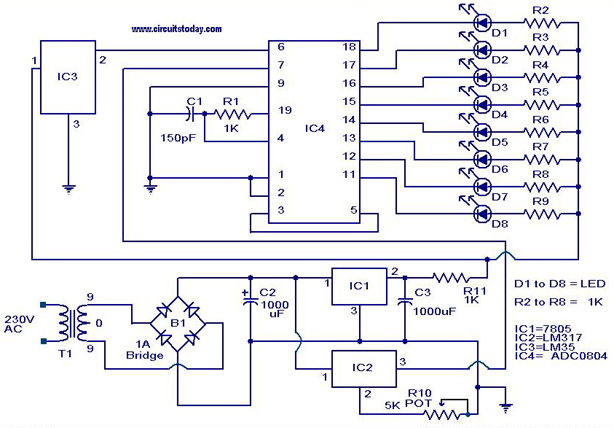
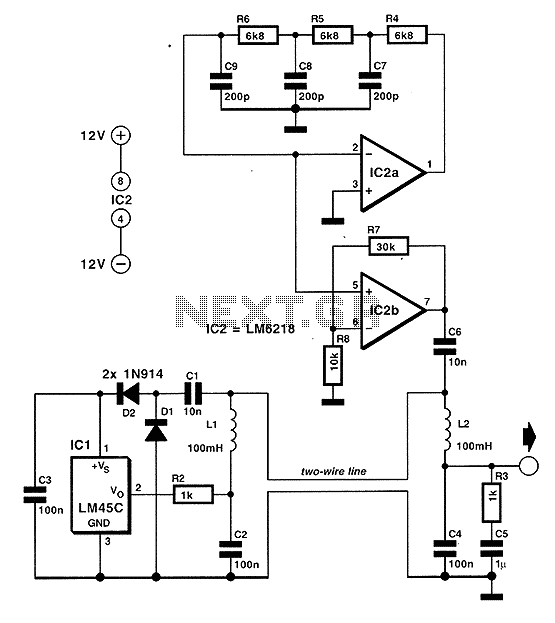
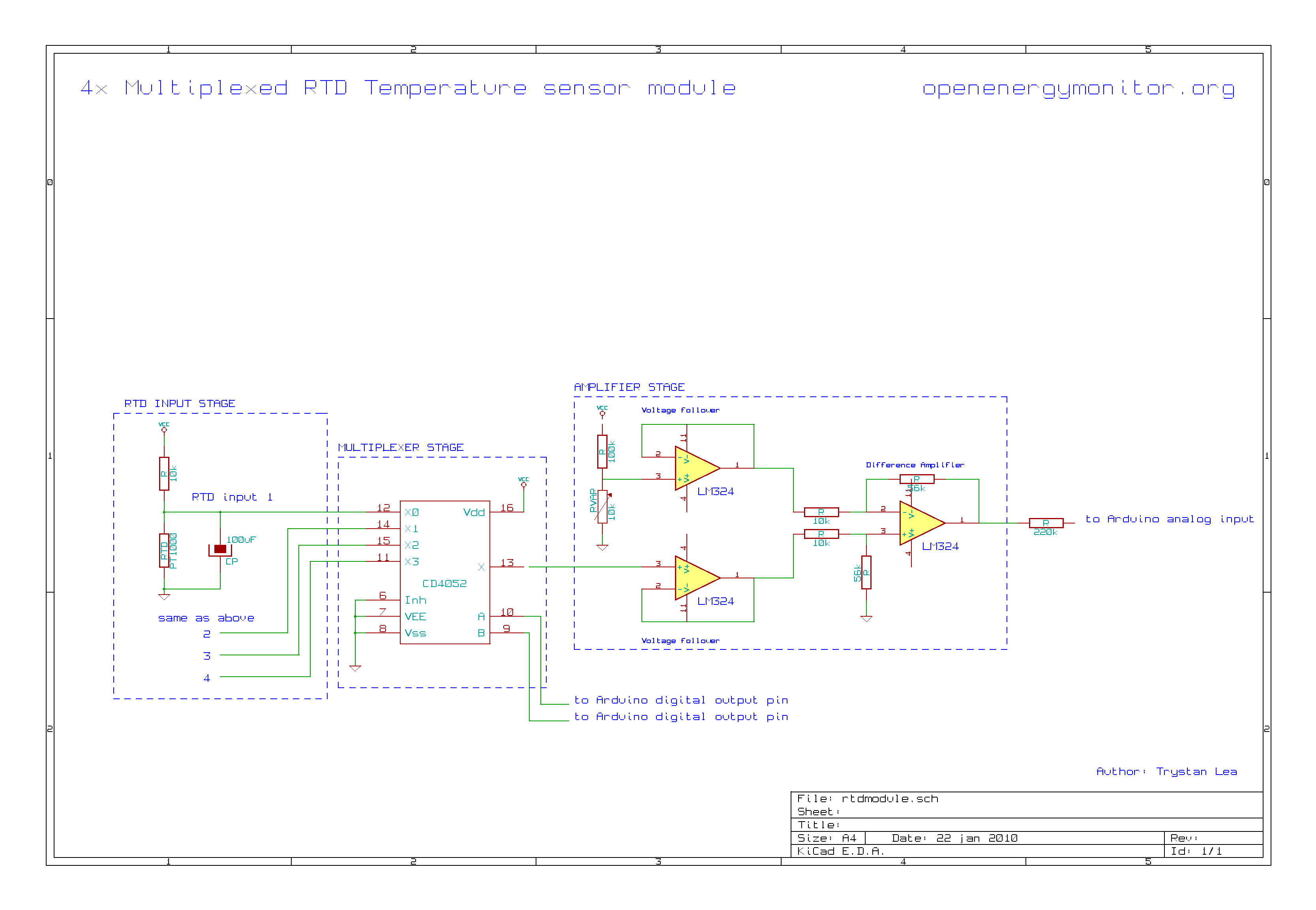
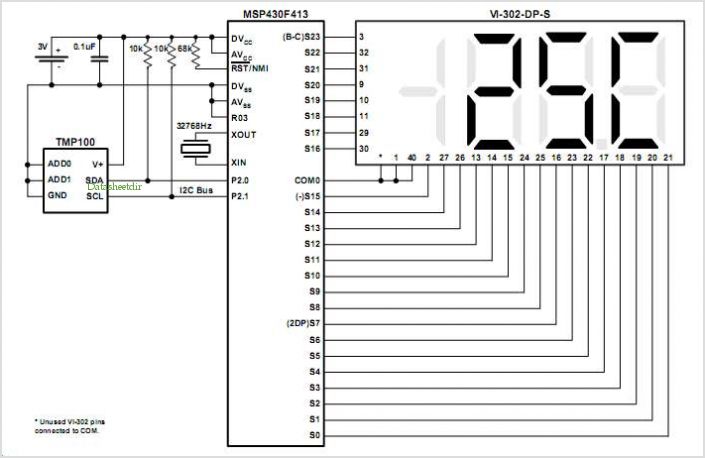
Temperature Monitors

A thermistor positioned as indicated creates a heat-activated sensor. Variations in temperature will modify the output of the operational amplifier, activating the relay and illuminating the LED. Interchanging the positions of the thermistor and the 47k resistor transforms the circuit into a cold or frost alarm.
The described circuit utilizes a thermistor, a type of temperature-sensitive resistor, to detect changes in temperature. When the temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, which in turn affects the voltage at the input of the operational amplifier (op-amp). The op-amp is configured in a comparator mode, where it compares the input voltage derived from the thermistor with a reference voltage set by a voltage divider network.
As the temperature rises, the change in resistance of the thermistor results in a corresponding change in the output voltage of the op-amp. Once this output voltage surpasses a predefined threshold, the op-amp's output switches from low to high, triggering the relay. The relay acts as a switch, allowing higher power devices to be controlled, such as an LED or an alarm system.
In this configuration, the LED will illuminate, indicating that the temperature has exceeded the set limit. This setup is useful for applications requiring temperature monitoring, such as in HVAC systems, refrigeration, or environmental controls.
Conversely, if the thermistor and the 47k resistor are swapped, the configuration becomes suitable for detecting cold temperatures or frost conditions. In this arrangement, as the temperature drops, the thermistor's resistance increases, leading to a decrease in the output voltage of the op-amp. When the voltage falls below the reference level, the op-amp output again switches states, activating the relay and consequently lighting the LED. This modification is particularly beneficial for frost protection in sensitive environments, such as agricultural applications or temperature-sensitive storage facilities.
