temp sensor circuit and code
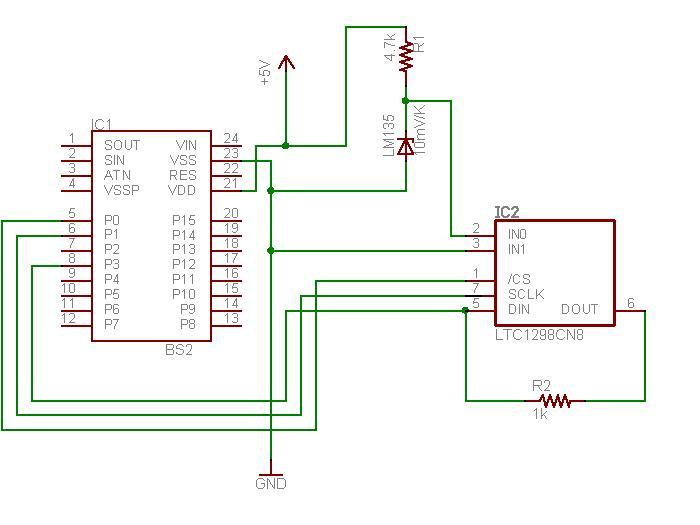
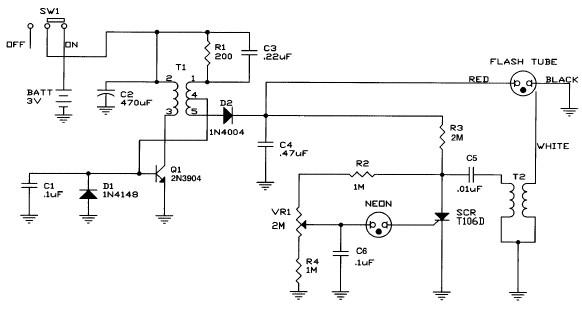
The schematic diagram illustrates the temperature sensor that is set to be launched. The LM135 sensor, functioning as a Zener diode, is connected via a foot-long cord to the circuit through a plug. This design allows the sensor to be positioned outside the payload housing while the electronic components remain securely housed.
The circuit design features the LM135 temperature sensor, which is a precision temperature sensor with an output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature in degrees Kelvin. The sensor operates by generating a reference voltage, which can be utilized to accurately measure temperature changes.
The foot-long cord serves as an extension, allowing the sensor to be placed in an environment where accurate temperature readings are essential, while the main electronic circuitry is protected within the payload housing. This separation not only ensures the safety of sensitive components but also enhances the accuracy of temperature measurements by reducing the influence of heat generated by the electronics on the sensor.
The plug connection is designed for ease of assembly and disassembly, facilitating maintenance and replacement of the sensor if necessary. The circuit may include additional components such as resistors for biasing, capacitors for noise filtering, and possibly an operational amplifier to condition the signal from the LM135 before further processing or transmission.
Overall, the schematic provides a clear and functional design for integrating a temperature sensor into a larger system, emphasizing both the practical application and the technical specifications required for optimal performance.Here is the schematic diagram of the temperature sensor we will be launching. The Zener diode is actually the LM135 sensor which is attached to the end of a foot-long cord and connects to the circuit through a plug. That way the sensor can be outside the payload housing while the electronics will be snug.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design features the LM135 temperature sensor, which is a precision temperature sensor with an output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature in degrees Kelvin. The sensor operates by generating a reference voltage, which can be utilized to accurately measure temperature changes.
The foot-long cord serves as an extension, allowing the sensor to be placed in an environment where accurate temperature readings are essential, while the main electronic circuitry is protected within the payload housing. This separation not only ensures the safety of sensitive components but also enhances the accuracy of temperature measurements by reducing the influence of heat generated by the electronics on the sensor.
The plug connection is designed for ease of assembly and disassembly, facilitating maintenance and replacement of the sensor if necessary. The circuit may include additional components such as resistors for biasing, capacitors for noise filtering, and possibly an operational amplifier to condition the signal from the LM135 before further processing or transmission.
Overall, the schematic provides a clear and functional design for integrating a temperature sensor into a larger system, emphasizing both the practical application and the technical specifications required for optimal performance.Here is the schematic diagram of the temperature sensor we will be launching. The Zener diode is actually the LM135 sensor which is attached to the end of a foot-long cord and connects to the circuit through a plug. That way the sensor can be outside the payload housing while the electronics will be snug.. 🔗 External reference