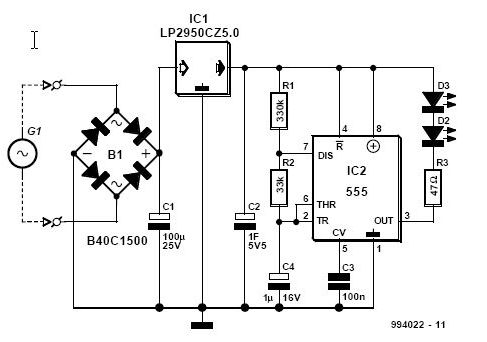
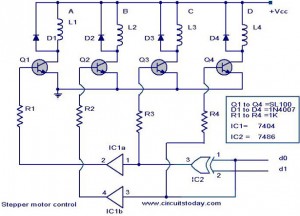
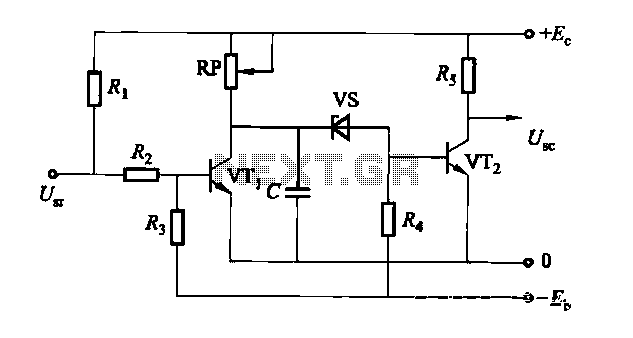
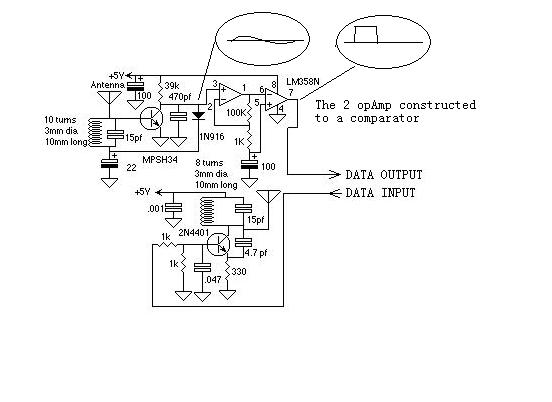
The crystal oscillator circuit with frequency in 2MHz
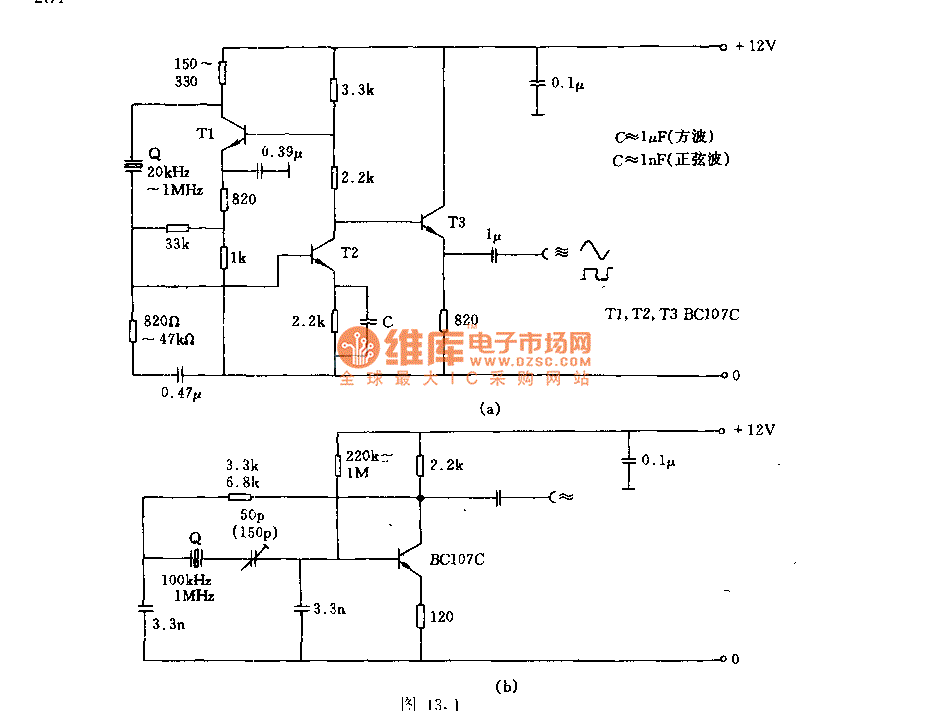
Figures (a) and (b) illustrate two basic oscillator circuits operating at 2 MHz. The circuit design allows for adjustment of the optimal operating point through testing.
The two oscillator circuits depicted in the figures utilize different configurations to achieve stable oscillation at the desired frequency of 2 MHz. The first circuit may employ a Colpitts or Hartley oscillator design, which is characterized by its use of capacitive and inductive components to establish feedback for oscillation. The second circuit might utilize a phase-shift oscillator configuration, relying on resistive and capacitive elements to create the necessary phase shift for sustained oscillation.
Both circuits incorporate a transistor or operational amplifier as the active component, which amplifies the feedback signal to maintain oscillation. The tuning elements, typically variable capacitors or inductors, facilitate fine-tuning of the frequency to ensure precision at 2 MHz. Testing and adjustment of these components are crucial for achieving the best operating point, as variations in component values can significantly affect the frequency stability and amplitude of the output signal.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, ensuring that the circuits are powered adequately to prevent distortion or signal degradation. Additionally, output coupling may be implemented to interface with other stages of a system, which could include filtering or impedance matching networks to optimize signal integrity and minimize losses.
In conclusion, the ability to adjust the operating point through testing is essential for maximizing the performance of these oscillator circuits, making them suitable for various applications in signal generation and modulation.Figure (a) and (b) show the two 2MHZ basic oscillator circuits. According to the circuit structure, it can adjust its best operating point by testing.. 🔗 External reference
The two oscillator circuits depicted in the figures utilize different configurations to achieve stable oscillation at the desired frequency of 2 MHz. The first circuit may employ a Colpitts or Hartley oscillator design, which is characterized by its use of capacitive and inductive components to establish feedback for oscillation. The second circuit might utilize a phase-shift oscillator configuration, relying on resistive and capacitive elements to create the necessary phase shift for sustained oscillation.
Both circuits incorporate a transistor or operational amplifier as the active component, which amplifies the feedback signal to maintain oscillation. The tuning elements, typically variable capacitors or inductors, facilitate fine-tuning of the frequency to ensure precision at 2 MHz. Testing and adjustment of these components are crucial for achieving the best operating point, as variations in component values can significantly affect the frequency stability and amplitude of the output signal.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, ensuring that the circuits are powered adequately to prevent distortion or signal degradation. Additionally, output coupling may be implemented to interface with other stages of a system, which could include filtering or impedance matching networks to optimize signal integrity and minimize losses.
In conclusion, the ability to adjust the operating point through testing is essential for maximizing the performance of these oscillator circuits, making them suitable for various applications in signal generation and modulation.Figure (a) and (b) show the two 2MHZ basic oscillator circuits. According to the circuit structure, it can adjust its best operating point by testing.. 🔗 External reference