Overall, this circuit design is versatile, allowing for both heat and cold detection by simply altering the arrangement of components. Proper selection of the thermistor type and the reference voltage is critical for ensuring accurate temperature detection and appropriate response from the relay and LED indicators.Using a thermistor in the position shown makes a heat activated sensor. A change in temperature will alter the output of the opamp and energize the relay and light the LED. Swapping the position of the< thermistor and 47k resistor makes a cold or frost alarm. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a thermistor, a type of temperature-sensitive resistor, to detect changes in temperature. When the temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor decreases, which in turn affects the voltage at the input of the operational amplifier (op-amp). The op-amp is configured in a comparator mode, where it compares the input voltage derived from the thermistor with a reference voltage set by a voltage divider network.
As the temperature rises, the change in resistance of the thermistor results in a corresponding change in the output voltage of the op-amp. Once this output voltage surpasses a predefined threshold, the op-amp's output switches from low to high, triggering the relay. The relay acts as a switch, allowing higher power devices to be controlled, such as an LED or an alarm system.
In this configuration, the LED will illuminate, indicating that the temperature has exceeded the set limit. This setup is useful for applications requiring temperature monitoring, such as in HVAC systems, refrigeration, or environmental controls.
Conversely, if the thermistor and the 47k resistor are swapped, the configuration becomes suitable for detecting cold temperatures or frost conditions. In this arrangement, as the temperature drops, the thermistor's resistance increases, leading to a decrease in the output voltage of the op-amp. When the voltage falls below the reference level, the op-amp output again switches states, activating the relay and consequently lighting the LED. This modification is particularly beneficial for frost protection in sensitive environments, such as agricultural applications or temperature-sensitive storage facilities.
Overall, this circuit design is versatile, allowing for both heat and cold detection by simply altering the arrangement of components. Proper selection of the thermistor type and the reference voltage is critical for ensuring accurate temperature detection and appropriate response from the relay and LED indicators.Using a thermistor in the position shown makes a heat activated sensor. A change in temperature will alter the output of the opamp and energize the relay and light the LED. Swapping the position of the< thermistor and 47k resistor makes a cold or frost alarm. 🔗 External reference