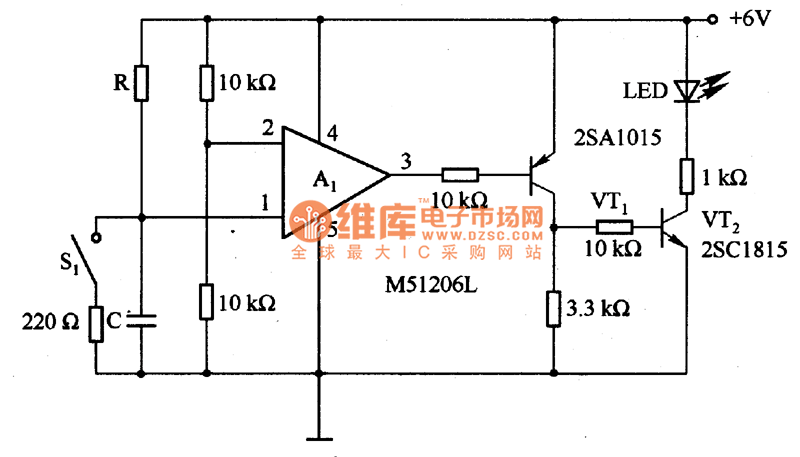
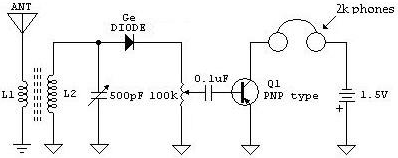
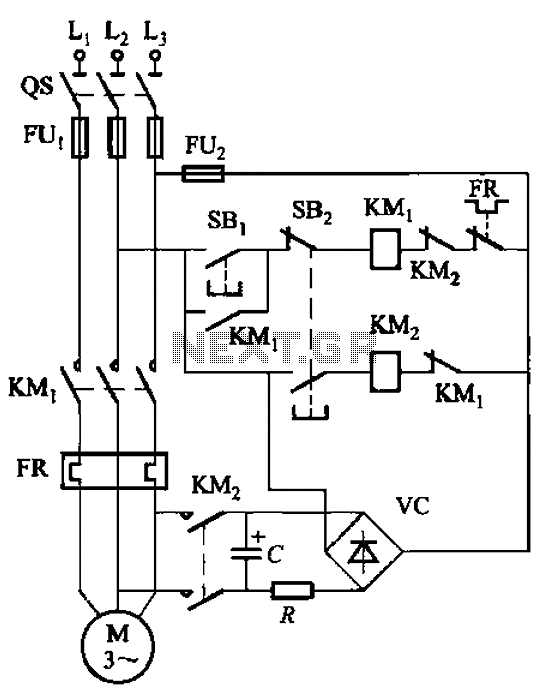
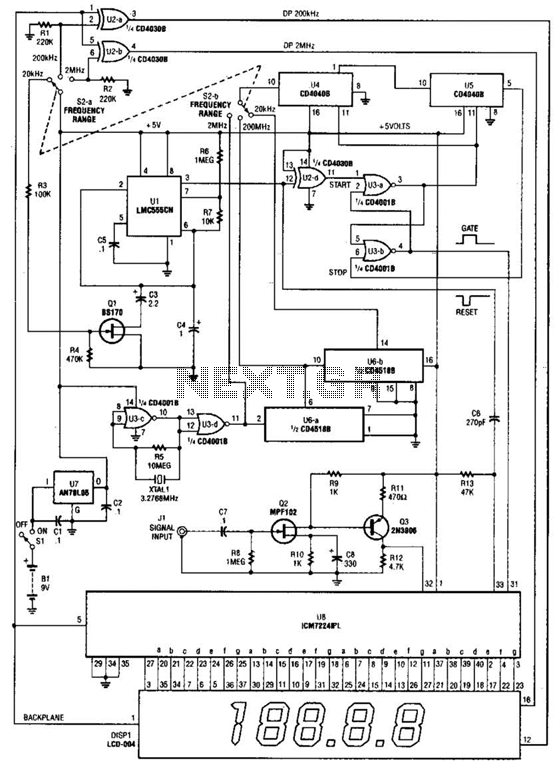
Alternately flashing lights chain multiple sets of high-power circuit 2
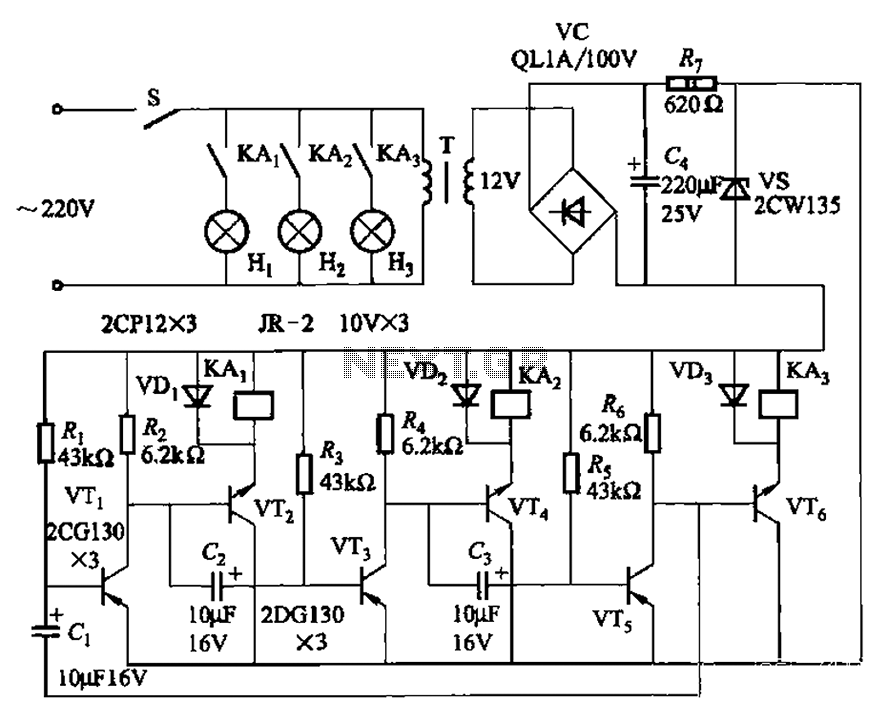
The transistors VTi, VT3, and VTs, along with the RC components, form three distinct multi-resonator oscillators. The oscillation frequency levels are dependent on the values of Ri, R3, Rs, and Cl, as well as Cz and C3s.
The circuit comprises three separate oscillators, each utilizing a transistor configuration to generate oscillations at designated frequencies. The transistors VTi, VT3, and VTs serve as the active elements in these oscillators, enabling signal amplification and frequency modulation. The oscillation frequency is primarily influenced by the resistive and capacitive components of the circuit, specifically Ri, R3, Rs, Cl, Cz, and C3s.
Resistors Ri, R3, and Rs are crucial in determining the time constants associated with the charging and discharging of the capacitors Cl, Cz, and C3s. The values of these components can be adjusted to achieve the desired oscillation frequency, allowing for precise tuning of each resonator.
The capacitors Cl, Cz, and C3s play a vital role in shaping the frequency response of the oscillators. Each capacitor interacts with its corresponding resistor to form a low-pass filter, which contributes to the stability and quality of the oscillation. The design of these resonators allows for a range of applications, including signal generation, modulation, and waveform shaping in various electronic systems.
