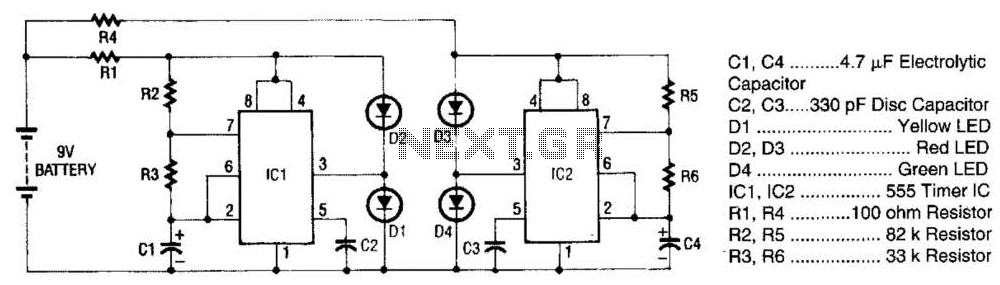
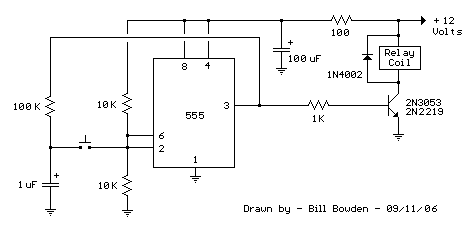
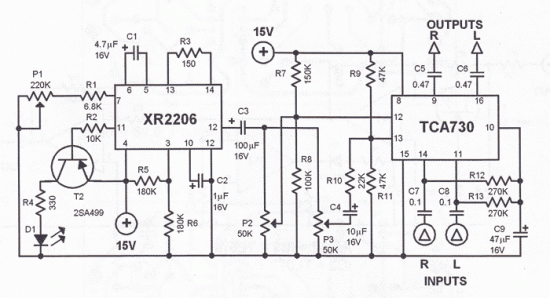
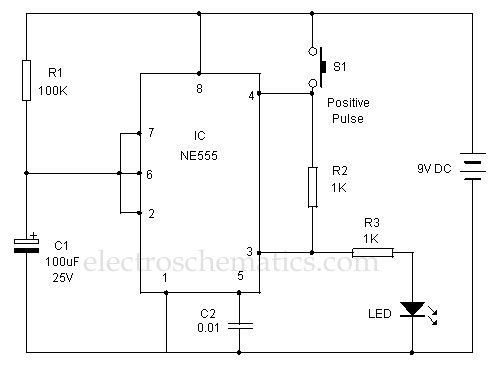
Telephone relay circuit
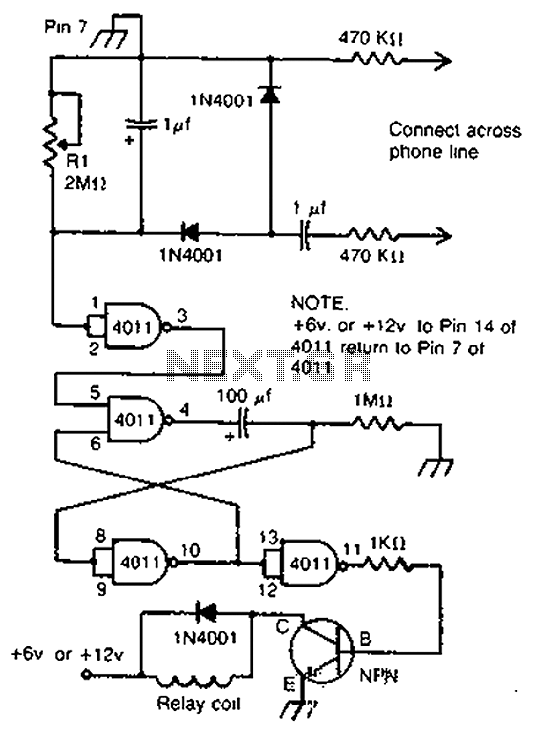
By cross-connecting the telephone ringing circuit, when the phone rings, the circuit activates the relay. It utilizes a delay in contact to drive various devices such as bells, sirens, buzzers, or lights.
The telephone ringing circuit is designed to detect the ringing signal from a telephone line and use this signal to control a relay. The relay acts as a switch that can activate other devices, providing an alert or notification when a call is incoming. The circuit typically includes a resistor-capacitor (RC) delay network that introduces a time delay before the relay is energized. This delay allows for a smooth transition and prevents false triggering due to transient signals.
In the schematic, the telephone line is connected to a detection circuit that identifies the ringing voltage, which is typically around 90 volts AC at 20 Hz. This detection circuit may consist of a transformer to step down the voltage and rectify it to a suitable level for triggering the relay. The relay contacts are rated to handle the load of the connected devices, which can include various audible or visual alert systems such as bells, sirens, buzzers, or lights.
Furthermore, the circuit may incorporate additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, ensuring that voltage spikes generated when the relay coil is de-energized do not damage the circuit. An LED indicator can also be included to provide a visual indication of the circuit's operation, illuminating when the relay is active.
Overall, this telephone ringing circuit is a versatile solution for alerting individuals of incoming calls, enhancing communication in various environments, including homes, offices, and industrial settings. Proper design and component selection are crucial for ensuring reliable performance and longevity of the circuit. By cross-connect telephone ringing circuit, when the phone rang, the circuit closes the relay. It uses the delay in contact, thus to drive any bells, sirens, buzzers or lights.
The telephone ringing circuit is designed to detect the ringing signal from a telephone line and use this signal to control a relay. The relay acts as a switch that can activate other devices, providing an alert or notification when a call is incoming. The circuit typically includes a resistor-capacitor (RC) delay network that introduces a time delay before the relay is energized. This delay allows for a smooth transition and prevents false triggering due to transient signals.
In the schematic, the telephone line is connected to a detection circuit that identifies the ringing voltage, which is typically around 90 volts AC at 20 Hz. This detection circuit may consist of a transformer to step down the voltage and rectify it to a suitable level for triggering the relay. The relay contacts are rated to handle the load of the connected devices, which can include various audible or visual alert systems such as bells, sirens, buzzers, or lights.
Furthermore, the circuit may incorporate additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, ensuring that voltage spikes generated when the relay coil is de-energized do not damage the circuit. An LED indicator can also be included to provide a visual indication of the circuit's operation, illuminating when the relay is active.
Overall, this telephone ringing circuit is a versatile solution for alerting individuals of incoming calls, enhancing communication in various environments, including homes, offices, and industrial settings. Proper design and component selection are crucial for ensuring reliable performance and longevity of the circuit. By cross-connect telephone ringing circuit, when the phone rang, the circuit closes the relay. It uses the delay in contact, thus to drive any bells, sirens, buzzers or lights.