In summary, the circuit's functionality hinges on the careful selection and arrangement of the transistors and RC components, enabling the creation of three independent multi-resonator oscillators with tunable frequency characteristics. By the transistor VTi, VT3 and VTs and RC components constitute three separate multi-resonator oscillator. Oscillation frequency levels dependent on the value Ri, R3, Rs and Cl , Cz, C3s.
The circuit comprises three separate oscillators, each utilizing a transistor configuration to generate oscillations at designated frequencies. The transistors VTi, VT3, and VTs serve as the active elements in these oscillators, enabling signal amplification and frequency modulation. The oscillation frequency is primarily influenced by the resistive and capacitive components of the circuit, specifically Ri, R3, Rs, Cl, Cz, and C3s.
Resistors Ri, R3, and Rs are crucial in determining the time constants associated with the charging and discharging of the capacitors Cl, Cz, and C3s. The values of these components can be adjusted to achieve the desired oscillation frequency, allowing for precise tuning of each resonator.
The capacitors Cl, Cz, and C3s play a vital role in shaping the frequency response of the oscillators. Each capacitor interacts with its corresponding resistor to form a low-pass filter, which contributes to the stability and quality of the oscillation. The design of these resonators allows for a range of applications, including signal generation, modulation, and waveform shaping in various electronic systems.
In summary, the circuit's functionality hinges on the careful selection and arrangement of the transistors and RC components, enabling the creation of three independent multi-resonator oscillators with tunable frequency characteristics. By the transistor VTi, VT3 and VTs and RC components constitute three separate multi-resonator oscillator. Oscillation frequency levels dependent on the value Ri, R3, Rs and Cl , Cz, C3s.